©2006 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 14, 2006; 12(46): 7488-7496
Published online Dec 14, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i46.7488
Published online Dec 14, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i46.7488
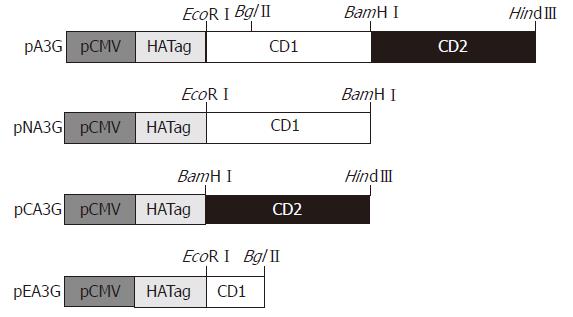
Figure 1 Construction of APOBEC3G and its N-terminal and C-terminal cytosine deaminase domain expression plasmids.
Full-length APOBEC3G sequence was cloned into EcoRI/HindIII restriction sites of the CMV-driven expression vector fused with a hemagglutinin fusion epitope tag at its N- terminal end (pXF3H) to construct APOBEC3G expression plasmid (pA3G). pA3G was digested with EcoRI/BamHIand BamHI/HindIII, these fragments were inserted into pXF3H to construct the N-terminal and C-terminal cytosine deaminase domain expression plasmids (pXFNA3G and pXFCA3G), respectively. pA3G was digested with EcoRI/BglII, and used for the construction of the N-terminal region of APOBEC3G which did not contain any cytosine deaminase domain plasmid (pXFEA3G). pCMV: CMV promoter; CD1: N-terminal cytosine deaminase domain; CD2: C-terminal cytosine deaminase domain.
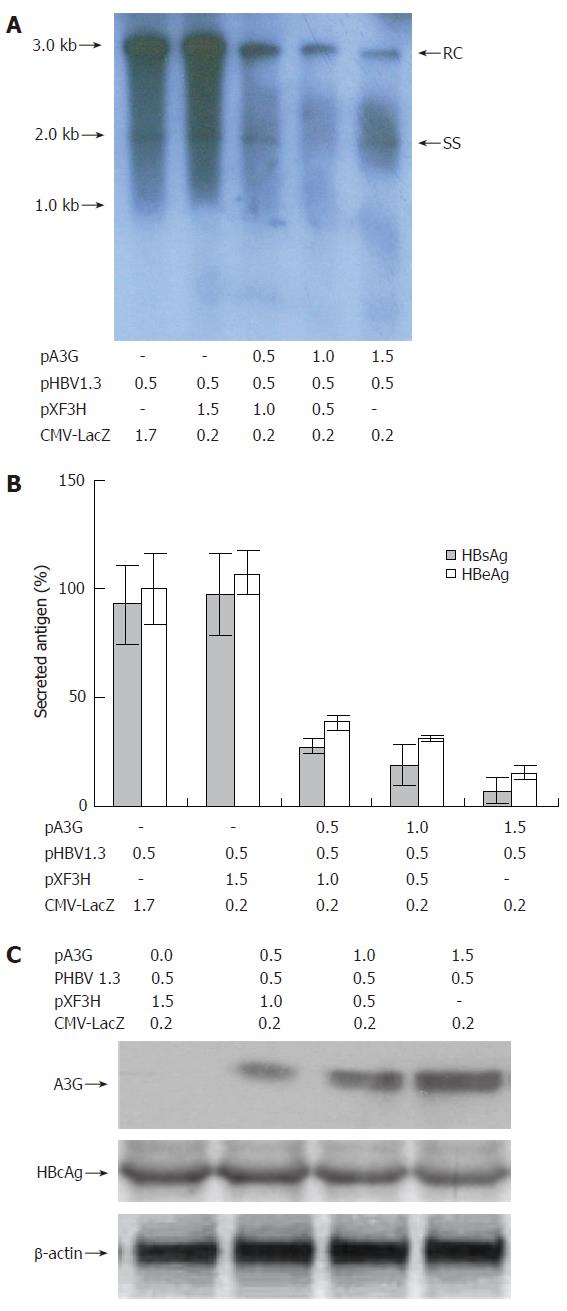
Figure 2 Effect of APOBEC3G on HBV replication in co-transfected HepG2 cells.
