©2005 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 28, 2005; 11(40): 6269-6276
Published online Oct 28, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i40.6269
Published online Oct 28, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i40.6269
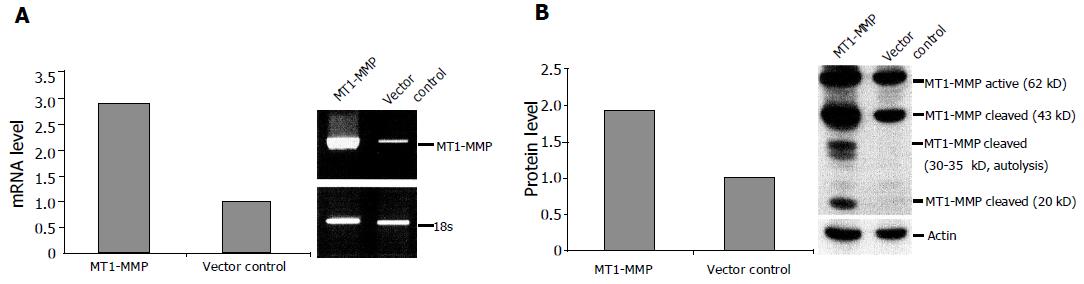
Figure 1 Establishment of stable MT1-MMP transfectants.
A: RNA transcript levels were compared in linear phases by semi-quantitative RT-PCR after normalization with 18S level; B: protein expression levels were compared by Western blotting analysis after normalization with actin level.
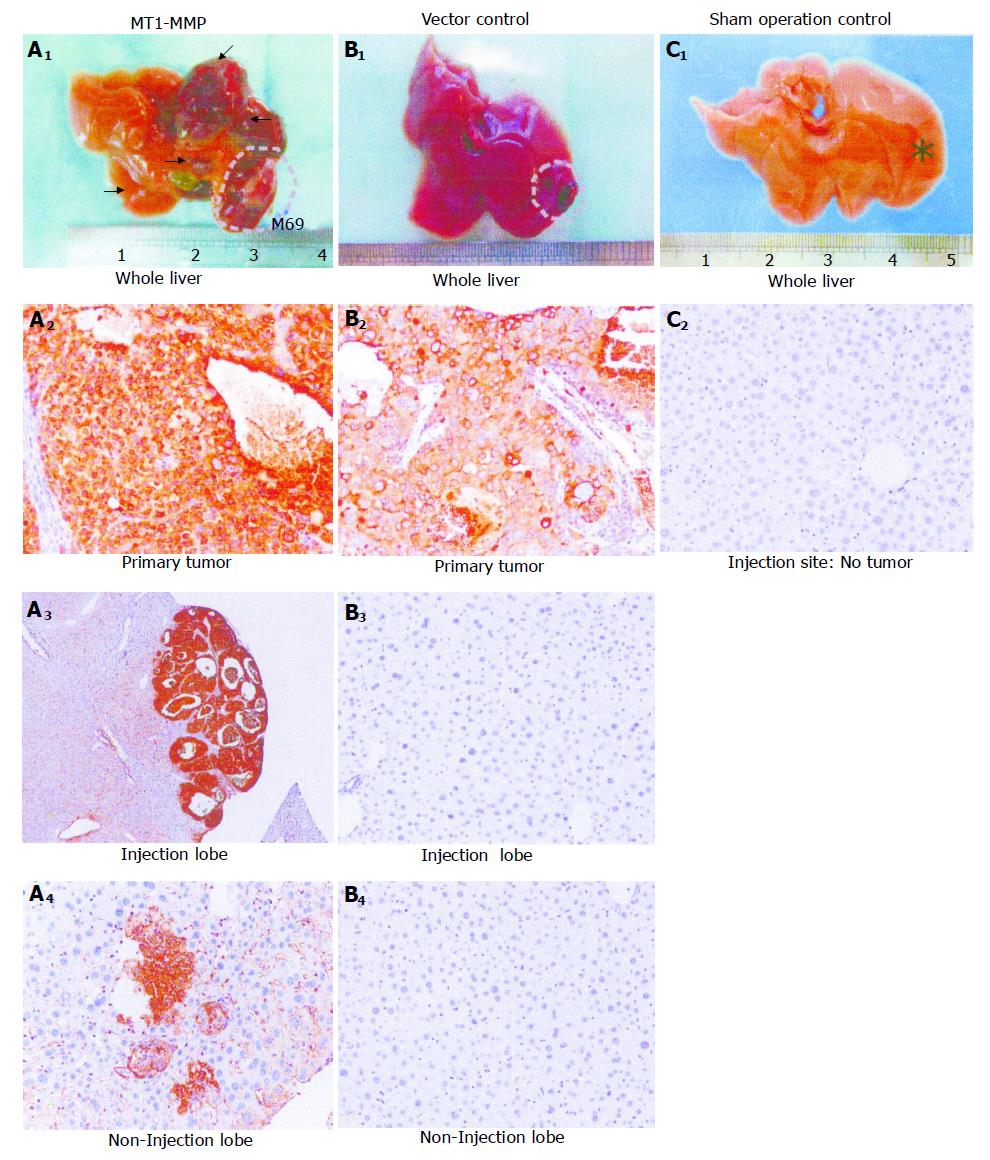
Figure 2 Tumorigenicity and metastasis in vivo enhanced by MT1-MMP.
