Copyright
©2005 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 28, 2005; 11(48): 7602-7606
Published online Dec 28, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i48.7602
Published online Dec 28, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i48.7602
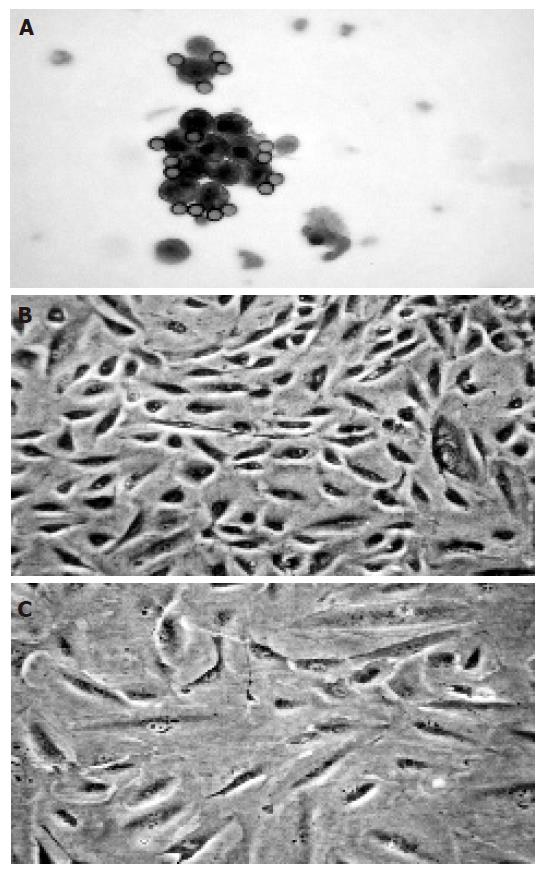
Figure 1 Freshly isolated (A) and proliferating human intrahepatic BECs (B) as well as BECs exposed to immunosuppressive agents (C).
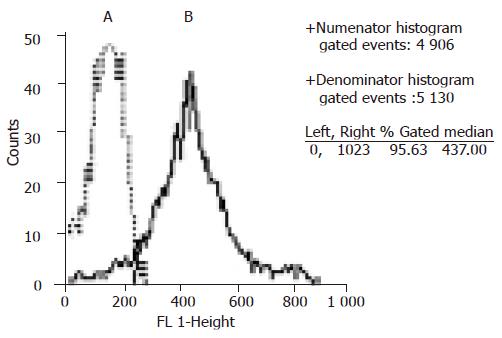
Figure 2 Flow cytometry analysis of CK19 expression.
A: negative control. B: with antibody against CK19.
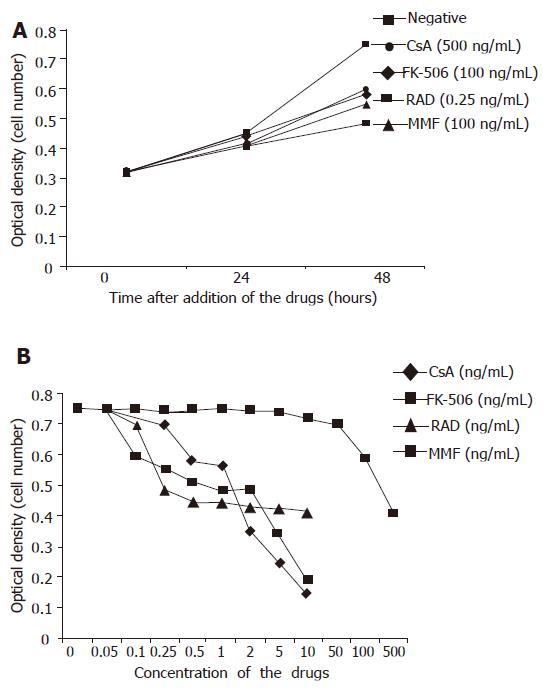
Figure 3 MTT analysis of proliferation of BECs exposed to drugs.
A: BECs exposed to the drugs for 24 and 48 h. At 48 h, CsA (500 µg/L), FK-506 (100 µg/L), RAD (0.25 µg/L), and MMF (100 µg/L) inhibited proliferation of BECs (P<0.05). B: BECs exposed to the drugs for 48 h. CsA, FK-506, RAD, and MMF inhibited the proliferation of BECs in a dose-dependent manner.
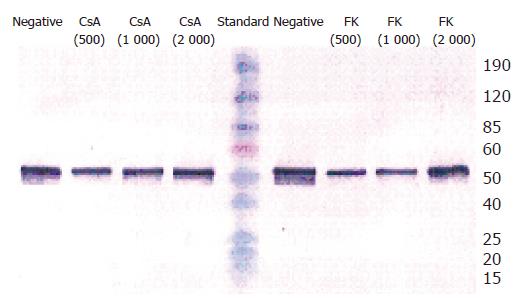
Figure 4 Western blot analysis of CK19 expression.
BECs were treated with 500, 1 000, 2 000 µg/L CSA, and FK-506, respectively for 48 h. CsA and FK-506 did not change the protein expression of CK19 in BECs.
- Citation: Liu C, Schreiter T, Frilling A, Dahmen U, Broelsch CE, Gerken G, Treichel U. Cyclosporine A, FK-506, 40-0-[2-hydroxyethyl]rapamycin and mycophenolate mofetil inhibit proliferation of human intrahepatic biliary epithelial cells in vitro. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11(48): 7602-7606
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v11/i48/7602.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v11.i48.7602