©2005 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. May 14, 2005; 11(18): 2720-2725
Published online May 14, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i18.2720
Published online May 14, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i18.2720
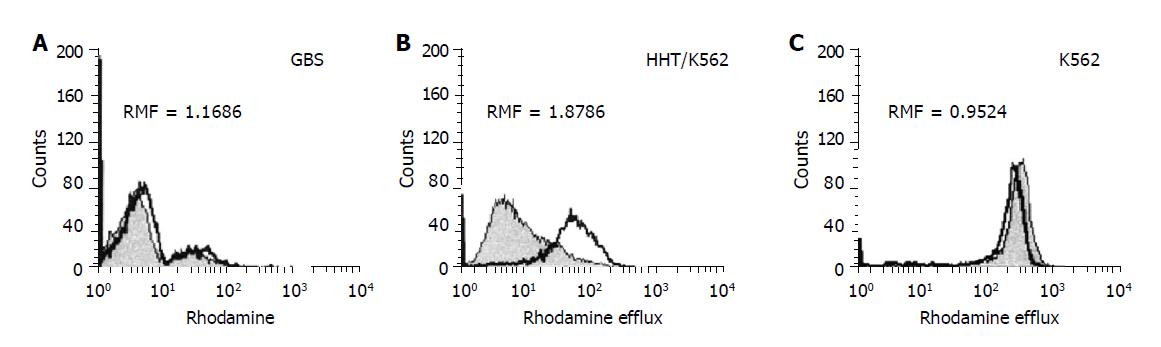
Figure 1 FACS analysis of Rh123 accumulation as a function of Pgp activity (A-C): (A) GBS were stained with a fluorescent substrate Rh123 in the presence (overlaid histogram) or absence (filled histogram) of the MDR reversing agent CyA.
Pgp activity is expressed as RMF, a ratio of mean fluorescences obtained from the gated viable cell population. RMF ≥1 considered positive; (B) resistant (Pgp-positive/active) and (C) sensitive (Pgp-negative/inactive) control cell lines.
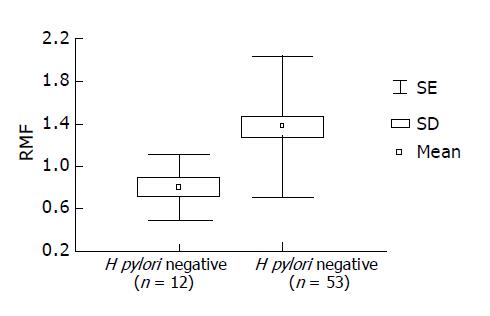
Figure 2 Enhanced Pgp activity in patients with H pylori infection.
RMF values of 53 H pylori positive patients and 12 H pylori negative (control) patients are presented (x = mean; SD = standard deviation; SE = standard error).
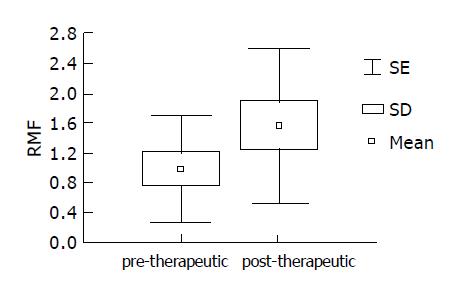
Figure 3 Therapeutic effect on Pgp activity in 10 randomly selected H pylori positive patients: significantly increased post-therapeutic RMF values.
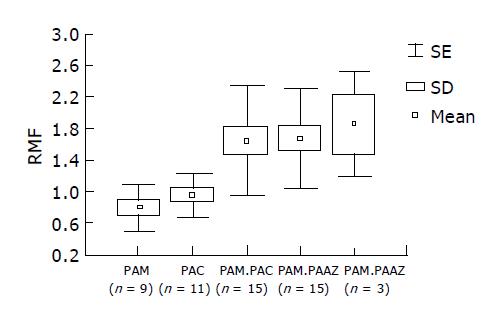
Figure 4 RMF values with five therapeutic protocols: combined therapy had no effect with enhanced Pgp activity.
First course: PAM (pantoprazole +amoxicillin+metronidazole), PAC (pantoprazole+amoxicillin+clarithromycin); second course: PAM+PAC, PAM+PAAZ (pantoprazole+amoxicillin+azithromycin), PAC+PAAZ.
-
Citation: Babic Z, Svoboda-Beusan I, Kucisec-Tepes N, Dekaris D, Troskot R. Increased activity of Pgp multidrug transporter in patients with
Helicobacter pylori infection. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11(18): 2720-2725 - URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v11/i18/2720.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v11.i18.2720