©The Author(s) 2005.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 14, 2005; 11(30): 4611-4617
Published online Aug 14, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i30.4611
Published online Aug 14, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i30.4611
Figure 1 Adult of E.
multilocularis.
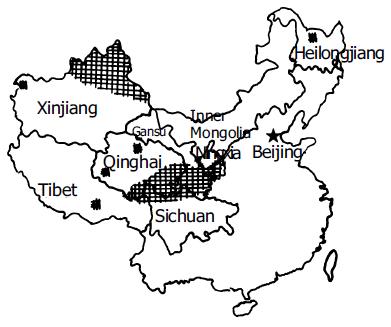
Figure 2 Distribution of AE in eight provinces in west China.
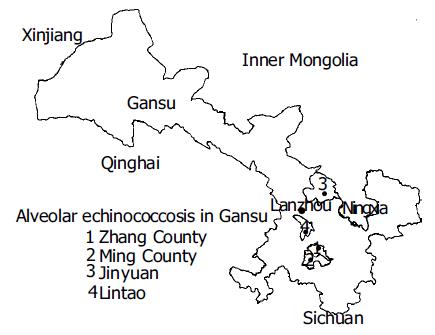
Figure 3 AE endemic counties in central eastern Gansu.
(1) Zhang County, (2) Ming County, (3) Lintao, (4) Jinyuan.
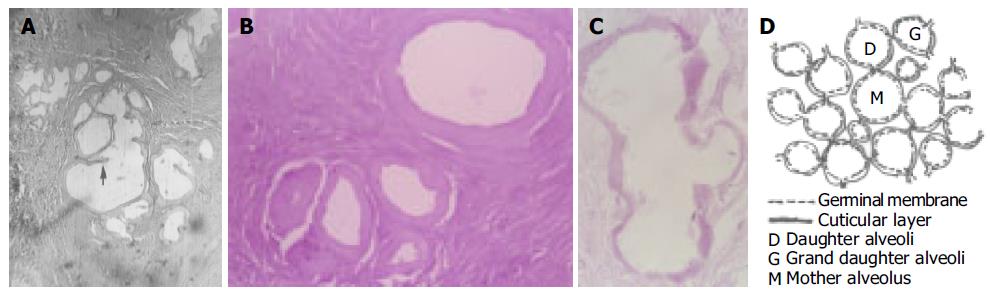
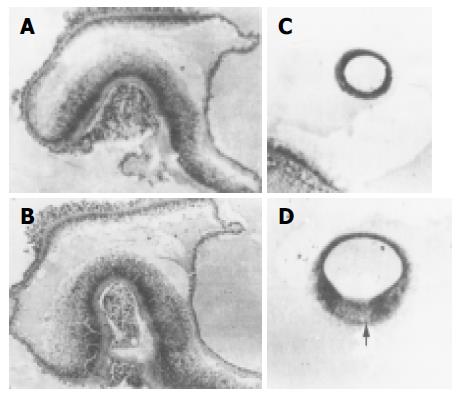
Figure 4 Modes of proliferation.
A: Endogenous budding of alveococcus (HE stain ×200). Arrow: Septum; B: One mother alveolus (left lower side) dividing into four daughter alveoli (HE stain ×400); C: Exogenous budding of alveococcus (HE stain ×400); D: Model of alveococcus exogenous budding.
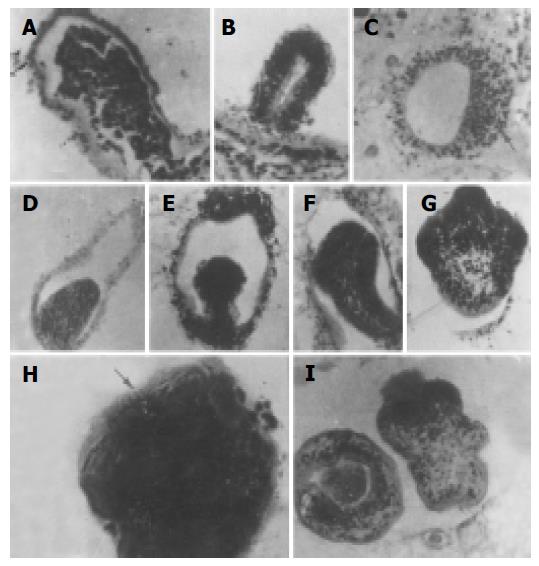
Figure 5 The entire process of mouse AE protoscolex histogenesis (HE stain×200-800).
A: local cellular hyperplasia of germinal membrane of alveococcus wall; B: re-arrangement of hyperplastic cells and formation of brood capsule; C: local cellular hyperplasia of brood capsule wall; D: elliptical protrusion into cavity; E: mushroom protrusion; F: lingural protrusion; G: showing rostellum and suckers of protoscolex; H: Hooklets on rostellum; I: mature protoscolex (right: evaginated type. Left: invaginated type).
Figure 6 Histogenesis process of brood capsule of liver AE protoscolex in Mus musculus (HE stain ×200 ).
A: local hyperplasia of alveococcus wall into the cavity, looking like a reversed pocket; B: gradually approximating and finally closing of two pocket edges; C: formation of brood capsule; D: local cellular hyperplasia of brood capsule wall.
