©2005 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Jun 21, 2005; 11(23): 3508-3513
Published online Jun 21, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i23.3508
Published online Jun 21, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i23.3508
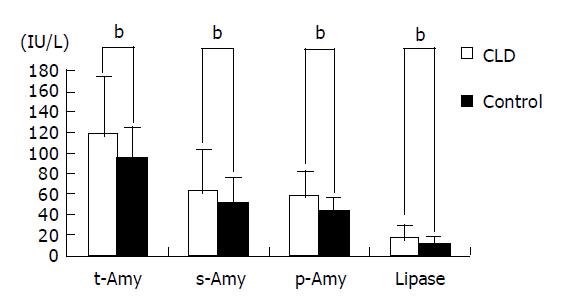
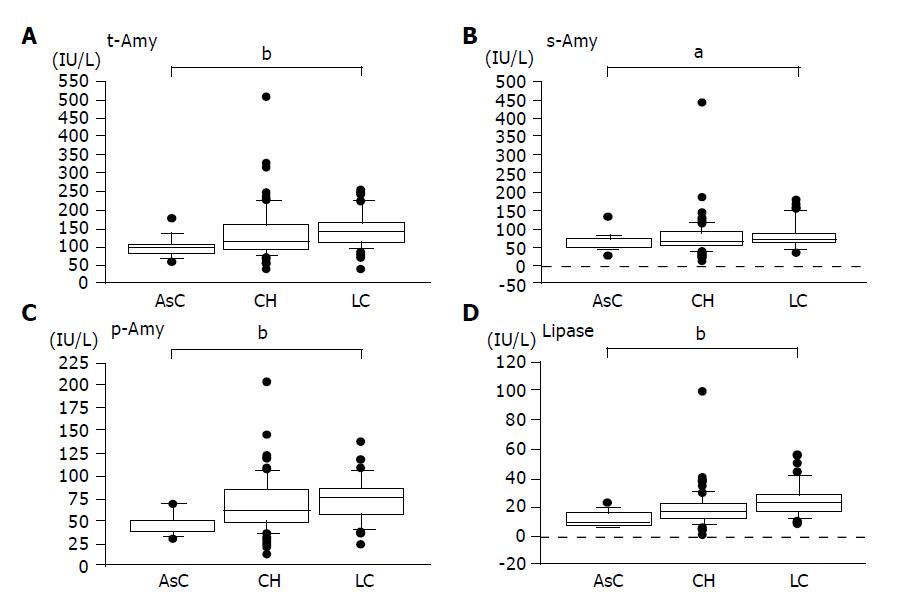
Figure 1 Levels of serum or tissue enzymes in patients with CLD compared to those measured in age and sex-matched control subjects.
bP<0.01 vs controls.
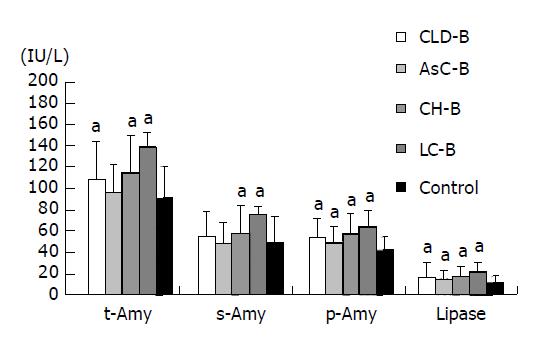
Figure 2 Levels of serum or tissue enzymes at each clinical stage of CH B.
aP<0.05 vs controls.
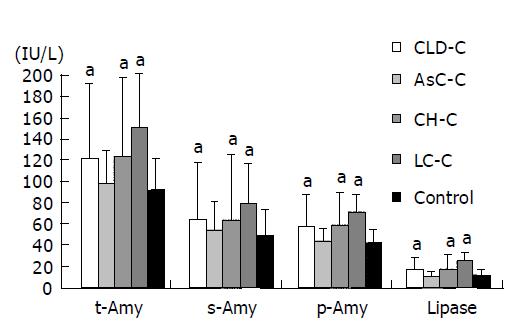
Figure 3 Levels of serum or tissue enzymes at several stages of CH C.
aP<0.05 vs controls.