(A) Human hepatoma HepG2 cells were transiently co-transfected with pHBV1.3 and various amounts of a CMV-driven expression vector encoding A3G or with empty vector pXF3H and pCMV-LacZ using Lipofectamine 2000 reagents. The cells were harvested 3 d after transfection. HBV core-associated viral DNA was prepared from nuclease-treated cytoplasmic lysates. Viral replicative DNA intermediates were analyzed by Southern blotting using a Dig-labeled full-length HBV DNA probe. (B) HBsAg and HBeAg levels were determined in the media of co-transfected HepG2 cells by ELISA, normalized to the activity of co-tansfected β-galactosidase in the cell lysates. The mean ± SE of six independent experiments is shown (error bar indicates standard error). (C) Western blot analysis of cytoplasmic extracts from HepG2 cells co-transfected with the indicated plasmids. Numbers at the end or top of the lines indicate the amount of transfected plasmid DNA in micrograms. HBV: hepatitis B virus; pA3G: APOBEC3G expression plasmids; RC: relaxed circular DNA; SS: single-stranded DNA; HBcAg: hepatitis B virus core antigen; HBsAg: hepatitis B virus surface antigen; HBeAg: hepatitis B virus e antigen.
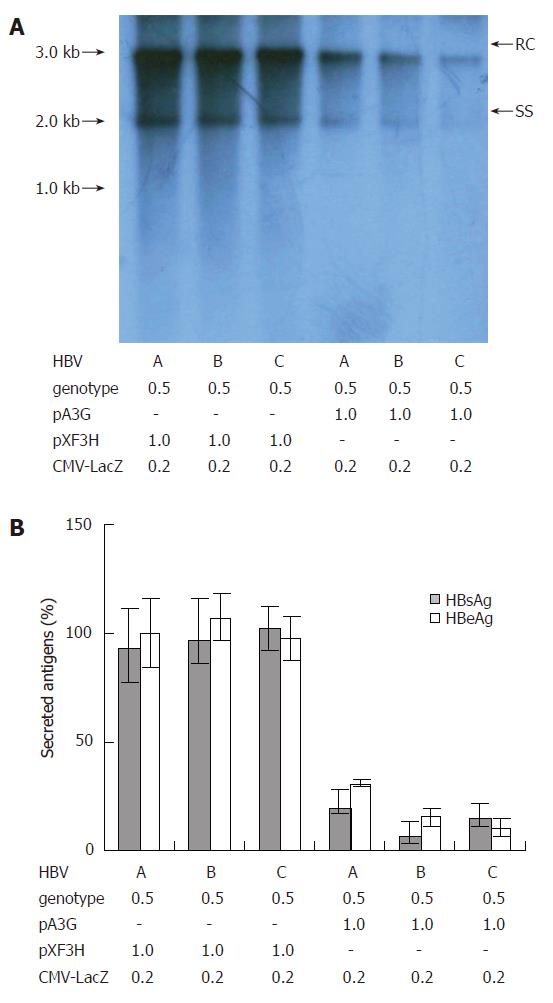
Figure 3 Suppression of replication of HBV clinical isolates of different genotypes by APOBEC3G.
(A) pHBV1.3 or the linear monomeric HBV genomes of genotype B and C were transiently co-transfected into HepG2 cells with the CMV-driven expression vector encoding A3G or empty vector pXF3H and pCMV-LacZ using Lipofectamine 2000 reagents. The cells were harvested 3 d after transfection. HBV core-associated viral DNA was prepared from nuclease-treated cytoplasmic lysates. Viral replicative DNA intermediates were analyzed by Southern blotting using a Dig-labeled full-length HBV DNA probe. (B) HBsAg and HBeAg levels were determined in the media of co-transfected HepG2 cells by ELISA, normalized to the activity of co-tansfected β-galactosidase in the cell lysates. The mean ± SEM of six independent experiments is shown (error bar indicates standard error). pA3G: APOBEC3G expression plasmids; RC: relaxed circular DNA; SS: single-stranded DNA.
