©The Author(s) 2005.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 14, 2005; 11(26): 4032-4039
Published online Jul 14, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i26.4032
Published online Jul 14, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i26.4032
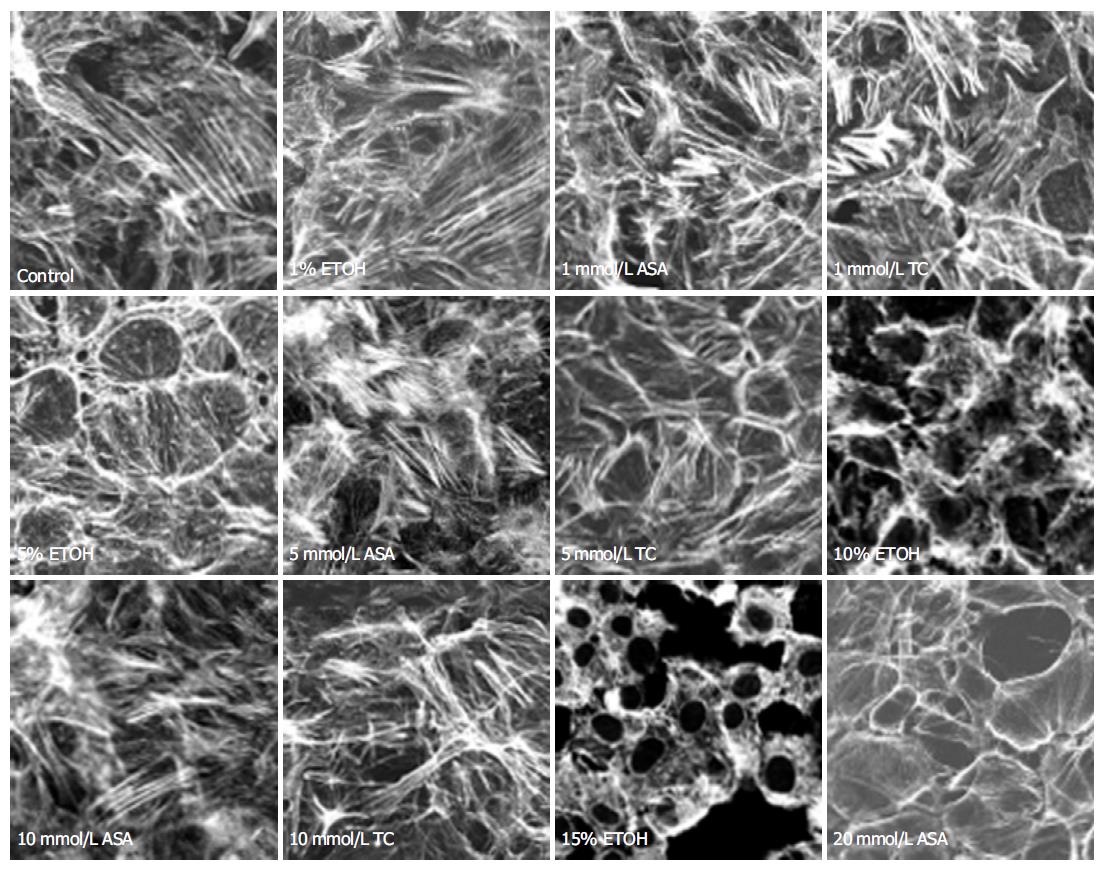
Figure 1 Effects of different doses of ethanol (ETOH), acetylsalicylic acid (ASA) and taurocholate (TC) on actin filaments of RGM rat gastric surface epithelial cells.
