©2005 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 21, 2005; 11(47): 7499-7507
Published online Dec 21, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i47.7499
Published online Dec 21, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i47.7499
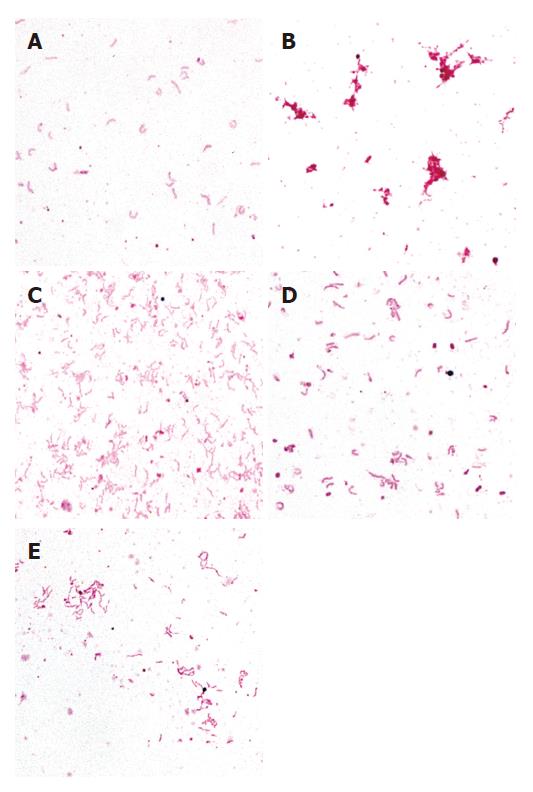
Figure 1 Bright-field images showing H pylori lysis experiment.
A: negative control (H pylori + distilled water); B: positive control (H pylori + cell lysis solution); C: H pylori + 0.05 g/mL turmeric; D: H pylori + 0.05 g/mL borage; E: H pylorii + 0.05 g/mL parsley. Images taken using x100 objective.
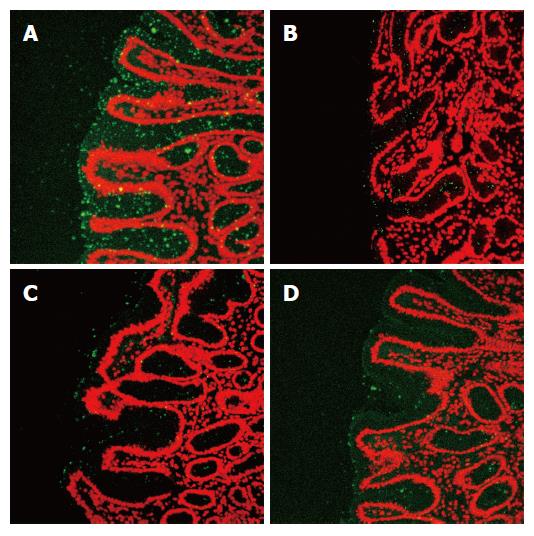
Figure 2 Confocal images showing inhibition of H pylori adhesion by A: distilled water (control); B: turmeric (0.
05 g/mL); C: borage (0.05 g/mL) and D: parsley (0.05 g/mL); to stomach sections expressing the Lewis b blood group antigen.
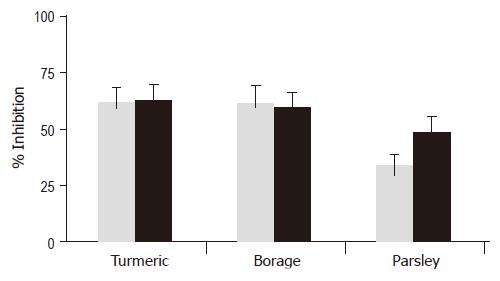
Figure 3 Inhibition of H pylori adhesion by turmeric, borage and parsley to stomach sections expressing either the Lewis a or Lewis b blood group antigen.
Experiments were performed three times using four strains of H pylori. Mean percentage of inhibition is shown for each plant. Gray bar, Lewis a stomach; Black bar, Lewis b stomach.
- Citation: O’Mahony R, Al-Khtheeri H, Weerasekera D, Fernando N, Vaira D, Holton J, Basset C. Bactericidal and anti-adhesive properties of culinary and medicinal plants against Helicobacter pylori. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11(47): 7499-7507
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v11/i47/7499.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v11.i47.7499