©2005 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Feb 14, 2005; 11(6): 797-802
Published online Feb 14, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i6.797
Published online Feb 14, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i6.797
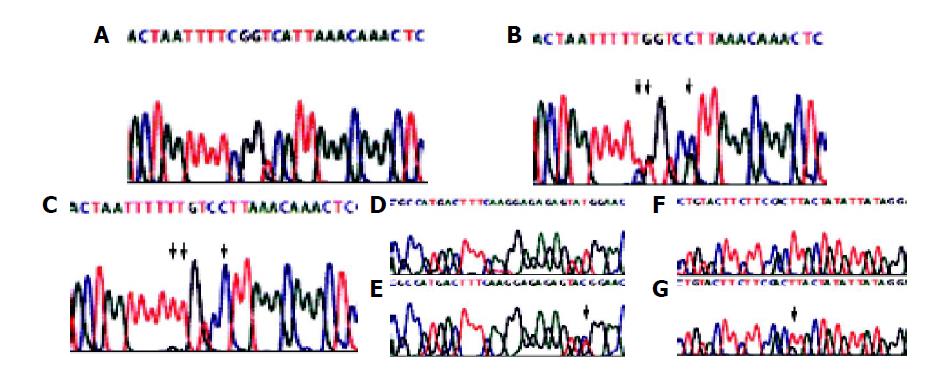
Figure 1 Representative electropherograms of (A) homozygous N129 R131 (nucleotides 387-392: TGACCG), (B) heterozygous K129 K131 (nucleotides 387-392: T/GGACC/AG/A), (C) homozygous K129 K131 (nucleotides 387- 392: GGACAA), (D) homozygous W208 (nucleotide 622: T), (E) heterozygous W208/R208 (nucleotide 622: T/C), (F) - 57 T, and (G) - 57 T/G.
Sequences were read reversely and nucleotides were translated into complements for (A), (B), and (C). The arrows indicate the sites of single nucleotide polymorphism.
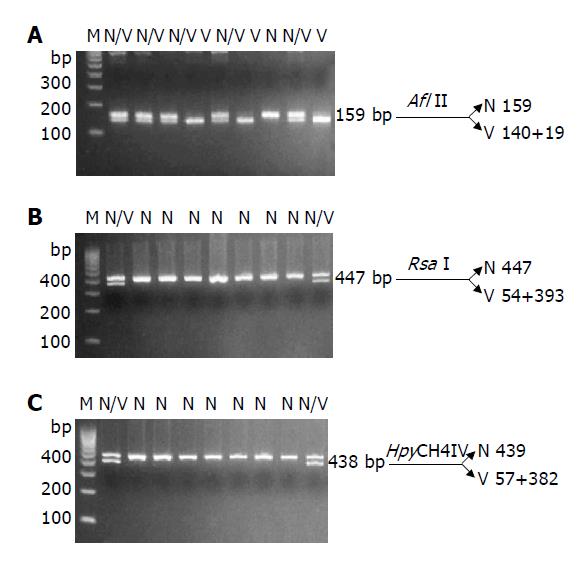
Figure 2 Results of restriction fragments at nucleotides (A) 387, (B) 622, and (C) -57, digested by Afl II, Rsa I, and HpyCH4 IV, respectively.
The bands of 19, 54, and 57 bp were too small to be seen (bp = base pair, M: DNA size marker, N: wild type, V: variant).
- Citation: Huang MJ, Yang SS, Lin MS, Huang CS. Polymorphisms of uridine-diphosphoglucuronosyltransferase 1A7 gene in Taiwan Chinese. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11(6): 797-802
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v11/i6/797.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v11.i6.797