©2006 Baishideng Publishing Group Co.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 28, 2006; 12(12): 1829-1841
Published online Mar 28, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i12.1829
Published online Mar 28, 2006. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i12.1829
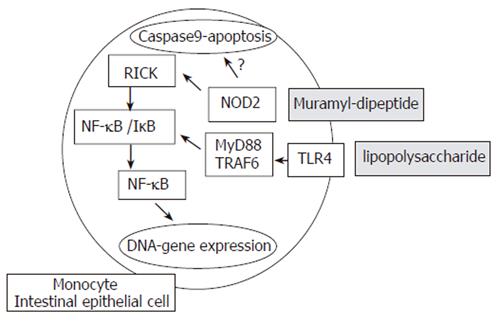
Figure 1 NOD2/TLR4 signaling pathway.
NOD2 activation by CARD-CARD dimmer formation results in binding to RICK kinase (RIP-like interacting CLARP kinase). RICK then activates the nuclear factor kB inhibitor (IkB) kinase complex (IKK) via phosphorylation of IKKc. The IKK complex next phosphorylates IkB resulting in nuclear factor kB (NFkB) translocation to the nuclei and transcriptional activation of NFkB responsive genes, such as pro-inflammatory cytokines or defensins. TLR4 induces activation through other molecules (Myd88, IRAK and TRAF6).
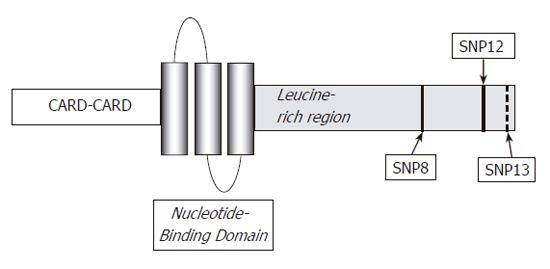
Figure 2 Structure of NOD2/CARD15 protein and locations of the three main mutations.
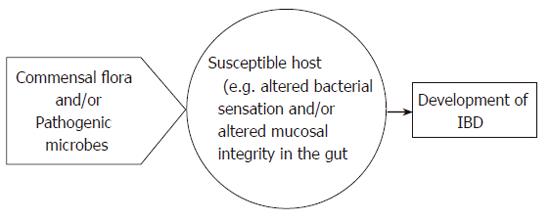
Figure 3 Role of microbial factors and genetics in the pathogenesis of IBD.
- Citation: Lakatos PL, Fischer S, Lakatos L, Gal I, Papp J. Current concept on the pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease-crosstalk between genetic and microbial factors: Pathogenic bacteria and altered bacterial sensing or changes in mucosal integrity take “toll”. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12(12): 1829-1841
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v12/i12/1829.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v12.i12.1829