©2006 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 28, 2006; 12(36): 5904-5906
Published online Sep 28, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i36.5904
Published online Sep 28, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i36.5904
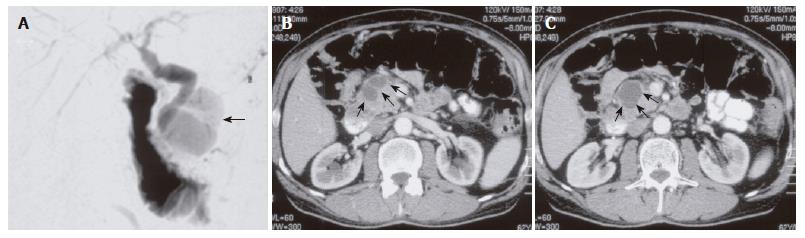
Figure 1 MRCP (A) depicting the dilated bile duct (13 mm) in close vicinity to the pancreatic cyst; CT scans (B, C) showing the cystic pancreatic lesion in the pancreatic head (arrows).
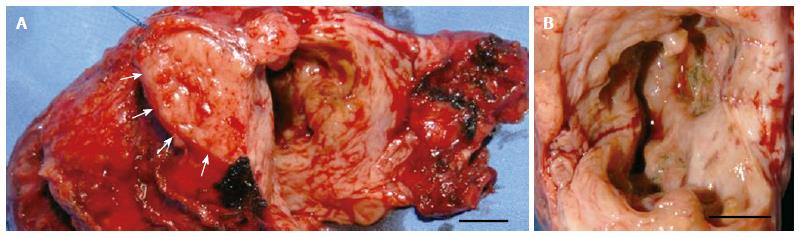
Figure 2 Intraoperative findings of the resected pancreatic specimen.
A, B: Macroscopic appearance of the pancreaticoduodenectomy specimen (A) and the opened pseudocyst (B). Arrows indicate the pancreatic cut margin. Scale bar: 1 cm.
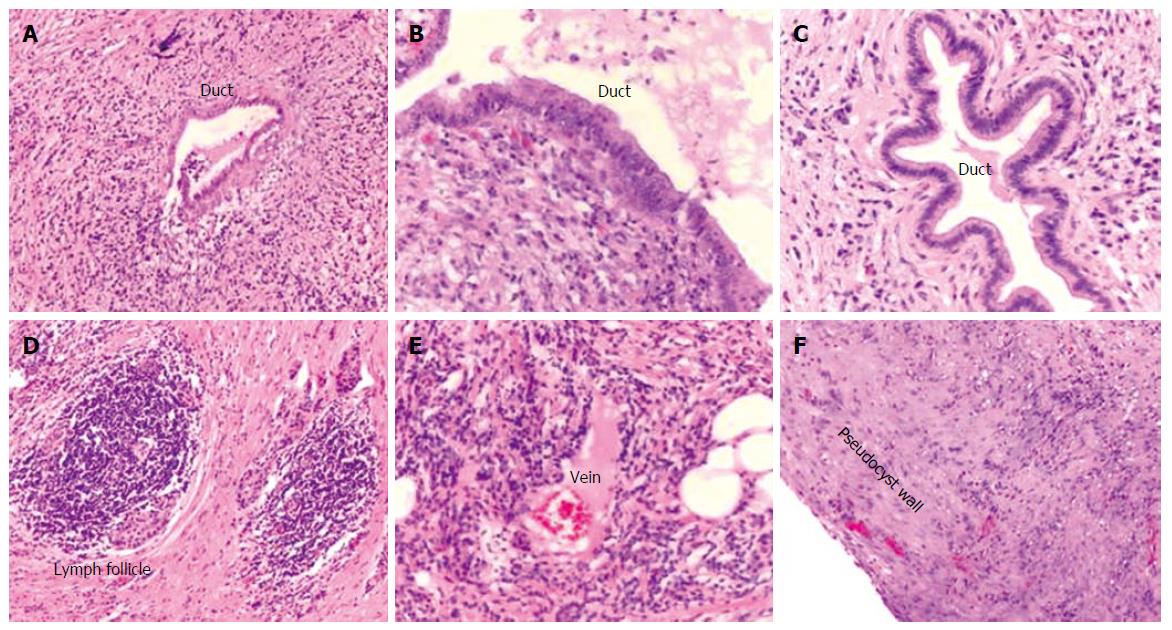
Figure 3 Histological findings of the resected pancreatic specimen.
Histological examination displaying marked chronic periductal lymphoplasmacytic inflammation and fibrosis (A-C), intrapancreatic lymph follicle (D), and venulitis (E). F depicts the wall of the pseudocyst without evidence of epithelial lining.
- Citation: Welsch T, Kleeff J, Esposito I, Büchler MW, Friess H. Autoimmune pancreatitis associated with a large pancreatic pseudocyst. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12(36): 5904-5906
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v12/i36/5904.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v12.i36.5904