©2006 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 7, 2006; 12(37): 6002-6007
Published online Oct 7, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i37.6002
Published online Oct 7, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i37.6002
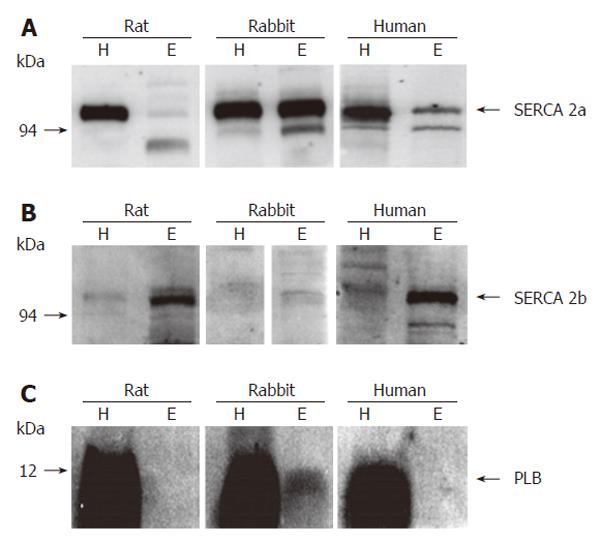
Figure 1 Protein expression of SERCA 2a (A), 2b (B), and PLB (C) in esophageal and ventricular homogenates of rat, rabbit, and human.
Protein loading for esophagus (100 μg) was 5 times higher than for heart (20 μg). For documentation of PLB, sensitivity of the PhosphorImager was optimized for detection of very weak signals. Therefore, signals in heart samples are overexposed. H: heart; E: esophagus.
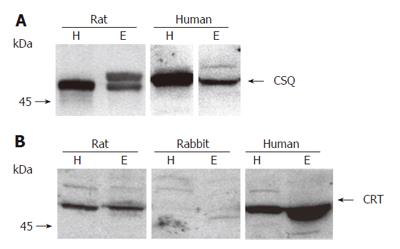
Figure 2 Protein expression of CSQ (A) and CRT (B) in esophageal and ventricular homogenates of rat, rabbit, and human.
Protein loading was 50 μg/lane for CSQ and 100 μg/lane for CRT. H: heart; E: esophagus.
Figure 3 Protein expression of SERCA 2b, CSQ, and CRT in biopsies of esophageal body (EB, A) and lower esophageal sphincter (LES, B) from patients with achalasia or healthy controls.
Protein expression was quantified using [125I]-labeled protein A for detection of primary antibodies. Radioactive bands were visualized and quantified using a PhosphorImager. Data are presented as mean ± SE of n patients. aP < 0.05 vs control.
- Citation: Fischer H, Fischer J, Boknik P, Gergs U, Schmitz W, Domschke W, Konturek JW, Neumann J. Reduced expression of Ca2+-regulating proteins in the upper gastrointestinal tract of patients with achalasia. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12(37): 6002-6007
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v12/i37/6002.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v12.i37.6002