©2007 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 21, 2007; 13(23): 3259-3261
Published online Jun 21, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i23.3259
Published online Jun 21, 2007. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v13.i23.3259
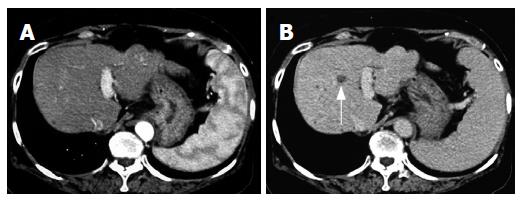
Figure 1 Enhanced computed-tomography (CT) scans in the arterial phase (A) and equilibrium phase (B) before administration of ACE-I in combination with VK.
In the arterial phase, no obvious lesion could be detected whereas a low-density area (arrow) was noticed in the equilibrium phase.
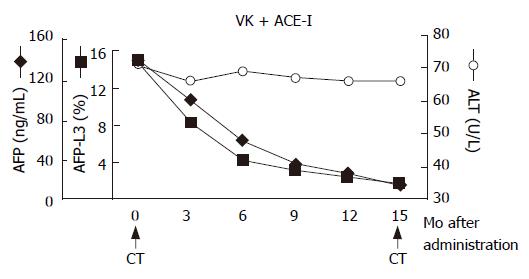
Figure 2 Schema of clinical course.
After administration of ACE-I and VK, the serum levels of both AFP and AFP-L3 gradually decreased. After one-year treatment, the serum levels of both AFP and AFP-L3 returned to the normal ranges. The arrows indicate the time points of CT examination before and after administration of this combined regimen.
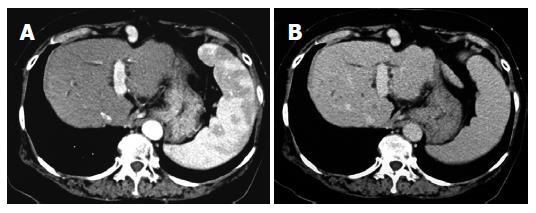
Figure 3 Enhanced computed-tomography (CT) scans in the arterial phase (A) and equilibrium phase (B) after administration of ACE-I in combination with VK.
After a 15-mo administration, the hepatic nodule disappeared in both the arterial phase and equilibrium phase.
- Citation: Yoshiji H, Noguchi R, Yamazaki M, Ikenaka Y, Sawai M, Ishikawa M, Kawaratani H, Mashitani T, Kitade M, Kaji K, Uemura M, Yamao J, Fujimoto M, Mitoro A, Toyohara M, Yoshida M, Fukui H. Combined treatment of vitamin K2 and angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor ameliorates hepatic dysplastic nodule in a patient with liver cirrhosis. World J Gastroenterol 2007; 13(23): 3259-3261
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v13/i23/3259.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v13.i23.3259