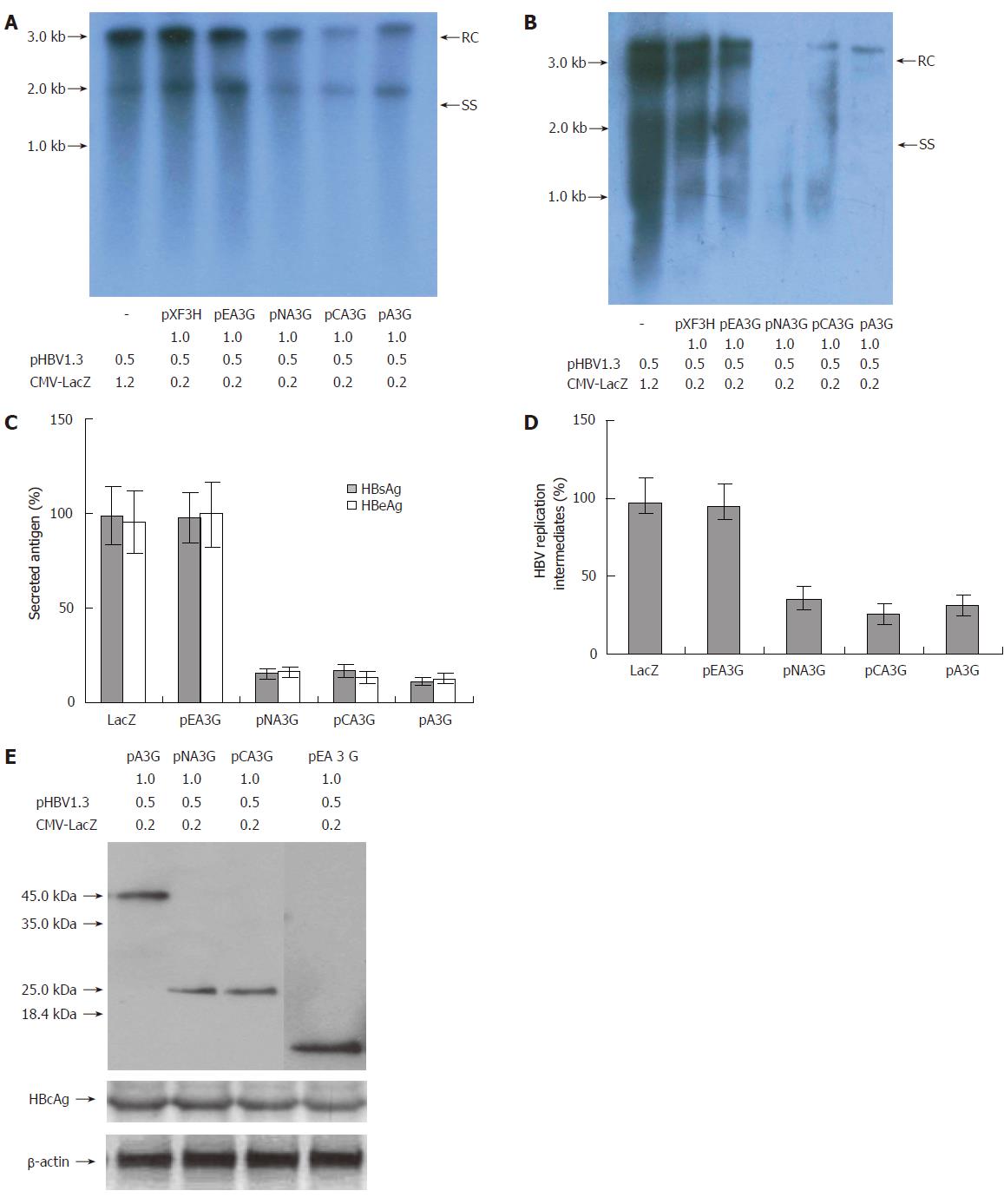
Figure 4 Inhibitory effect of the N-terminal and C-terminal cytosine deaminase domain on HBV production in the co-transfected cells.
(A and B) Human hepatoma HepG2 and HuH7cells were transiently co-transfected with the pHBV1.3 and CMV-driven expression vector encoding A3G and its N-terminal or C-terminal cytosine deaminase domain or with the empty vector pXF3H and pCMV-LacZ using Lipofectamine 2000 reagents. The cells were harvested 3 d after transfection. HBV core-associated viral DNA was prepared from nuclease-treated cytoplasmic lysates. Viral replicative DNA intermediates were analyzed by Southern blotting using a Dig-labeled full-length HBV DNA probe. (C) HBsAg and HBeAg levels were determined in the media of co-transfected HepG2 cells by ELISA, normalized to the activity of co-tansfected β-galactosidase in the cell lysates. The mean ± SE of six independent experiments is shown (error bar indicates standard error). (D) The hybridized HBV DNA from the replicative intermediates was quantified by radiophosphorimaging, normalized to the amount of secreted HBsAg (normalized for co-transfected β-galactosidase activity) and calculated relative to the empty vector control (pXF3H). The mean ± SE of six independent experiments is shown. (E) Anti-HA monoclonal antibody for Western blot analysis of cytoplasmic extracts from HepG2 cells co-transfected with the indicated plasmids. Numbers at the end or top of the lines indicate the amount of transfected plasmid DNA in micrograms. pXF3H: empty vector; pA3G: APOBEC3G expression plasmids; pNA3G: N-terminal cytosine deaminase domain of APOBEC3G expression plasmids; pCA3G: C-terminal cytosine deaminase domain of APOBEC3G expression plasmids; pEA3G: N-terminal region of APOBEC3G which does not contain any cytosine deaminase domain plasmid; HBV: hepatitis B virus; RC: relaxed circular DNA; SS: single-stranded DNA; HBcAg: hepatitis B virus core antigen; HBsAg: hepatitis B virus surface antigen; HBeAg: hepatitis B virus e antigen.