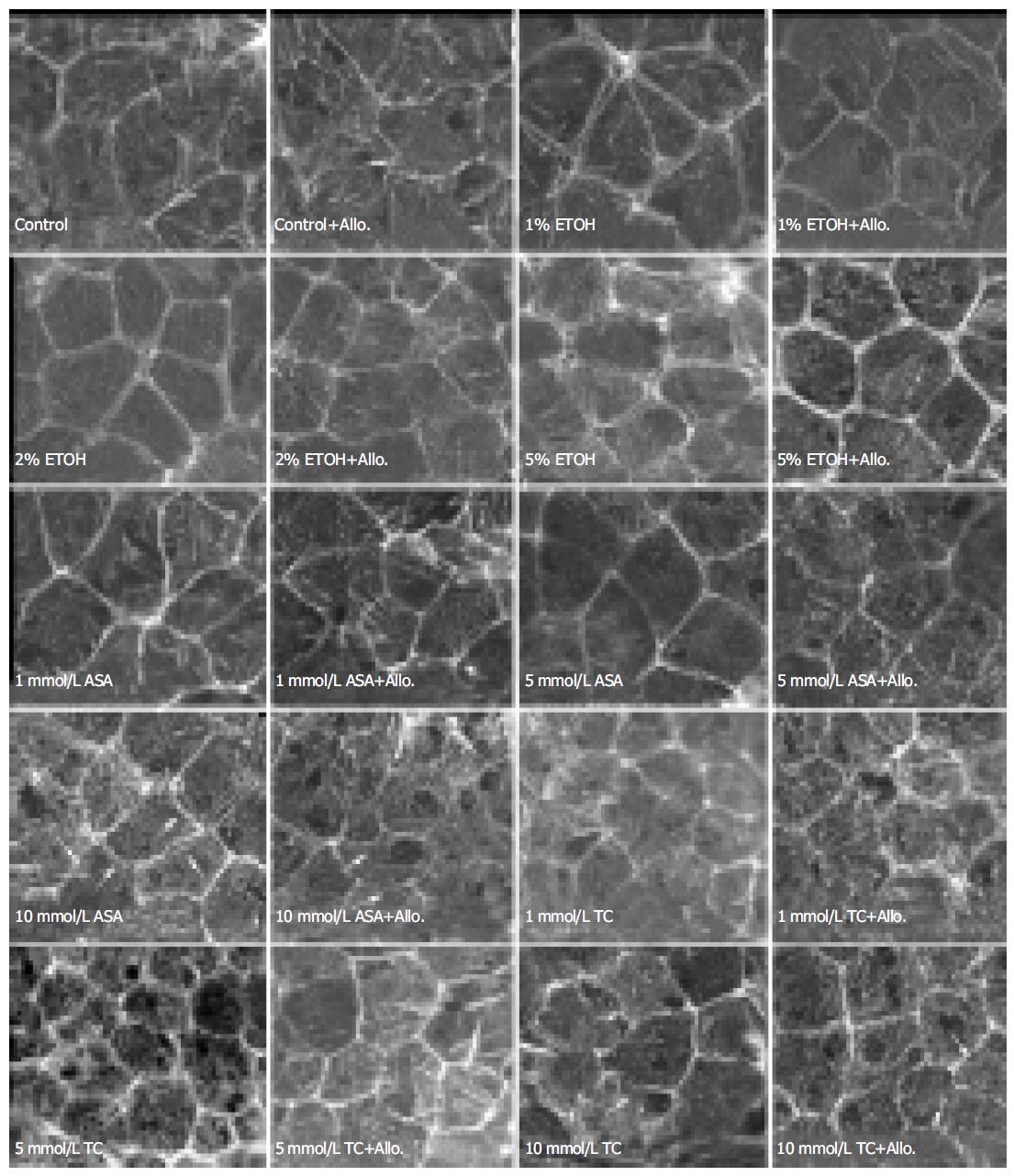
Figure 2 Effects of different doses of ethanol (ETOH), acetylsalicylic acid (ASA) and taurocholate (TC) on the zonula adherens-associated belt-like actin bundles in RGM cells and their modulation by allopurinol (2 mmol/L) treatment.
Arrows indicate perturbations in the actin belt organization.
