©2006 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 28, 2006; 12(28): 4445-4451
Published online Jul 28, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i28.4445
Published online Jul 28, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i28.4445
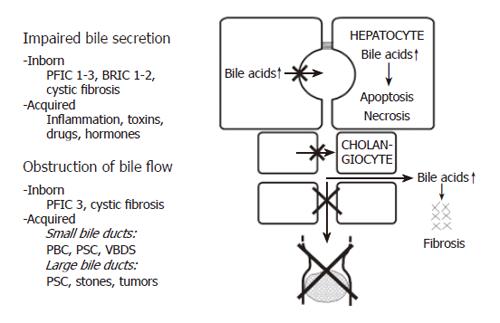
Figure 1 Causes of cholestasis.
PBC: Primary biliary cirrhosis; PFIC: Progressive familial intrahepatic cholestasis; PSC: Primary sclerosing cholangitis; VBDS: Vanishing bile duct syndrome. For details see text.
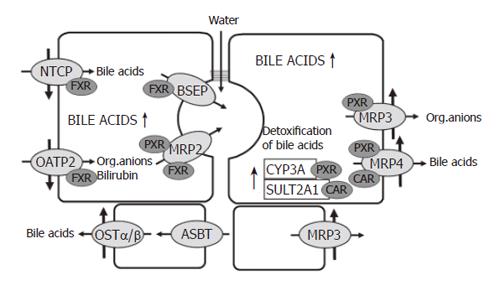
Figure 2 Adaptive responses to cholestasis.
BSEP: Bile salt export pump; CAR: Constitutive androstane receptor; CYP3A: Cytochrome P450 enzyme 3A; FXR: Farnesoid X receptor; OATP: Organic anion transporting polypeptide; OST: Organic solute transporter; MRP: Multidrug resistance associated protein; NTCP: Sodium taurocholate co-transporting polypeptide; PXR: Pregnane X receptor; SULT2A1: Sulphotranferase 2A1. For details see tect.
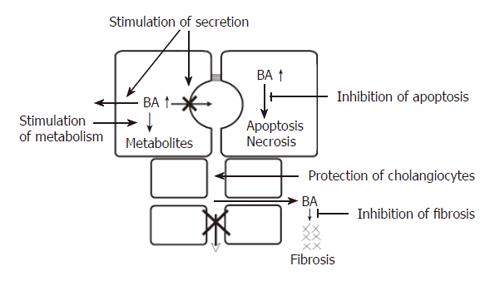
Figure 3 Targets for medical treatment of intrahepatic cholestasis.
BA: Bile acids. For details see text.
- Citation: Paumgartner G. Medical treatment of cholestatic liver diseases: From pathobiology to pharmacological targets. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12(28): 4445-4451
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v12/i28/4445.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v12.i28.4445