©2005 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 28, 2005; 11(16): 2456-2461
Published online Apr 28, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i16.2456
Published online Apr 28, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i16.2456
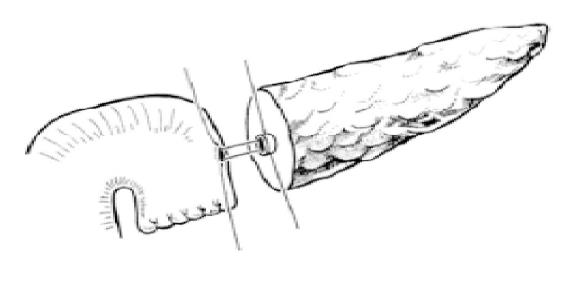
Figure 1 End-to-side duct-to-mucosa pancreaticojejunal anastomosis.
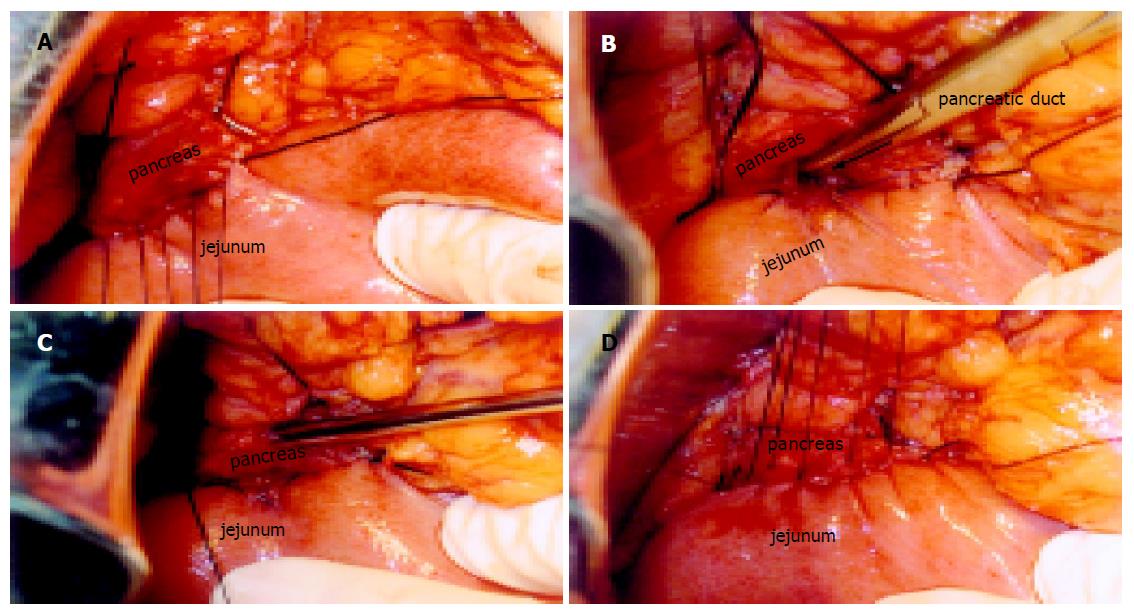
Figure 2 Duct-to-mucosa pancreaticojejunal anastomosis.
A: Posterior suture with 3-0 silk sutures between posterior capsular parenchyma of the pancreatic remnant and the seromuscular layer of the jejunum. B: Posterior layer anastomosis with 6-0 Prolene interrupted sutures between the pancreatic duct and jejunum (all layers). C: Anterior layer anastomosis with 6-0 Prolene interrupted sutures between the pancreatic duct and jejunum. D: Anterior suture with 3-0 silk sutures between anterior interrupted sutures between the pancreatic duct and capsular parenchyma of the pancreatic remnant and the seromuscular layer of the jejunum.
- Citation: Yang YM, Tian XD, Zhuang Y, Wang WM, Wan YL, Huang YT. Risk factors of pancreatic leakage after pancreaticoduodenectomy. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11(16): 2456-2461
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v11/i16/2456.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v11.i16.2456