©2005 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 28, 2005; 11(48): 7591-7596
Published online Dec 28, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i48.7591
Published online Dec 28, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i48.7591
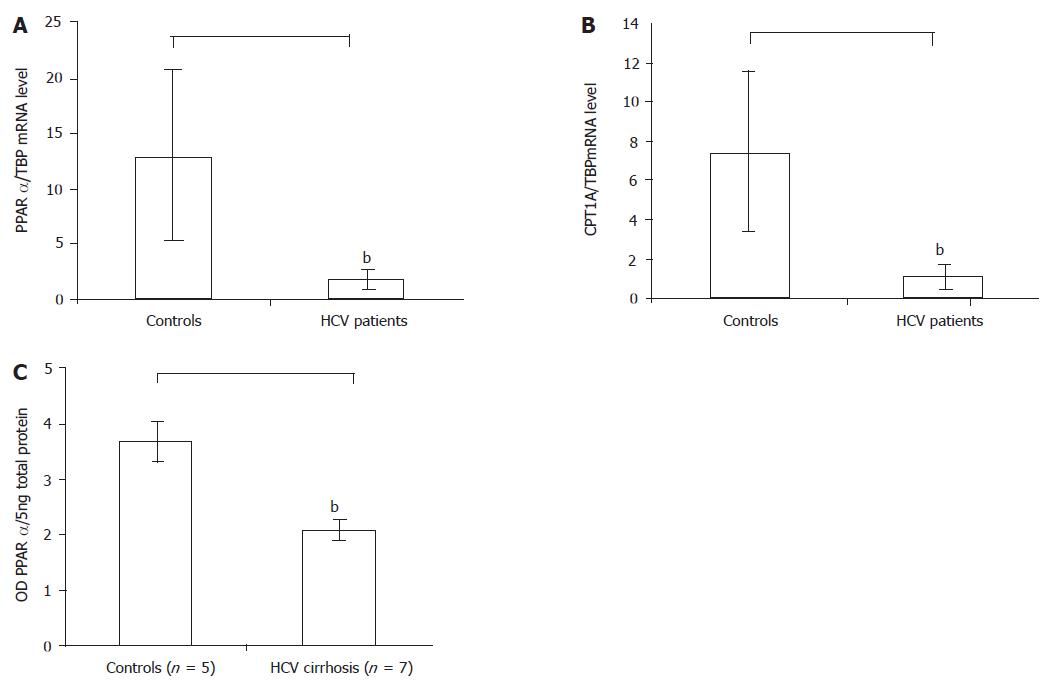
Figure 1 A: The PPARα mRNA level in the HCV patients reduced compared with controls by real-time RT-PCR, bP<0.
01 vs control; B: The PPARα target gene CPT1A mRNA level in the HCV patients also reduced compared with controls by real-time RT-PCR, bP<0.01 vs control; C: The PPARα protein level in the HCV cirrhotic patients reduced compared with controls by Western blot. Results were expressed as mean±SD, bP<0.01 vs control.
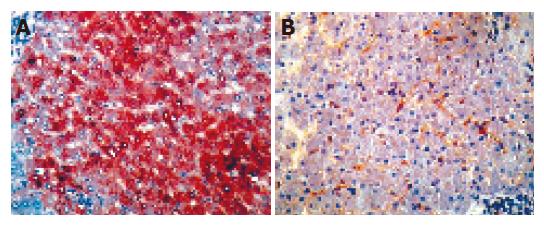
Figure 2 Representative PPARα immunostainings in liver specimens.
The left: a control liver, PPARα staining was detected in the majority of hepatocytes (magnification ×160); The right: a severe hepatitis patient liver, the number of PPARα-stained hepatocytes was decreased markedly (magnification ×160).
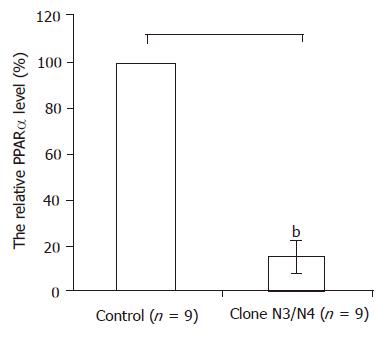
Figure 3 In the N3 colon and N4 colon which were stably expressing the HCV core protein PPARα mRNA levels decreased more than 80% compared with controls by real-time RT-PCR.
Results were expressed as mean±SD, bP<0.01 vs control.
- Citation: Cheng Y, Dharancy S, Malapel M, Desreumaux P. Hepatitis C virus infection down-regulates the expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α and carnitine palmitoyl acyl-CoA transferase 1A. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11(48): 7591-7596
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v11/i48/7591.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v11.i48.7591