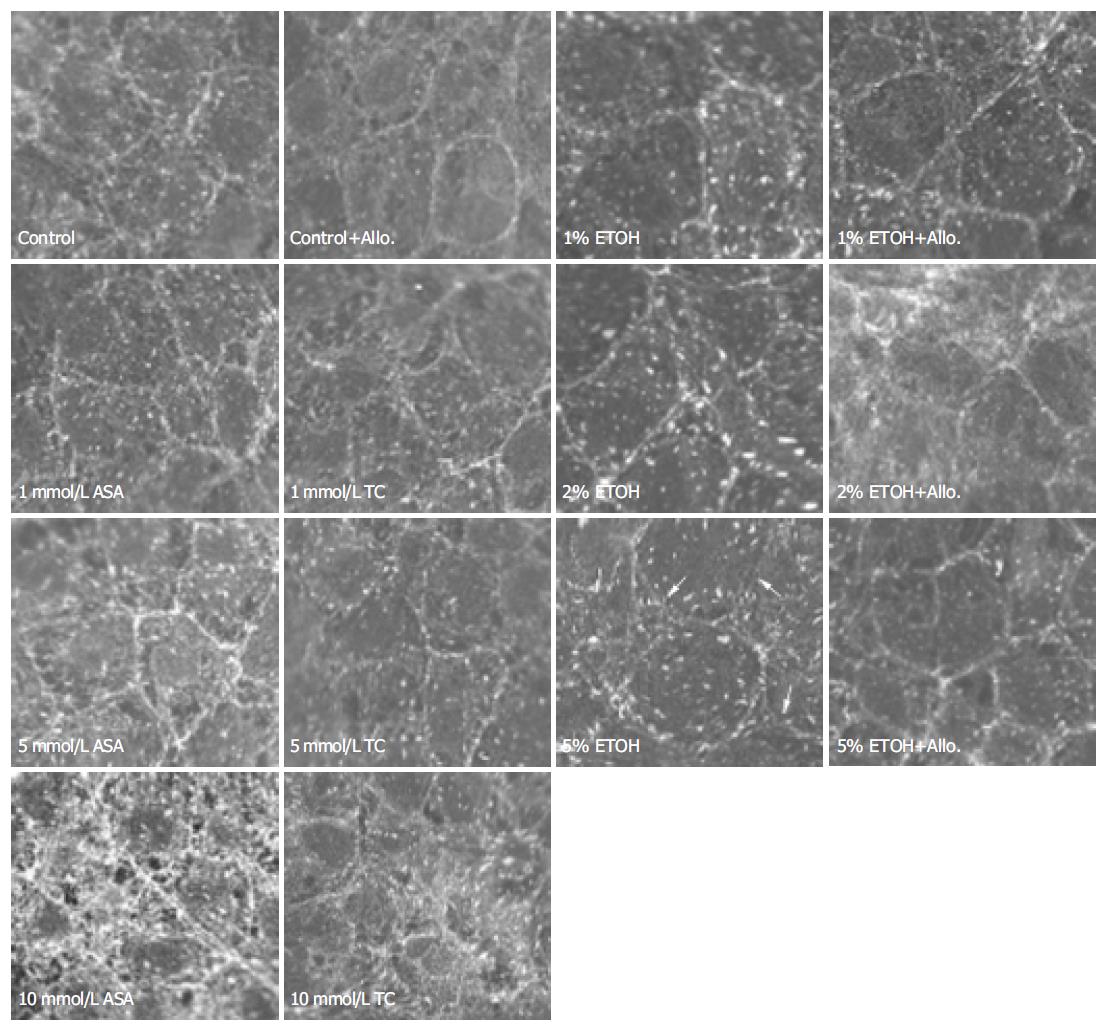
Figure 3 Effects of different doses of ethanol (ETOH), acetylsalicylic acid (ASA) and taurocholate (TC) on vinculin distribution in RGM cells and their modulation by allopurinol (2 mmol/L) treatment.
Arrows indicate perturbations in vinculin organization.
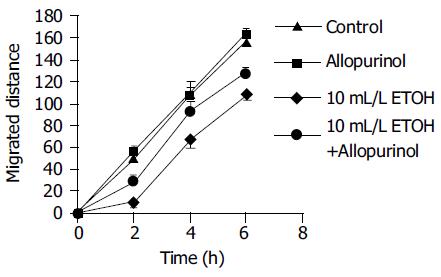
Figure 4 Effect of ethanol on cellular migration distance, with and without allopurinol treatment.
Ethanol significantly reduced the migrated distance. Allopurinol partially abolished the ethanol promoted inhibition of cell migration.
- Citation: Bidel S, Mustonen H, Khalighi-Sikaroudi G, Lehtonen E, Puolakkainen P, Kiviluoto T, Kivilaakso E. Effect of the ulcerogenic agents ethanol, acetylsalicylic acid and taurocholate on actin cytoskeleton and cell motility in cultured rat gastric mucosal cells. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11(26): 4032-4039
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v11/i26/4032.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v11.i26.4032