©2006 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 28, 2006; 12(44): 7216-7220
Published online Nov 28, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i44.7216
Published online Nov 28, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i44.7216
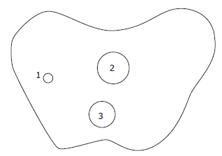
Figure 1 Diagrammatic representation of three lesions.
1: Carcinoid nodule of 0.7 cm in diameter near the greater curvature of gastric corpus; 2: SRC sizing 3.0 cm × 2.0 cm within mucosa at the lesser curvature of gastric corpus; 3: Ectopic pancreas nodule of 2.5 cm in diameter between submucosa and serosa in gastric corpus-antrum.
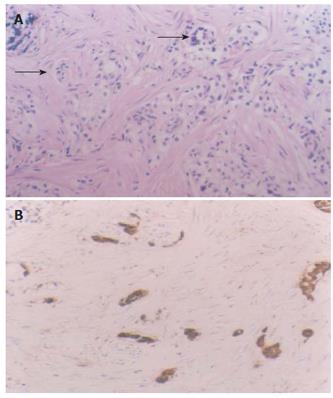
Figure 2 Lesion 1, intramucosal carcinoid with the muscularis mucosa infiltrated (A) (arrows, HE × 20), positively expresses CgA (B) (S-P method, conterstained with hematoxylin, × 20).
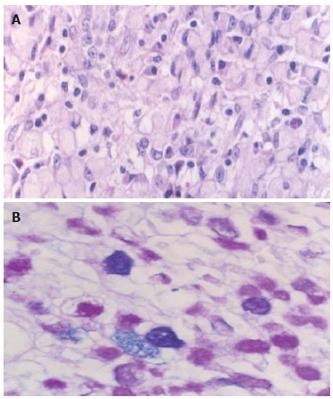
Figure 3 Lesion 2, intramucosal signet-ring cell carcinoma (A) (HE × 40) with cytoplasmic mixed mucin (B) (AB/PAS reaction, × 40).
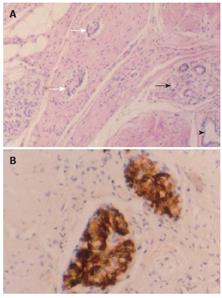
Figure 4 Lesion 3, heterotopic pancreatic tissue in gastric wall, which was composed of well developed pancreatic acini (darker arrow), ducts (arrowhead), and islets (lighter arrow) intermingled with the hyperplastic smooth muscle tissue, giving rise to the pattern of an adenomyoma (A) (HE × 20); Small-cell nodules of 0.
1-0.4 mm in diameter scattered within the muscularis propria and serosa of the gastric wall and strongly positive for insulin (B) (S-P method, conterstained with hematoxylin).
- Citation: Yang L, Zhang HT, Zhang X, Sun YT, Cao Z, Su Q. Synchronous occurrence of carcinoid, signet-ring cell carcinoma and heterotopic pancreatic tissue in stomach: A case report and literature review. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12(44): 7216-7220
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v12/i44/7216.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v12.i44.7216