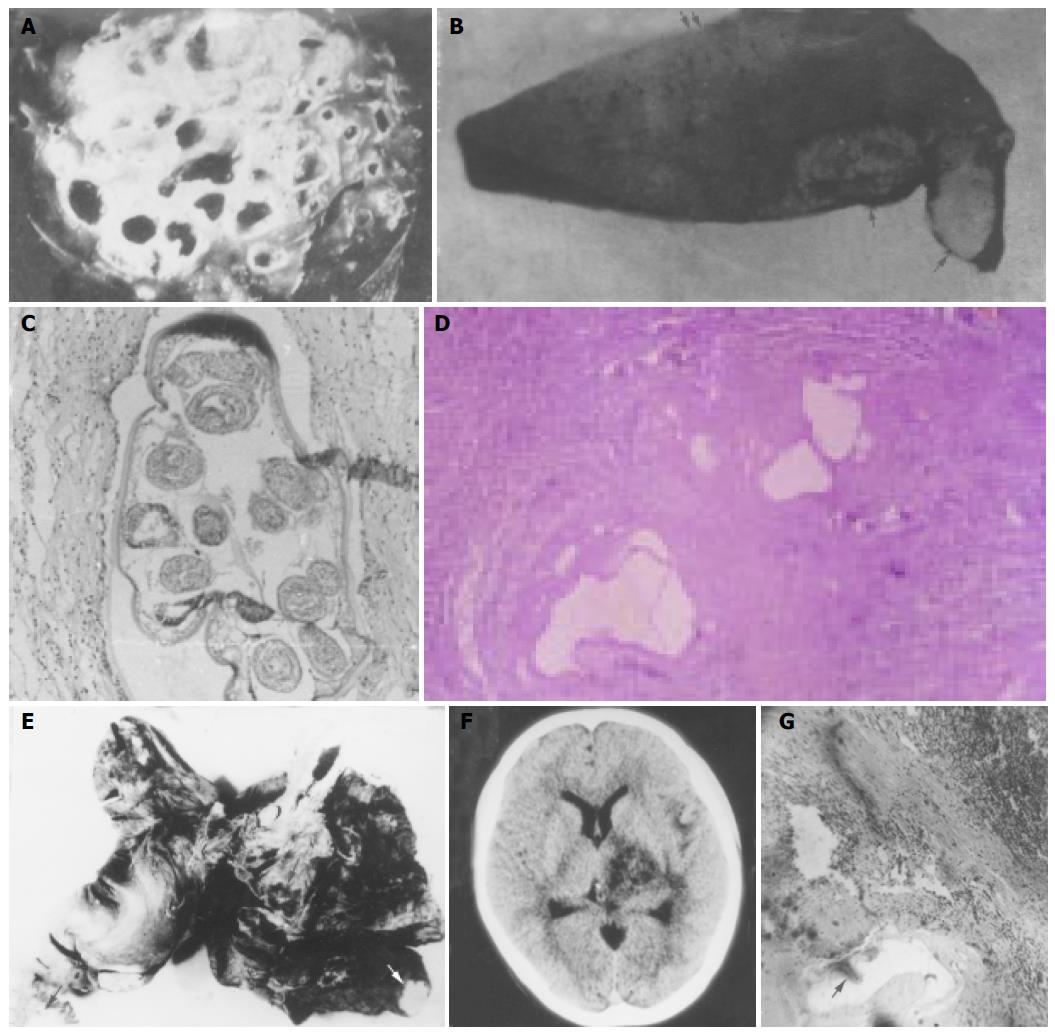
Figure 7 Pathology.
A: A cross section of human liver AE showed alveolate appearance; B: Types of liver AE.↑: Nodular type, ↑↑: Mixed type; C: Protoscolices inside brood capsule (HE stain×100); D: Alveococcus nodule (HE stain×200); E: Three arrows indicating metastatic bilateral lung AE; F: ↑: metastatic right brain AE; G: lymph node metastasis near porta hepatis (HE stain×200). ↑: AE. The left upper side: Metastatic lymph nodes.
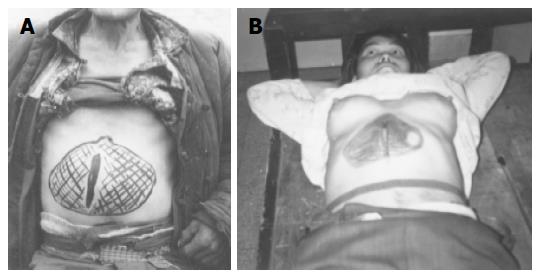
Figure 8 The size of upper abdominal mass with the largest reaching the umbilicus level.
A: After external drainage of pseudocyst, the patient survived for 23 years. B: The patient survived only for 3 years.
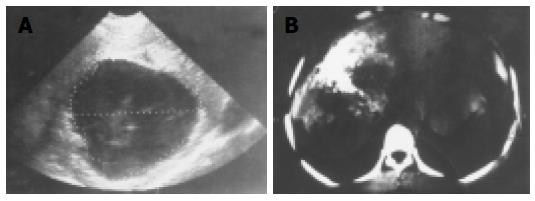
Figure 9 Imaging examinations.
A: Ultrasonic scanning of liver AE showed a central necrotic pseudocystic cavity, but the cystic wall was irregular; B: Liver CT showed partial AE calcification (left) and pseudocyst (right) on the left upper side. The patient was confirmed surgically and pathologically.
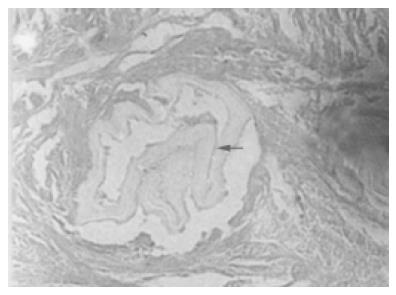
Figure 10 Liver needle biopsy.
Arrow: alveococcus (HE stain×200).
- Citation: Jiang CP, Don M, Jones M. Liver alveolar echinococcosis in China: Clinical aspect with relative basic research. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11(30): 4611-4617
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v11/i30/4611.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v11.i30.4611