©2005 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 21, 2005; 11(35): 5498-5505
Published online Sep 21, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i35.5498
Published online Sep 21, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i35.5498
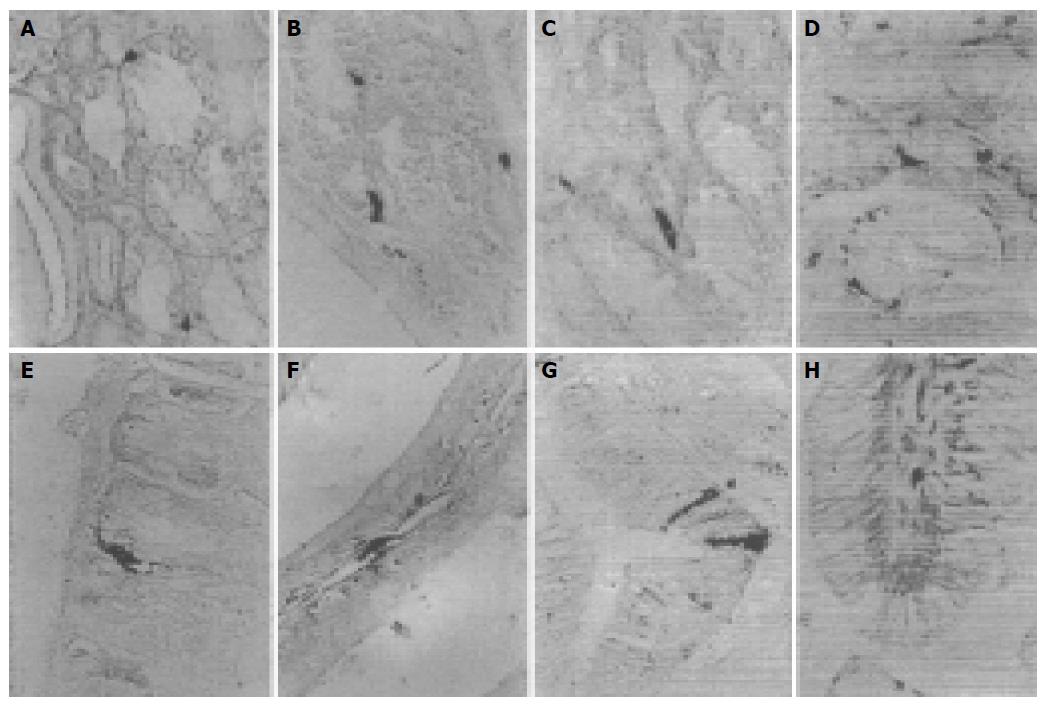
Figure 2 SS-IR cells in cardia of S.
indicus (A) and E. elegans (B), fundus of S. indicus (C) and G. japonicus (D), pylorus of G. japonicus (E), duodenum of G. japonicus (F), ileum of E. chinensis (G), rectum of E. chinensis (H).
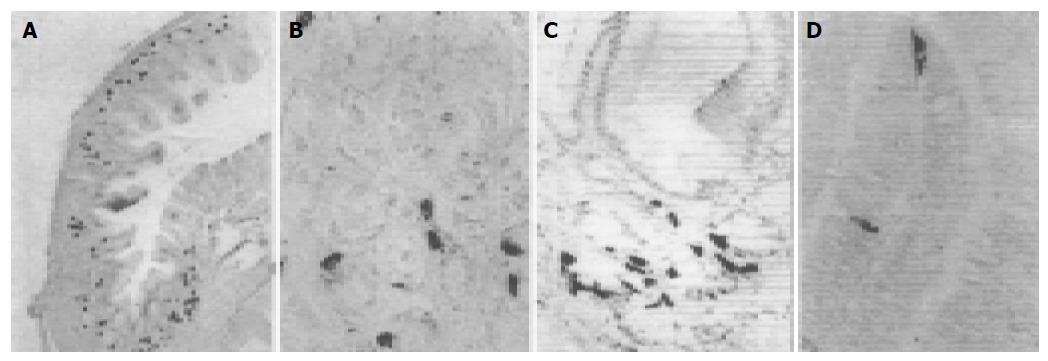
Figure 3 GAS-IR cells in pylorus of E.
elegans (A) and E. chinensis (B) and S. indicus (C), duodenum of G. japonicus (D).
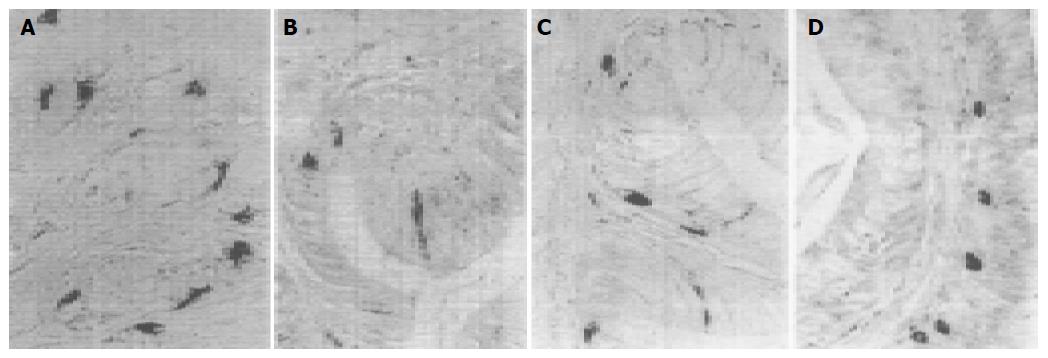
Figure 4 GLU-IR cells in fundus of G.
japonicus (A), ileum of E. chinensis (B), rectum of E. chinensis (C) and S. indicus (D).
