©2005 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 7, 2005; 11(41): 6495-6502
Published online Nov 7, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i41.6495
Published online Nov 7, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i41.6495
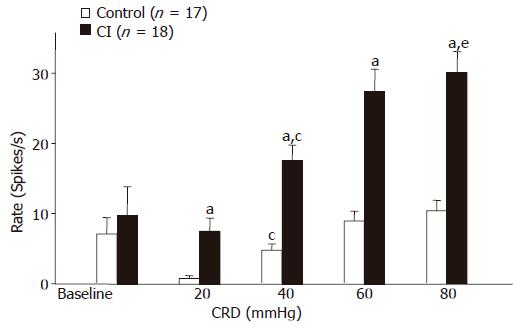
Figure 1 Average responses of LS neurons to CRD (20, 40, 60, 80 mmHg).
Bar graph summarizes the average background activity (baseline; control, n = 17; CI, n = 18) and the responses of LS neurons to all intensities of CRD in control and CI rats. The responses to CRD are reported as the mean increase in firing rate above baseline. Responses recorded in CI rats were significantly higher than those recorded in control rats. aP<0.05 vs the values of normal rats with the same intensity; cP<0.05 vs 20 mmHg CRD in each group; eP<0.05 vs 40mmHg CRD in CI rats.
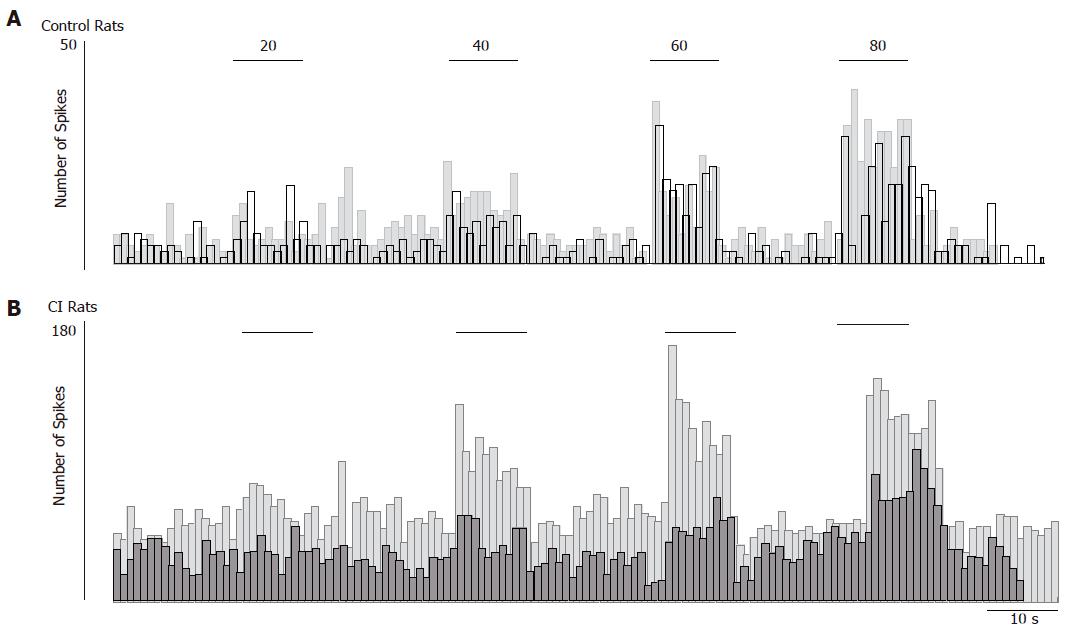
Figure 2 Effect of AP7 (0.
01 mmoL) on dorsal horn neuronal responses to CRD in control or CI rats. Rate histograms illustrate the responses of a dorsal horn neuron isolated from a control rat (A) and of another neuron isolated from a CI rat (B) before (grey) and after (black) spinal administration of AP-7 (0.01 mmoL). Horizontal bars indicate the timing and duration (10 s) of CRD (20- 80 mmHg).
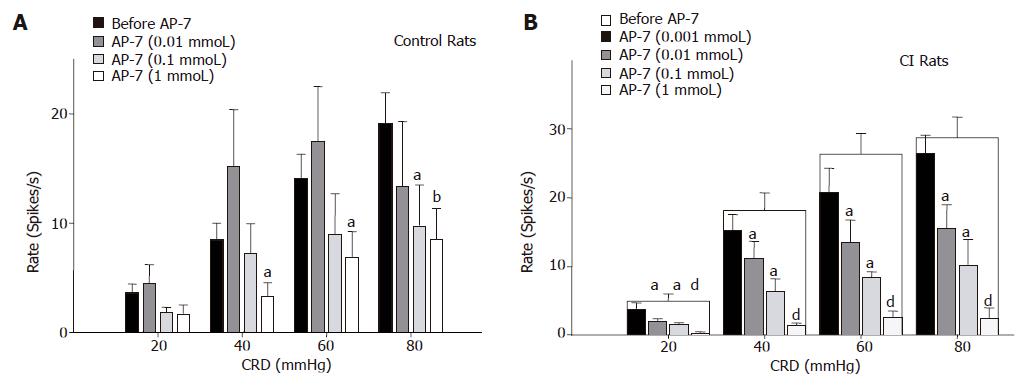
Figure 3 Effect of spinal AP7 on average responses of LS neurons to CRD.
