©The Author(s) 2005.
World J Gastroenterol. Oct 14, 2005; 11(38): 5931-5937
Published online Oct 14, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i38.5931
Published online Oct 14, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i38.5931
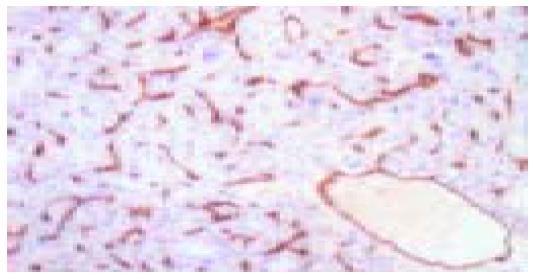
Figure 1 Immunohistochemical staining for CD34 in HCC (×100).
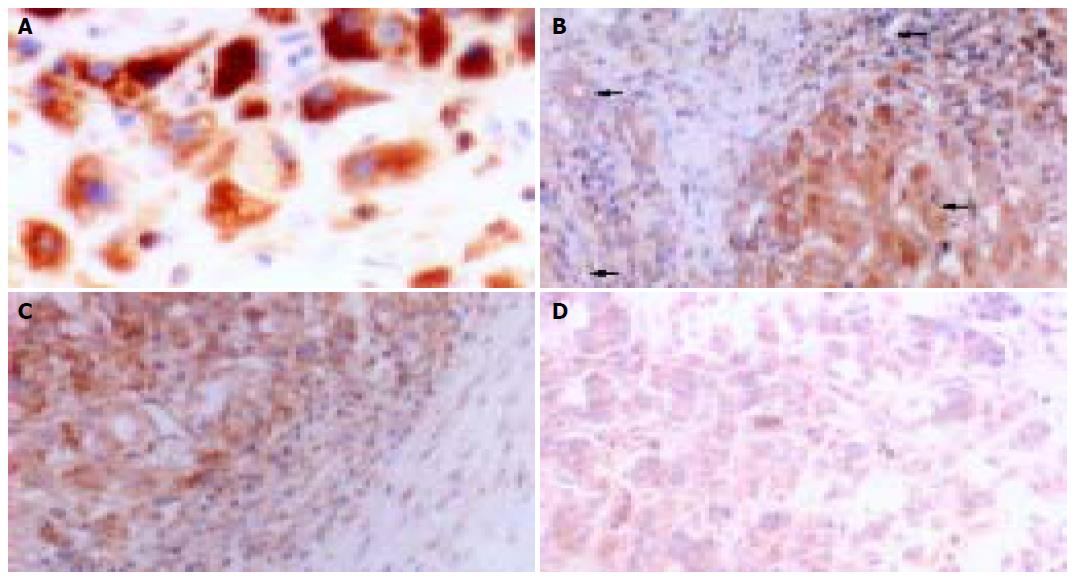
Figure 2 Immunohistochemical staining for MMP-9.
A: MMP-9 in cytoplasm and cytoplasmic membranes in HCC (×400); B: MMP-9 in vascular endothelial cells, bile ducts, HCC cells, and stromal fibroblasts (arrow heads from top to bottom) within HCC (×200); C: MMP-9 expression in neighboring capsule of HCC (×200); and D: weak expression of MMP-9 in central areas of HCC tissues (×200).
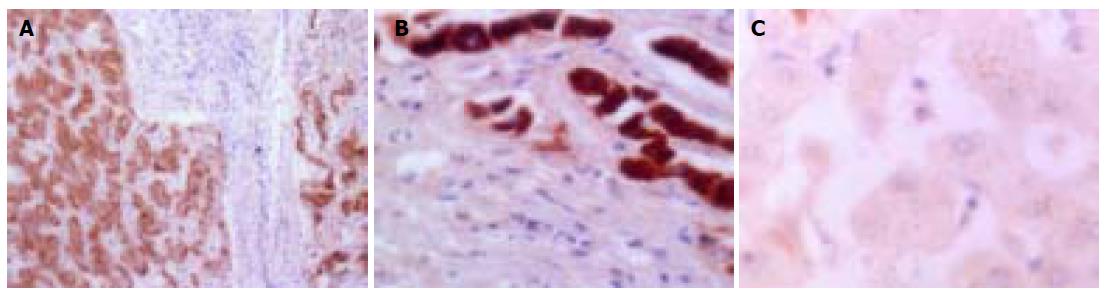
Figure 3 Immunohistochemical staining for iNOS.
A: iNOS expression in tumor cytoplasm (×100); B: strong expression of iNOS in neighboring capsule of HCC tissues (×400); and C: weak expression of iNOS in central areas of HCC tissues (×400).
- Citation: Sun MH, Han XC, Jia MK, Jiang WD, Wang M, Zhang H, Han G, Jiang Y. Expressions of inducible nitric oxide synthase and matrix metalloproteinase-9 and their effects on angiogenesis and progression of hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11(38): 5931-5937
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v11/i38/5931.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v11.i38.5931