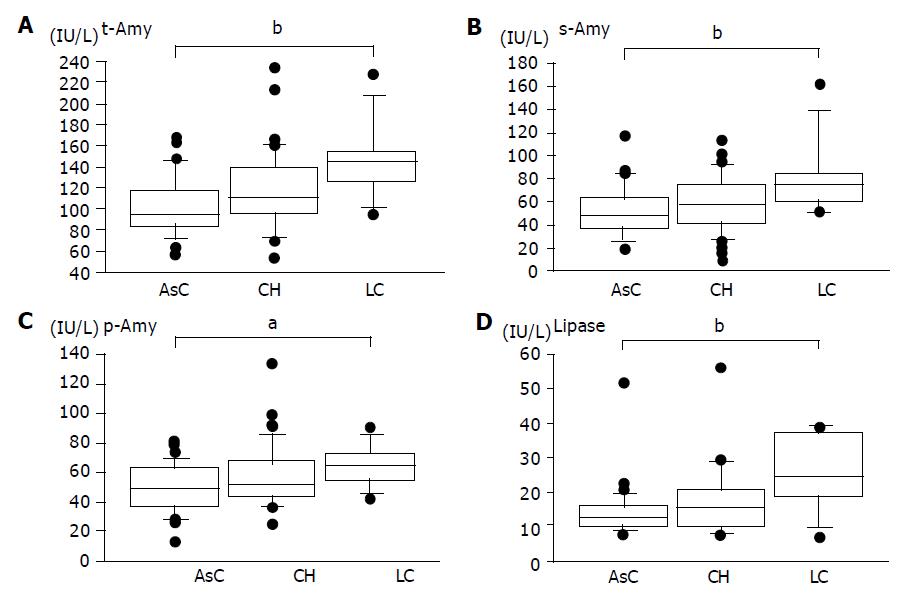
Figure 4 Distribution of serum enzyme levels at several stages of CH B.
Box plots are given with horizontal lines for the medians, upper and lower edges indicating the 25th and 75th percentiles, respectively, and bars represent the extremes without including outliers. _ indicates outliers and ● indicates extremities. P values indicate the correlation between the enzyme levels and the progression of liver disease (A-D). aP<0.05, bP<0.01 vs others.
Figure 5 Distribution of serum enzyme levels in several stages of CH C.
Box plots are given with horizontal lines for the medians, upper and lower edges indicating the 25th and 75th percentiles, respectively, and bars represent the extremes without including outliers. _ indicates outliers and ● indicates extremities. P values indicate the correlation between the enzyme levels and the progression of liver disease (A-D). aP<0.05, bP<0.01 vs others.
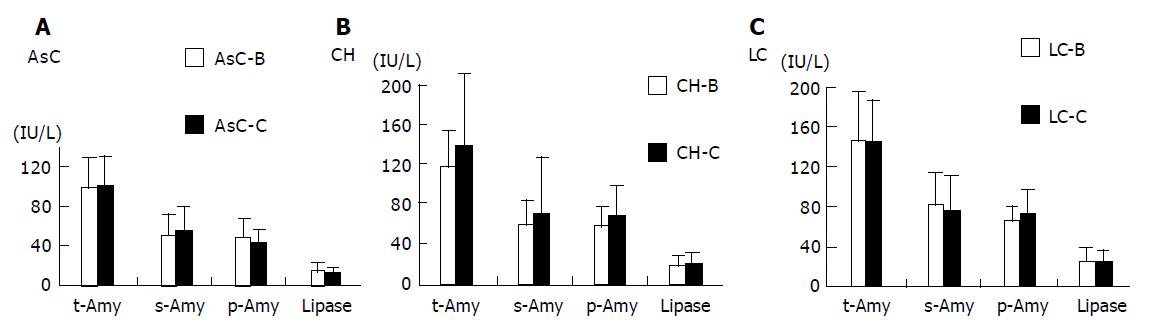
Figure 6 Comparison of serum and tissue enzyme levels between HBV and HCV carriers (A-C).
- Citation: Katakura Y, Yotsuyanagi H, Hashizume K, Okuse C, Okuse N, Nishikawa K, Suzuki M, Iino S, Itoh F. Pancreatic involvement in chronic viral hepatitis. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11(23): 3508-3513
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v11/i23/3508.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v11.i23.3508