©The Author(s) 2005.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 21, 2005; 11(39): 6159-6164
Published online Oct 21, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i39.6159
Published online Oct 21, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i39.6159
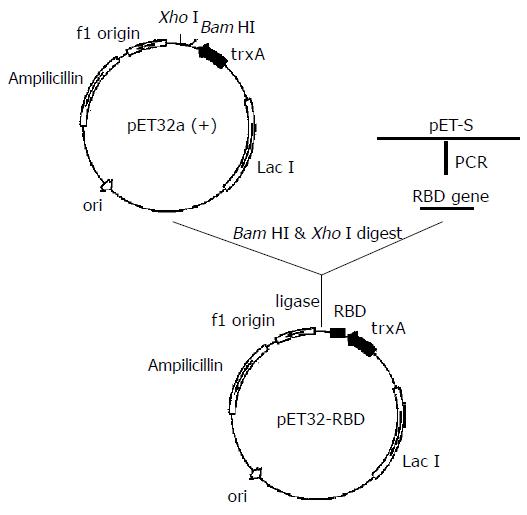
Figure 1 Schematic illustration of the constructs of expression vector pET32-RBD.
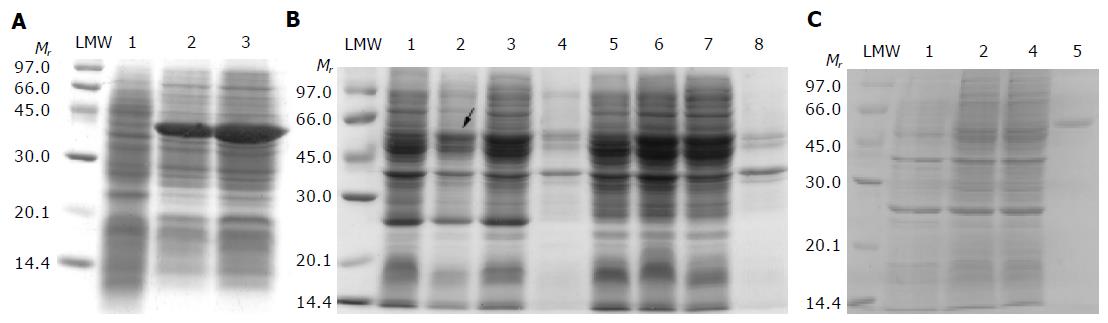
Figure 2 A: RBD expressed in E.
coli R-TB as inclusion body form. LMW: protein low molecule weight marker (Amersham-Pharmacia); lane 1: E.coli BL21(DE3) negative control; lane 2: E.coliR-TB 5 mmol/L IPTG induced 4 h later; lane 3: E.coli R-TB 5 mmol/L IPTG induced 6 h later; B: E.coli BL-GB and BL-MB expression and solubility analysis. LMW: protein low molecule weight marker (Amersham-Pharmacia); lane 1: E.coli BL21(DE3) negative control; lane 2: E.coli BL-GB in FML medium; lane 3: soluble fraction; lane 4: insoluble fraction; lane 5: E.coli BL21(DE3) negative control; lane 6: E.coli BL-MB induced at 5 mmol/L IPTG 6 h later; lane 7: soluble fraction; lane 8: insoluble fraction; C: The purified recombinant RBD protein expressed in E.coli BL-GB. LMW: protein low molecule weight marker (Amersham-Pharmacia); lane 1: E.coli BL21(DE3) negative control; lane 2: IPTG induced E.coli BL-GB; lane 2: soluble fraction; lane 4: purified RBD protein.
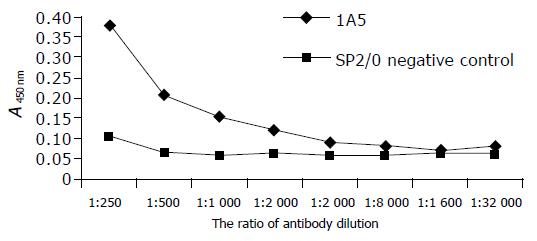
Figure 3 ELISA of GST.
RBD antigen.
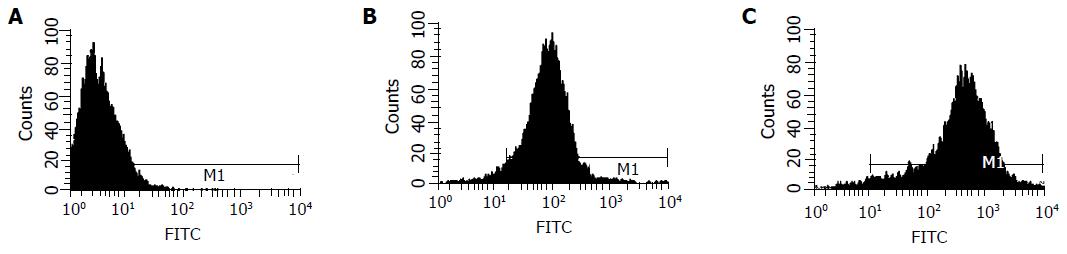
Figure 4 Cell binding test preformed by flow cytometry assay.
A: Vero E6 cells alone, geometrical mean 3.3; B: Vero E6 cells+GST protein+two antibodies, geometrical mean 77.08; C: Vero E6 cells+GST.RBD+two antibodies, geometrical mean 352.73.
-
Citation: Chen J, Miao L, Li JM, Li YY, Zhu QY, Zhou CL, Fang HQ, Chen HP. Receptor-binding domain of SARS-Cov spike protein: Soluble expression in
E.coli , purification and functional characterization. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11(39): 6159-6164 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v11/i39/6159.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v11.i39.6159