©2006 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 14, 2006; 12(38): 6207-6211
Published online Oct 14, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i38.6207
Published online Oct 14, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i38.6207
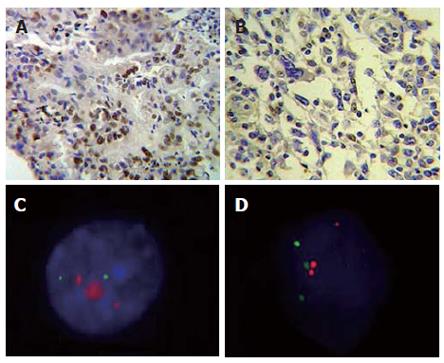
Figure 1 Cells submitted to immunohistochemistry and FISH techniques.
A: Infiltrating gastric adenocarcinoma of intestinal type shows intense nuclear marcation for C-MYC, × 400; B: Gastric adenocarcinoma of diffuse type nuclear marcation and cytoplasmatic light marcation for C-MYC, × 400; C: Interphase nuclei presenting C-MYC high amplification (red) and chromosome 8 (green); D: Interphase nuclei presenting chromosome 8/C-MYC rearrangement.
-
Citation: Calcagno DQ, Leal MF, Seabra AD, Khayat AS, Chen ES, Demachki S, Assumpção PP, Faria MHG, Rabenhorst SHB, Ferreira MVP, Smith MAC, Burbano RR. Interrelationship between chromosome 8 aneuploidy,
C-MYC amplification and increased expression in individuals from northern Brazil with gastric adenocarcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12(38): 6207-6211 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v12/i38/6207.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v12.i38.6207