©2005 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 21, 2005; 11(23): 3528-3532
Published online Jun 21, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i23.3528
Published online Jun 21, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i23.3528
Figure 1 Structural and physiochemical characteristics of flagellin A.
A: Sequence of antigen determinant region in the central part of flagellin A. Underlined: hydrophilic peaks; shaded: β-turn short fragment; framed: residues accessible to molecular surface with high probability; B: secondary structure of flagellin A. Long bar: α-helices; short bar: β-sheets; other residues: irregular coils.
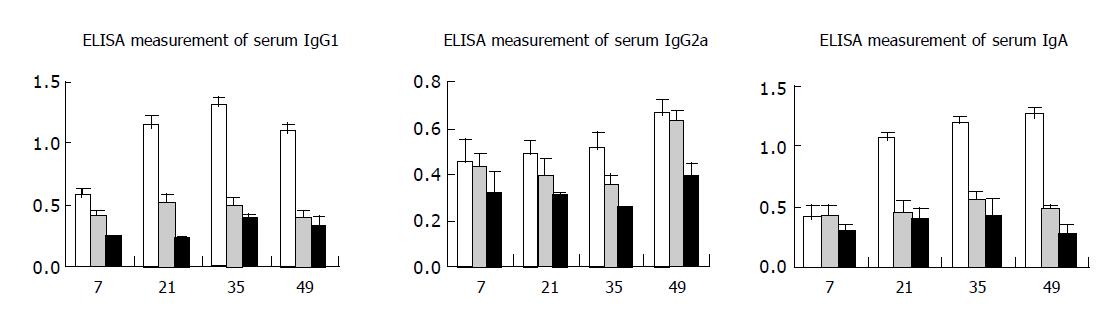
Figure 2 ELISA measurements of antibody subtypes in mouse serum Blue: immunized group; brown: adjuvant control group; light yellow: nude mice control group.
Abscissa: time for exsanguination after prime inoculation; ordinate: A value (mean±SD).
Figure 3 Titer measurements of IgG1, IgA in mice serum (A and B) and IgA in gastrointestinal fluid (C) Blue: immunized group; brown: adjuvant control group; light yellow: nude mice control group.
Abscissa: dilution of mouse gastrointestinal washing fluid; ordinate, A value (mean±SD).
-
Citation: Ji WS, Hu JL, Wu KC, Qiu JW, Han ZY, Ding J, Fan DM.
Helicobacter pylori specific immune response induced by conservative flagellin linear B-cell epitope. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11(23): 3528-3532 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v11/i23/3528.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v11.i23.3528