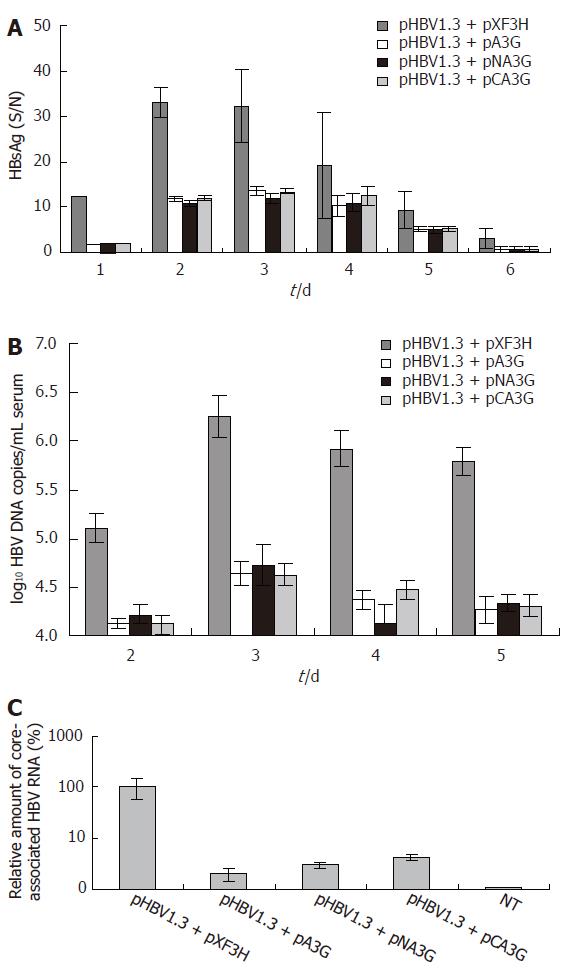
Figure 5 The N-terminal or C-terminal cytosine deaminase domain of APOBEC3G inhibits HBV replication and gene expression in mice.
(A) Serum HBsAg levels in the mice treated with APOBEC3G and its N-terminal and C-terminal cytosine deaminase domain expression vector. HBsAg levels (S/N, S: absorbance of the sample, N: absorbance of the negative control) in the sera of BALB/c mice were significantly reduced after treatment with APOBEC3G and its N-terminal and C-terminal cytosine deaminase domain expression plasmids (error bar indicates standard error) in the indicated time points. (B) Real-time PCR quantification of HBV DNA in the sera of mice treated with APOBEC3G and its N-terminal and C-terminal cytosine deaminase domain expression plasmid. BALB/c mice were co-injected with pHBV1.3 vector (10 μg) and the indicated expression plasmids (10 μg). HBV DNA levels of sera were determined by quantitative PCR (n = 6 per treatment group). (C) Real-time PCR quantification of core-associated HBV RNA in the liver of mice treated with APOBEC3G and its N-terminal or C-terminal cytosine deaminase domain expression plasmids. BALB/c mice were co-injected with pHBV1.3 vector (10 μg) and the N-terminal or C-terminal cytosine deaminase domain expression vector of APOBEC3G (10 μg) 3 d after injection, and the levels of the liver HBV RNA were determined by quantitative RT-PCR, normalized to GAPDH mRNA and reported as a ratio of HBV mRNA/GAPDH mRNA (± SD) (n = 6 per treatment group). NT: non-treated group; pXF3H: empty vector; pA3G: APOBEC3G expression plasmids; pNA3G: N-terminal cytosine deaminase domain of APOBEC3G expression plasmids; pCA3G: C-terminal cytosine deaminase domain of APOBEC3G expression plasmids; HBsAg: hepatitis B virus surface antigen.
- Citation: Lei YC, Tian YJ, Ding HH, Wang BJ, Yang Y, Hao YH, Zhao XP, Lu MJ, Gong FL, Yang DL. N-terminal and C-terminal cytosine deaminase domain of APOBEC3G inhibit hepatitis B virus replication. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12(46): 7488-7496
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v12/i46/7488.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v12.i46.7488