A1-4: Large primary tumor nodule with prominent metastases produced by MT1-MMP overexpression; B1-4: Small primary tumor nodule and rare metastasis produced by vector control transfectants; C1-2: Tumor-free control liver injected with saline. Primary tumors, metastases, and injection site were indicated by dotted lines, arrows, and an asterisk, respectively. Sections from all tissues collected were then subjected to AFP staining.
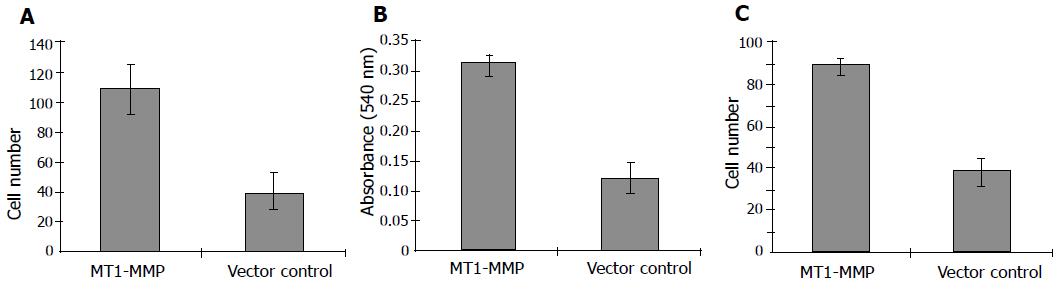
Figure 3 Cell invasion, adhesion efficiency, and cell motility in vitro enhanced by MT1-MMP.
A: Cell invasive ability in standard Boyden chamber; B: Adhesion efficiency on collagen I; C: Directional migration ability by cell motility assay.
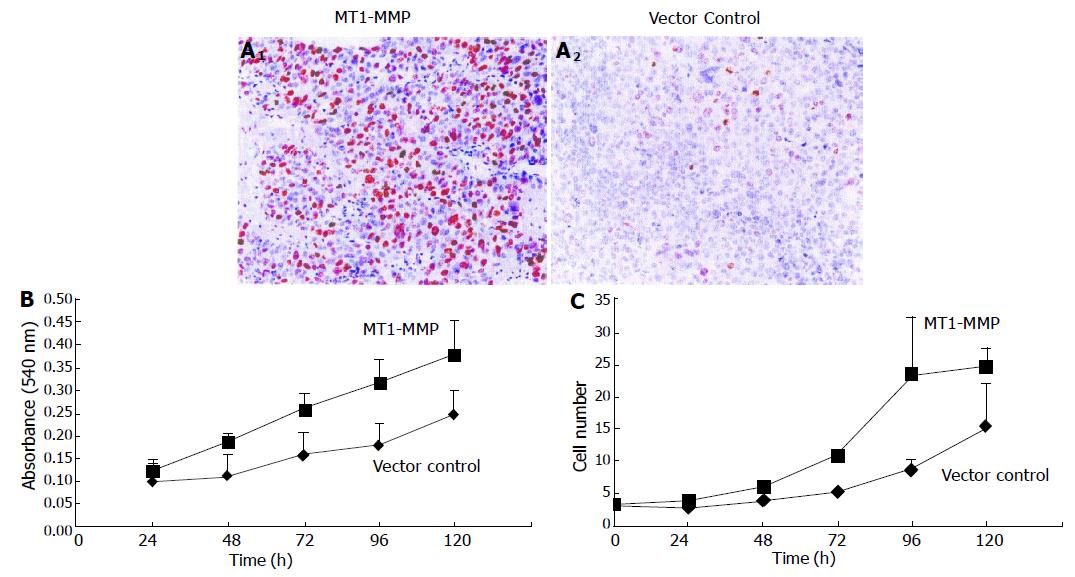
Figure 4 Cell proliferation in vivo and in vitro enhanced by MT1-MMP.
A1-2: Primary tumors in athymic nude mice examined by Ki67 staining; B: Cells examined by MTT assay; C: Cell number counted at regular time intervals.
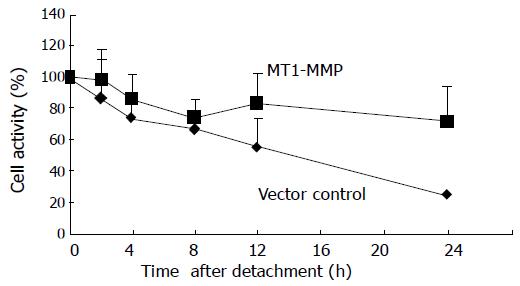
Figure 5 MT1-MMP delayed anoikis.
The cell metabolic activity of two transfectants after detachment was compared.
- Citation: Ip YC, Cheung ST, Leung KL, Fan ST. Mechanism of metastasis by membrane type 1-matrix metalloproteinase in hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11(40): 6269-6276
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v11/i40/6269.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v11.i40.6269