Copyright
©2005 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 28, 2005; 11(48): 7615-7619
Published online Dec 28, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i48.7615
Published online Dec 28, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i48.7615
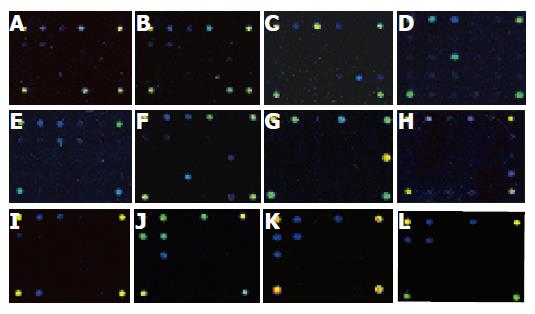
Figure 1 Typical hybridization results from Vibrio parahaemolyticus (A), Yersinia enterocolitica (B), Listeria monocytogenes (C), Bacillus cereus (D), Staphylococcus aureus (E), Proteus sp.
(F), Campylobacter jejuni (G), Vibrio cholerae (H), Enterococcus faecalis (I), Salmonella sp. (J), Shigella sp. (K) and Escherichia coli (L).
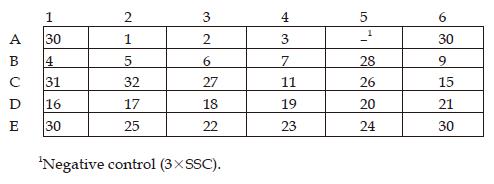
Figure 2 Layout of oligonucleotide probes.
- Citation: Jin LQ, Li JW, Wang SQ, Chao FH, Wang XW, Yuan ZQ. Detection and identification of intestinal pathogenic bacteria by hybridization to oligonucleotide microarrays. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11(48): 7615-7619
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v11/i48/7615.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v11.i48.7615