©2005 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 7, 2005; 11(41): 6433-6439
Published online Nov 7, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i41.6433
Published online Nov 7, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i41.6433
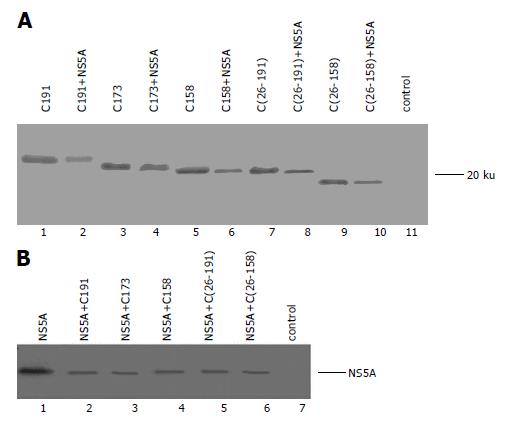
Figure 1 Expression of core mutant fragments (A) and NS5A protein (B).
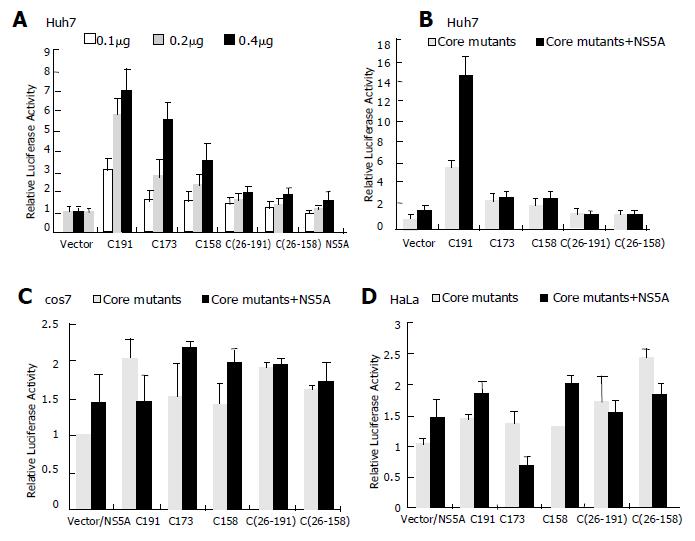
Figure 2 Effect of HCV core and NS5A proteins on NF-κB activity.
A: NF-κB activation capacity of the core mutant fragments and NS5A protein individually expressing in Huh7 cell line; B: NF-κB activation capacity of the core mutants and NS5A protein expressing in Huh7 cells, C: Cos-7 cells; D: HeLa cells.
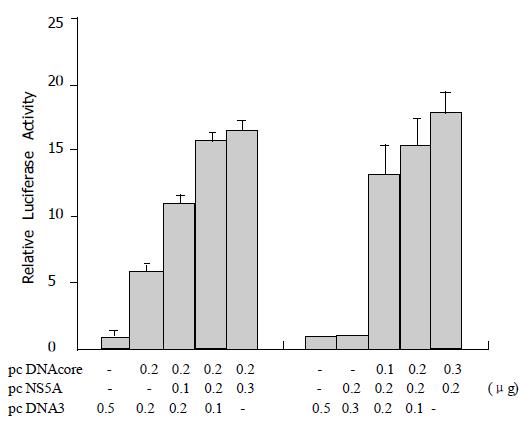
Figure 3 Enhancement of core protein-induced NF-kB activation in a NS5A protein dose-dependent manner.
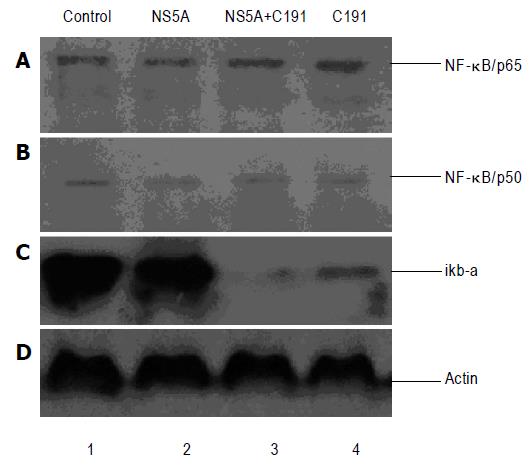
Figure 4 Expression of NF-κB/p65, NF-κB/p50 and IkB-a.
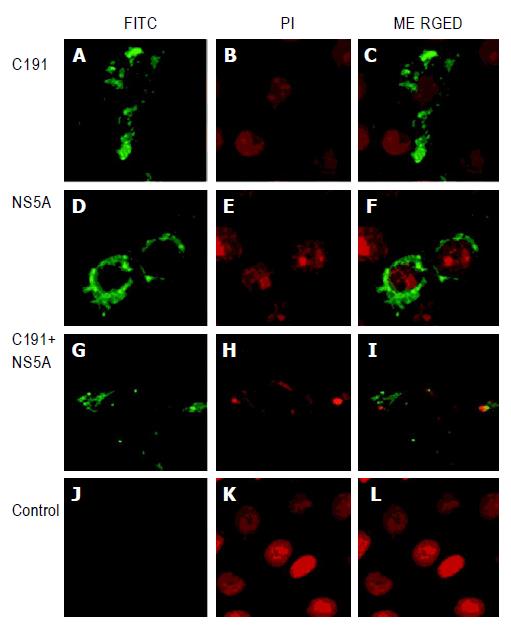
Figure 5 Localization of C191 and NS5A proteins.
A-C: C191; D-F: NS5A protein; G: NS5A protein (FITC-labeled); H: C191 protein (TRITC-labeled); I: merged localization of C191 and NS5A proteins; J-L: pcDNA3 vector alone as a negative control.
- Citation: Liao QJ, Ye LB, Timani KA, She YL, Yang XJ, Ye L, Wu ZH. Hepatitis C virus non-structural 5A protein can enhance full-length core protein-induced nuclear factor-κB activation. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11(41): 6433-6439
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v11/i41/6433.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v11.i41.6433