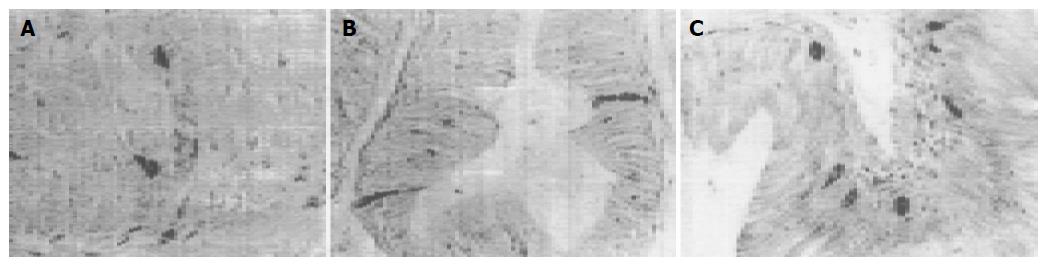
Figure 5 SP-IR cells in cardia of G.
japonicus (A), ileum of E. chinensis (B), rectum of S. indicus (C).
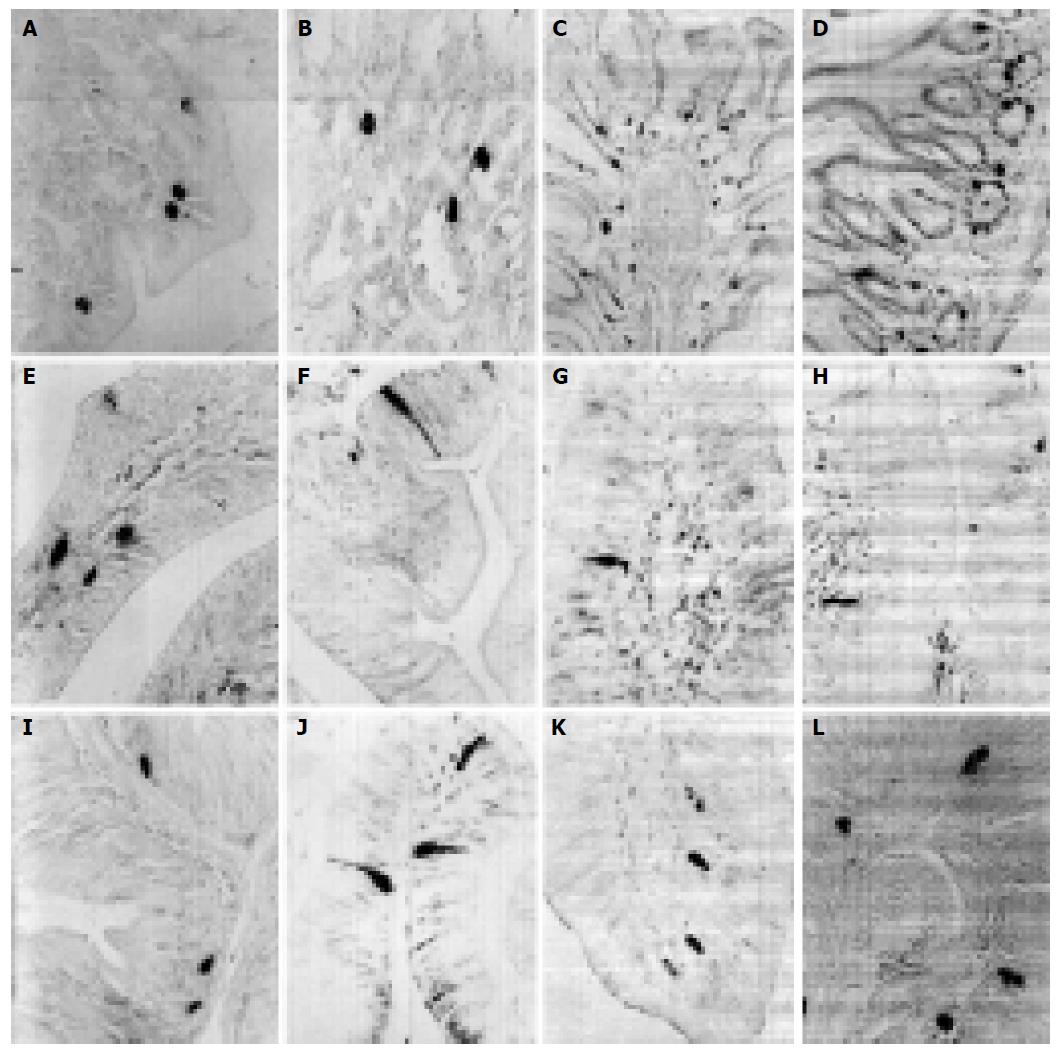
Figure 1 5-HT-IR cells in cardia of E.
chinensis (A), fundus of E. elegans (B), pylorus of S. indicus (C) and E. elegans (D), duodenum of G. japonicus (E) and S. indicus (F), jejunum of S. indicus (G) and E. elegans (H), ileum of S. indicus (I) and E. elegans (J), rectum of E. elegans (K) and E. chinensis (L).
- Citation: Huang XG, Wu XB. Immunohistochemical study on gastrointestinal endocrine cells of four reptiles. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11(35): 5498-5505
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v11/i35/5498.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v11.i35.5498