©The Author(s) 2005.
World J Gastroenterol. Aug 7, 2005; 11(29): 4530-4535
Published online Aug 7, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i29.4530
Published online Aug 7, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i29.4530
Figure 1 Dose- and time-dependent CYP2E1 activity by ethanal administration.
A: Ethanol dose-dependent induction of CYP450 2E1. Hepatocytes were incubated with various concentrations of ethanol (0-100 mmol/L) for 9 h. CYP2E1 enzyme activity was measured as described in Materials and methods. CT: control; aP<0.05, bP<0.01 vs untreated control cultures. Each point represents the mean±SE of triplicates of five independent experiments; B: Ethanol time-dependent induction of CYP2E1 enzyme activity in human hepatocytes. Hepatocytes were incubated with medium in the presence or absence of 100 mmol/L ethanol for various lengths of time (0-24 h). CYP2E1 enzyme activity was measured. CT: control; aP<0.05, bP<0.01 vs untreated control cultures. Each point represents the mean±SE of triplicates of five independent experiments.
Figure 2 Western blot analysis of time-dependent induction of CYP2E1 protein expression in human hepatocytes.
Human hepatocytes were incubated with medium alone or medium containing 100 mmol/L ethanol for 0-24 h. Each was loaded with 100 mg of the sample. Experiments were carried out as described under Materials and methods (CT: control).
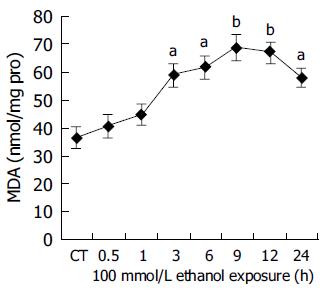
Figure 3 Ethanol-dependent formation of MDA in human hepatocytes.
Hepatocytes were incubated with 100 mmol/L ethanol for various lengths of time (0-24 h). MDA formation was measured as described in Materials and methods. CT: control; aP<0.05, bP<0.01 vs untreated control cultures. Each point represents the mean±SE of triplicates of five independent experiments.
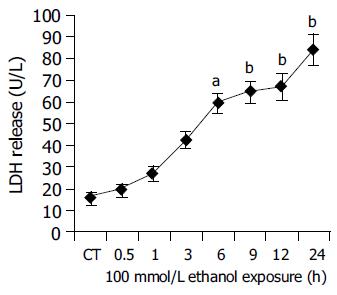
Figure 4 Time course experiments for LDH release after ethanol (100 mmol/L) exposure between 0.
5 and 24 h. CT: control; aP<0.05, bP<0.01 vs untreated control cultures. Each point represents the mean±SE of triplicates of five independent experiments.
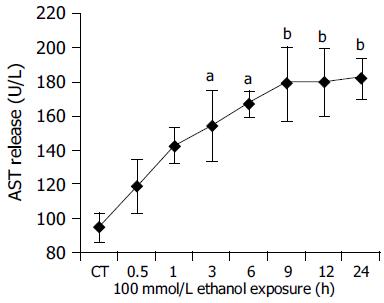
Figure 5 Time course experiments for AST release after ethanol 100 mmol/L exposure between 0.
5 and 24 h. CT: control; aP<0.05, bP<0.01 vs untreated control cultures. Each point represents the mean±SD of triplicates of five independent experiments.
- Citation: Liu LG, Yan H, Yao P, Zhang W, Zou LJ, Song FF, Li K, Sun XF. CYP2E1-dependent hepatotoxicity and oxidative damage after ethanol administration in human primary hepatocytes. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11(29): 4530-4535
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v11/i29/4530.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v11.i29.4530