©2005 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Apr 28, 2005; 11(16): 2438-2443
Published online Apr 28, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i16.2438
Published online Apr 28, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i16.2438
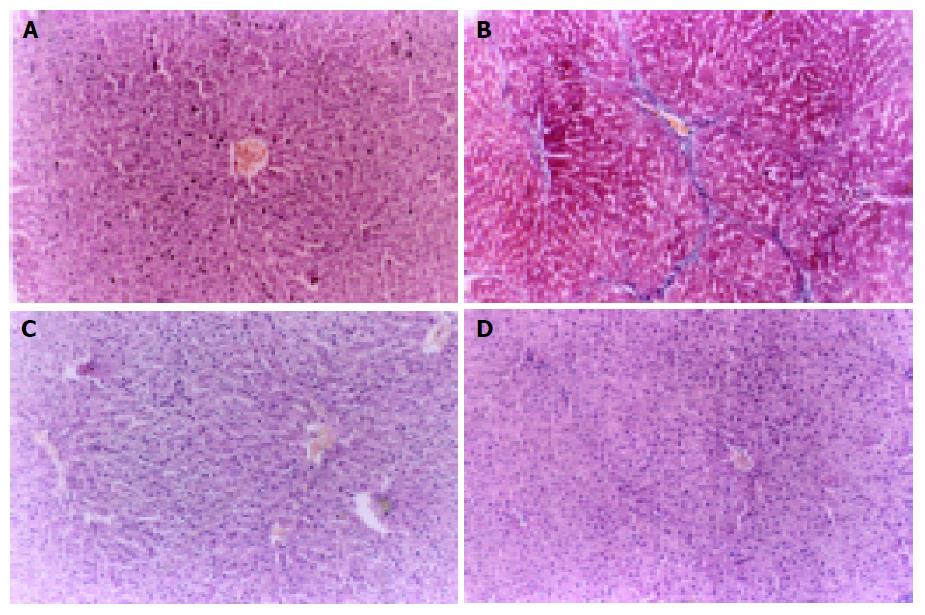
Figure 1 Histologic section of experimental groups (HE´200).
A: Normal rat liver tissue, hepatic cords were well arranged; the structure of hepatic lobule was intact. B: Model rat liver tissue, collagen deposition extending from central veins, fibrotic septa and even pseudolobuli formation. C: ALR1 group rat liver tissue, apparent amelioration of hepatocyte degeneration. D: ALR2 group rat liver tissue, marked reduction in collagen deposition with no obvious pseudolobuli formation.
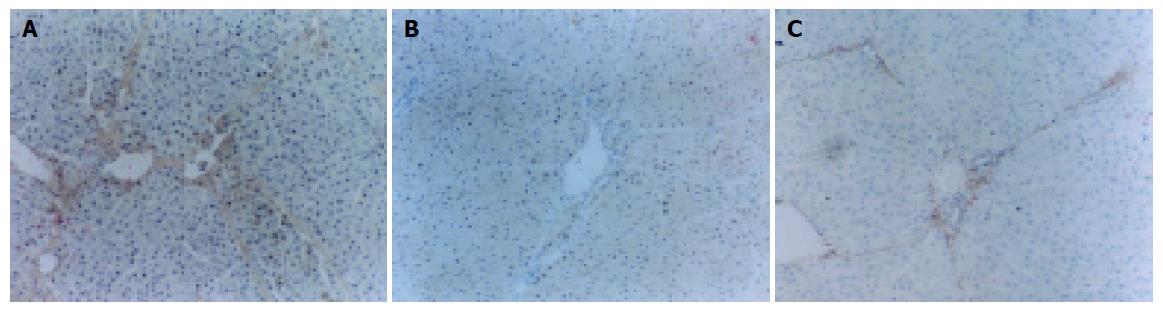
Figure 2 Immunohistochemistry section of TIMP-1 expressed (×200).
A: Model rat liver tissue, positive staining was seen at interstitial cells, inflammatory cells, impaired hepatocytes as well as normal hepatocytes. B: ALR1 group rat liver tissue, staining of TIMP-1 was decreased. C: ALR2 group rat liver tissue, staining of TIMP-1 was markedly decreased.
- Citation: Li Q, Liu DW, Zhang LM, Zhu B, He YT, Xiao YH. Effects of augmentation of liver regeneration recombinant plasmid on rat hepatic fibrosis. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11(16): 2438-2443
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v11/i16/2438.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v11.i16.2438