©2006 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 28, 2006; 12(12): 1889-1894
Published online Mar 28, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i12.1889
Published online Mar 28, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i12.1889
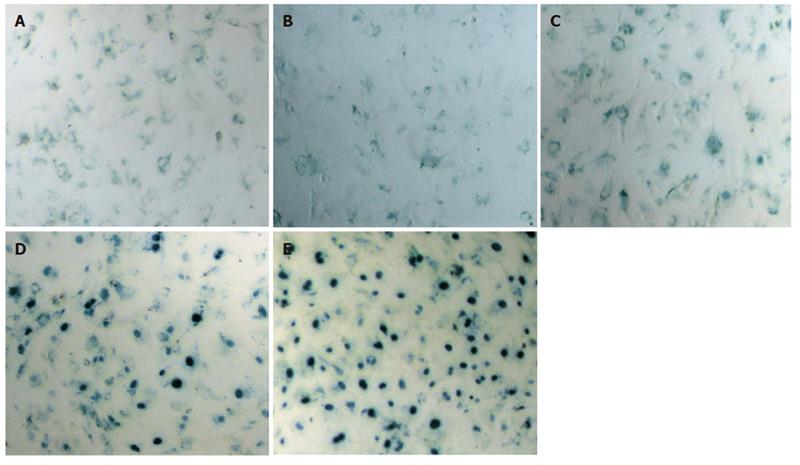
Figure 1 X-gal assay of hamster BMSCs transfected with Ad/ Lac Z at 0 (A), 10 (B), 20 (C), 50 (D), and 100 (E) MOI.
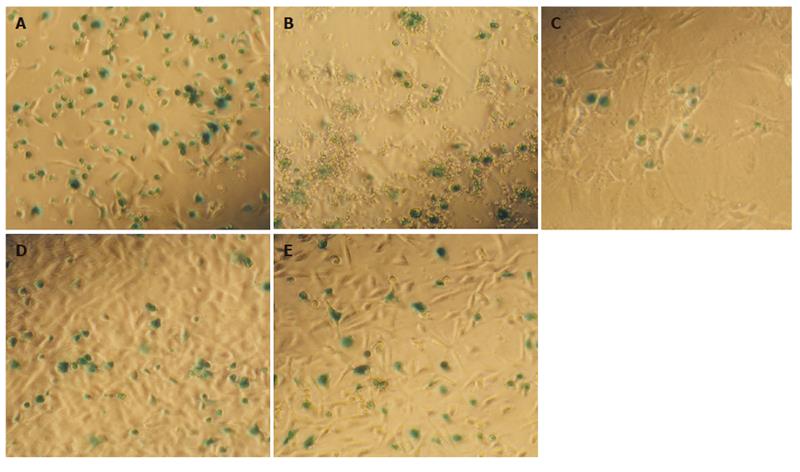
Figure 2 X-gal assay of post -transfection in BM (A), spleen (B), kidney (C), lung (D), and liver (E).
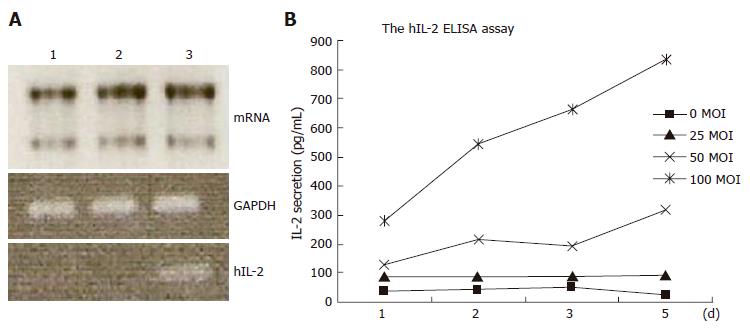
Figure 3 Expression and quantitative analysis of human IL-2.