Bar graphs illustrate the responses of LS neurons to CRD (20-80 mmHg) recorded in control rats (A; left panel) or CI rats (B; right panel) before and after spinal administration of AP7. A: AP-7 (0.1 mmoL) significantly attenuated the average response to high intensity CRD (80 mmHg) and AP-7 (1 mmoL) significantly attenuated the responses to CRD (40-80 mmHg) in controls; B: AP-7 (0.01 mmoL) significantly attenuated the average responses to graded CRD in CI rats in a dose-dependant manner. aP<0.05, bP<0.01, dP<0.001 vs before AP-7 application at that distention pressure in each group.
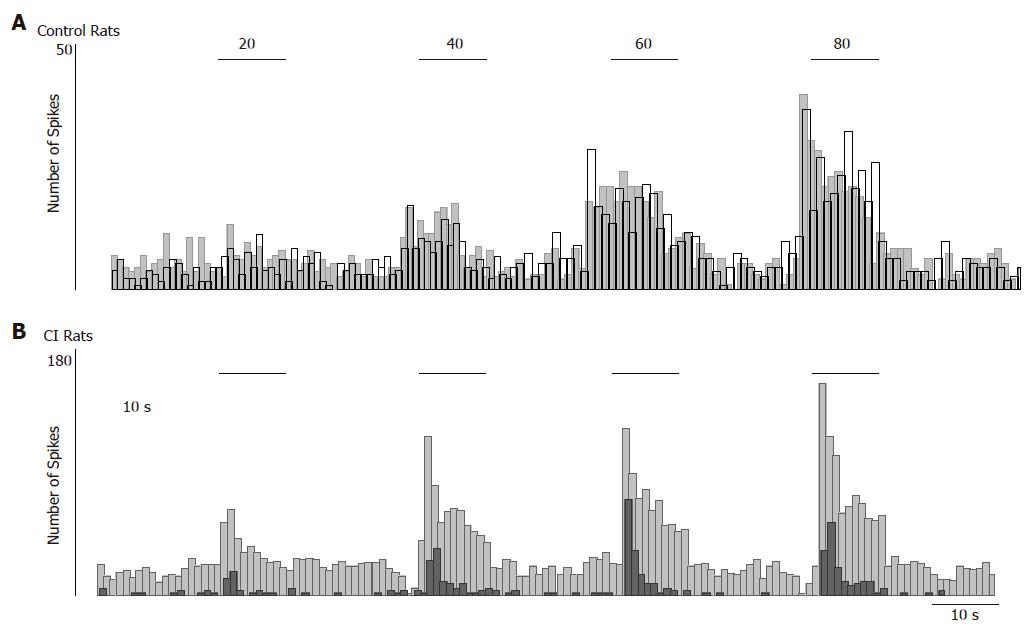
Figure 4 Effect of CNQX (2 µmoL) on dorsal horn neuronal responses to CRD in control or CI rats.
Rate histograms illustrate the responses of a dorsal horn neuron isolated from a control rat (A) and of another neuron isolated from a CI rat (B) before (grey) and after (black) spinal administration of CNQX (2 µmoL).
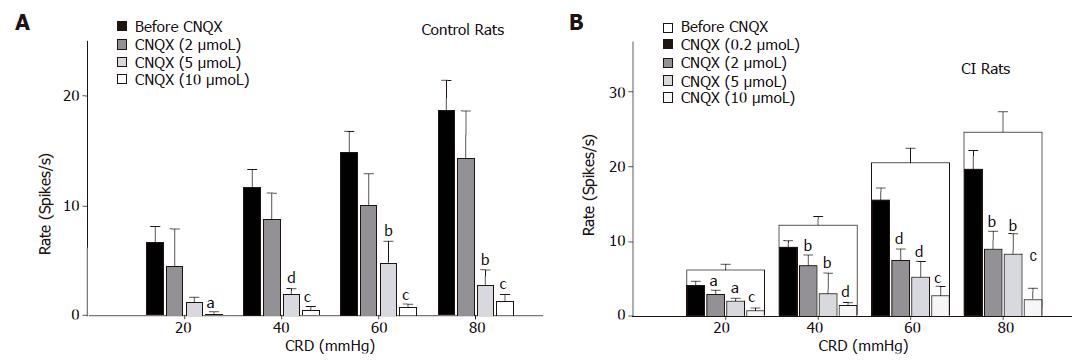
Figure 5 Effect of spinal CNQX on average responses of LS neurons to CRD.
Bar graphs illustrate the responses of LS neurons to graded CRD (20-80 mmHg) recorded in control rats (A; left panel) or CI rats (B; right panel) before and after spinal administration of CNQX. A: In control rats, CNQX (5 µmoL) significantly attenuated the responses to CRD in the 40-80 mmHg range and CNQX (10 µmoL) significantly attenuated the response to all intensities of CRD; B: In CI rats, CNQX (2-10 µmoL) significantly decreased the response to all intensities of CRD in a dose-dependent manner. aP<0.05, bP<0.01, dP<0.001 vs before CNQX application at that distention pressure in each group; cP <0.05 vs 2 µmoL CNQX.
- Citation: Lin C, Al-Chaer ED. Differential effects of glutamate receptor antagonists on dorsal horn neurons responding to colorectal distension in a neonatal colon irritation rat model. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11(41): 6495-6502
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v11/i41/6495.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v11.i41.6495