©2005 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 7, 2005; 11(41): 6416-6421
Published online Nov 7, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i41.6416
Published online Nov 7, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i41.6416
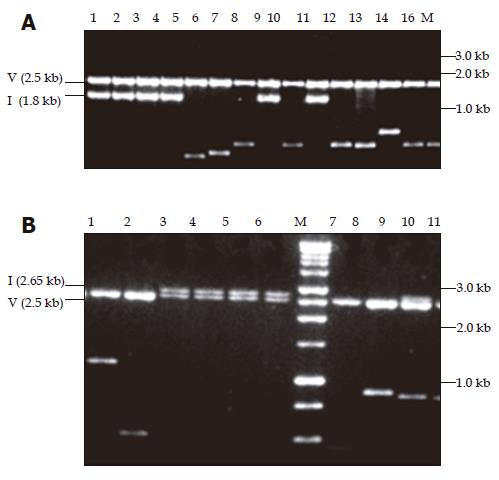
Figure 1 Ethidium bromide stained with 1% agarose gel showing pPCR-Script Amp SK(+) plasmid containing amplicons restricted with PvuII.
In panel A, the fragments cloned were amplified with primers 455(+) and 1 800(–). Lanes 1-4, 8, and 10 show the expected size insert of -1.8 kb for fragment A amplicon (1.3 kb) whereas lanes 5-7, 9, and 11-16 show shorter inserts ranging in size 0.6-1.1 kb. In panel B, the fragments cloned were amplified with primers 1 687(+) and 685(–). Lanes 3-6 and 9 show the expected size insert of -2.65 kb for fragment B amplicon (2.2 kb), lane 7 is vector alone and lanes 1, 2, 8-11 show shorter inserts ranging in size 0.5-1.2 kb. M: Promega 1 kb molecular weight marker, V: vector, I: insert of expected size (A and B).
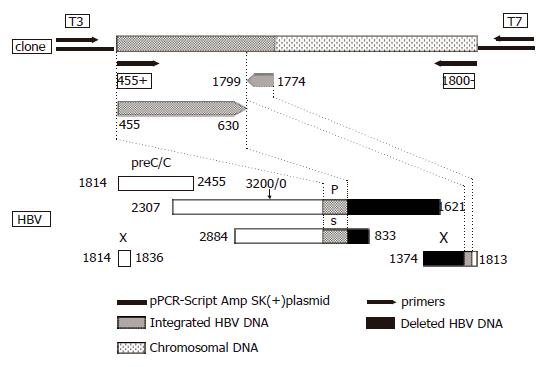
Figure 2 Schematic representation of the HBV DNA integrant amplified from the serum of acute hepatitis patient (#0962) using primers 455 (+) and 1 800 (–) and cloned into pPCR-Script Amp SK (+) plasmid relative to the HBV genome.
The lower part of the figure represents the genetic organization of the four open reading frames of HBV, preC/C: precore/core, P: polymerase gene, S: surface gene and X: X gene. Numbering according to nucleotide position of HBV GenBank accession no. V00866 where the EcoRI cleavage site is position 1.
- Citation: Kimbi GC, Kramvis A, Kew MC. Integration of hepatitis B virus DNA into chromosomal DNA during acute hepatitis B. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11(41): 6416-6421
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v11/i41/6416.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v11.i41.6416