A: RT-PCR of in vitro cultured BMSC. Lane 1: 1x106 stromal cells; lane 2: 1x106 stromal cells containing 20 MOI Ad/∆E1; lane 3: 1x106 stromal cells containing 20 MOI Ad/hIL-2; B: ELISA assay of IL-2 secretion from in vitro cultured BMSCs (2.5 X 105/mL) of Syrian golden hamster after transduction with Ad/hIL-2 at MOI of 0(◆), 25(■), 50(▲), and 100 (●). Culture supernatants were harvested on different days and tested for hIL-2 secretion levels by ELISA.
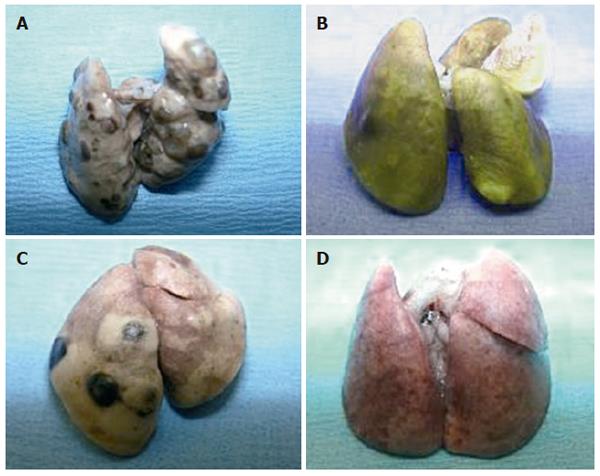
Figure 4 Gross findings of metastatic lung lesions in Syrian hamsters 8 wk after injection of KIGB-5 tumor cells in RPMI control (A), BMSCs (2.
5 x 106 cells/d) (B), BMSCs containing 50 MOI Ad/∆E1 (2.5 x 106 cells/day) (C), and BMSCs containing 50 MOI Ad/hIL-2 (2.5 x 106 cells/d) (D). Hamsters injected with RPMI, BMSCs, or BMSCs containing Ad/∆E1 showed multiple metastatic lung lesions 8 wk after tumor injection, whereas hamsters injected with BMSCs containing Ad/IL-2 showed no evidence of disease.
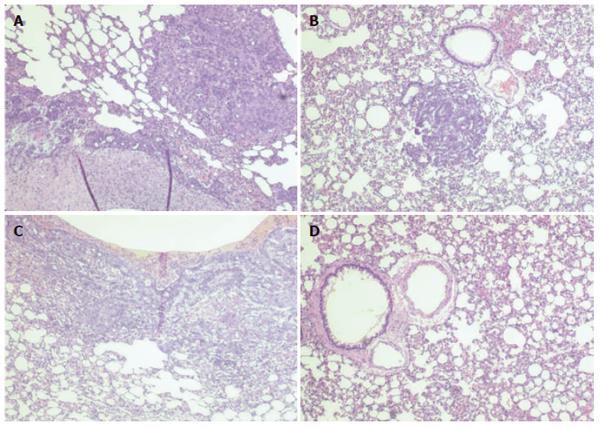
Figure 5 Microscopic findings in Syrian hamsters 8 wk after injection of KIGB-5 tumor cells in RPMI control (A), BMSCs (2.
5 x 106 cells/d) (B), BMSCs containing 50 MOI Ad/∆E1 (2.5 x 106 cells/d) (C), and BMSCs containing 50 MOI Ad/hIL-2 (2.5 x 106 cells/d) (D). Hamsters injected with RPMI, BMSCs, or BMSCs containing Ad/∆E1 showed multiple metastatic lesions in both lungs, whereas hamsters injected with BMSCs containing Ad/IL-2 showed no evidence of disease.
- Citation: Kim MH, Lee SS, Lee SK, Lee SG, Suh CW, Gong GY, Park JS, Kim YH, Kim SH. Interleukin-2 gene-encoded stromal cells inhibit the growth of metastatic cholangiocarcinomas. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12(12): 1889-1894
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v12/i12/1889.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v12.i12.1889