©2005 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 21, 2005; 11(7): 1077-1082
Published online Feb 21, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i7.1077
Published online Feb 21, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i7.1077
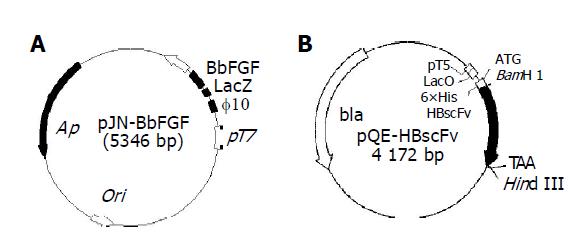
Figure 1 Structure of the expression plasmids pJN-BbFGF (A) and pQE-HBscFv (B).
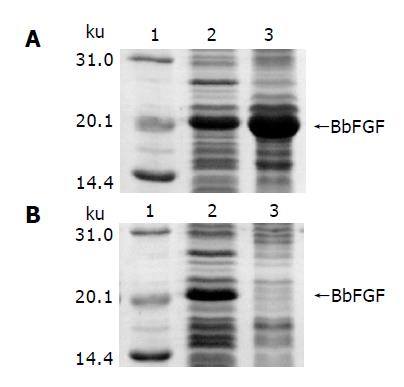
Figure 2 Characteristics of BbFGF in different host bacteria.
A: E. coli BL21(DE3), B: E. coli Origami(DE3), lane 1: Molecular weight standard, lane 2: Supernatant of the bacteria lysate, lane 3: Pellet of the bacteria lysate.
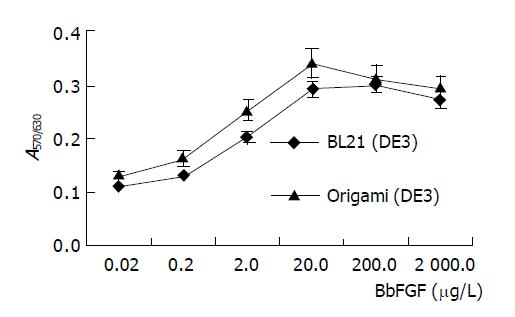
Figure 3 Bioactivity of BbFGFs produced from different host bacteria.
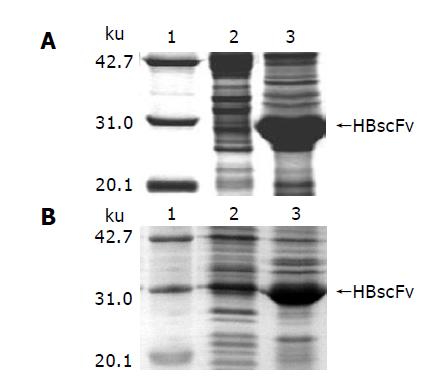
Figure 4 Characteristics of HBscFv in different host bacteria.
A: E. coli M15[pREP4], B: E. coli Origami(DE3), lane 1: Molecular weight standard, lane 2: Supernatant of the bacteria lysate, lane 3: Pellet of the bacteria lysate.
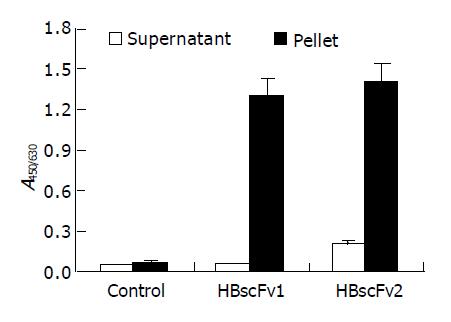
Figure 5 Antigen-binding activity of recombinant HBscFvs produced from different E.
coli (mean±SD). HBscFv1: HBscFv produced from M15[pQE-HBscFv], HBscFv2: HBscFv produced from Origami[pQE-HBscFv].
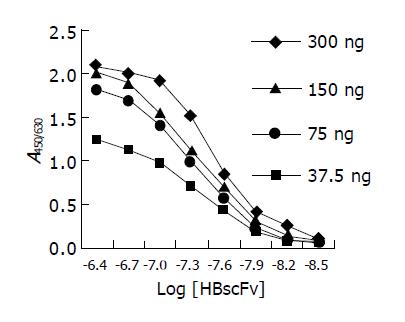
Figure 6 ELISA curves of HBscFv purified from the supernatant of Origami[pQE-HBscFv].
-
Citation: Xiong S, Wang YF, Ren XR, Li B, Zhang MY, Luo Y, Zhang L, Xie QL, Su KY. Solubility of disulfide-bonded proteins in the cytoplasm of
Escherichia coli and its “oxidizing” mutant. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11(7): 1077-1082 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v11/i7/1077.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v11.i7.1077