©The Author(s) 2005.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 14, 2005; 11(26): 4102-4107
Published online Jul 14, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i26.4102
Published online Jul 14, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i26.4102
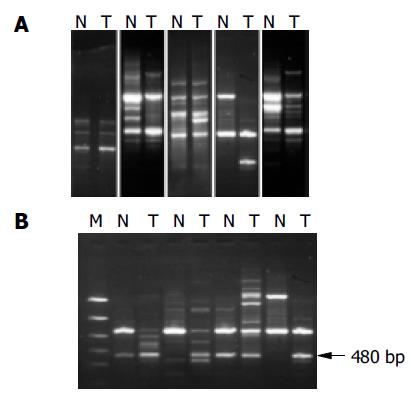
Figure 1 RAPD-PCR analysis of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Corresponding noncancerous liver tissue DNA (N), and tumor DNA (T) were amplified by PCR with obvious primers and electrophoresed in agarose gels. A: Genetic alterations identified as band loss, gain, shift and intensity change in the tumor DNA lane as compared to the paired normal DNA lane; B: Amplified 480 bp fragments from HCC DNA using the primer P4, the 1.5 kb ladder was used as a marker (M).
Figure 2 Electropherogram from sequencing with an amplified 476-bp fragment using P4 primer.
- Citation: Xian ZH, Cong WM, Zhang SH, Wu MC. Genetic alterations of hepatocellular carcinoma by random amplified polymorphic DNA analysis and cloning sequencing of tumor differential DNA fragment. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11(26): 4102-4107
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v11/i26/4102.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v11.i26.4102