©2006 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 28, 2006; 12(44): 7221-7224
Published online Nov 28, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i44.7221
Published online Nov 28, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i44.7221
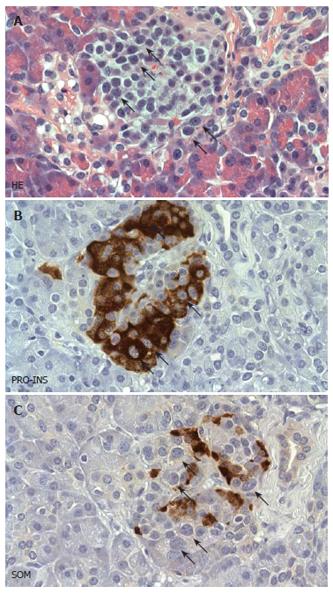
Figure 1 Histopathological features of diffuse nesidioblastosis.
A: HE stained sections demonstrating a prominent lobulation of an islet. Some of the endocrine cells showing hyperchromatic and enlarged nuclei are labelled with arrows. B, C: Adjacent section analysis demonstrating cytoplasmic positivity for proinsulin (PRO-INS) in those endocrine cells with hyperchromatic nuclei (arrows in B). In contrast, these cells are negative for somatostatin (SOM) (arrows in C).
- Citation: Raffel A, Anlauf M, Hosch S, Krausch M, Henopp T, Bauersfeld J, Klofat R, Bach D, Eisenberger C, Klöppel G, Knoefel W. Hyperinsulinemic hypoglycemia due to adult nesidioblastosis in insulin-dependent diabetes. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12(44): 7221-7224
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v12/i44/7221.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v12.i44.7221