©2005 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Gastroenterol. Mar 14, 2005; 11(10): 1535-1539
Published online Mar 14, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i10.1535
Published online Mar 14, 2005. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i10.1535
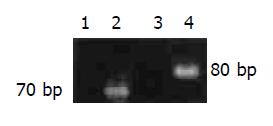
Figure 1 RT-PCR analysis of HIF-1 alpha (lane 1: negative control; lane 2: rectal mucosa) and VEGF (lane 3: negative control; lane 4: rectal mucosa).
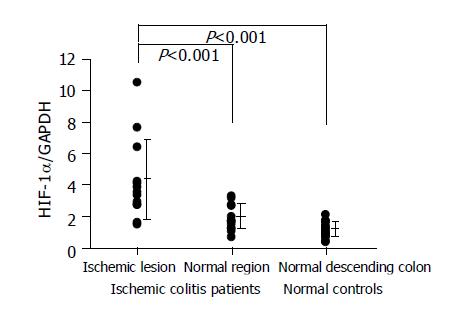
Figure 2 HIF-1 alpha RNA expression levels in the colon tissues.
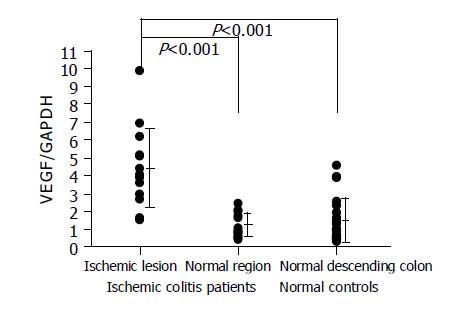
Figure 3 VEGF RNA expression levels in the colon tissues.
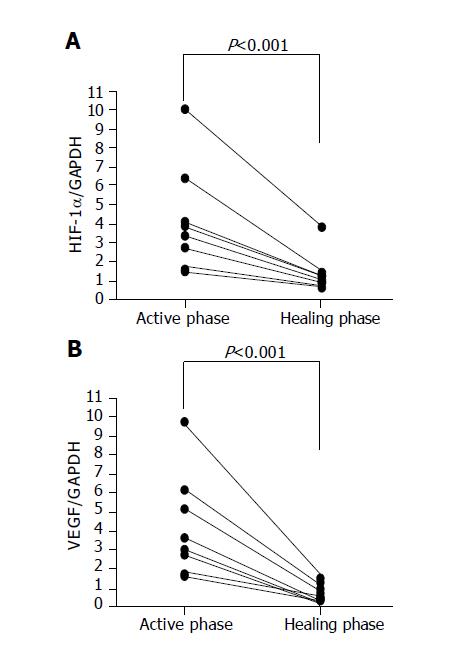
Figure 4 HIF-1 alpha and VEGF RNA expression levels in the colon tissues in the active and healing phases of ischemic colitis.
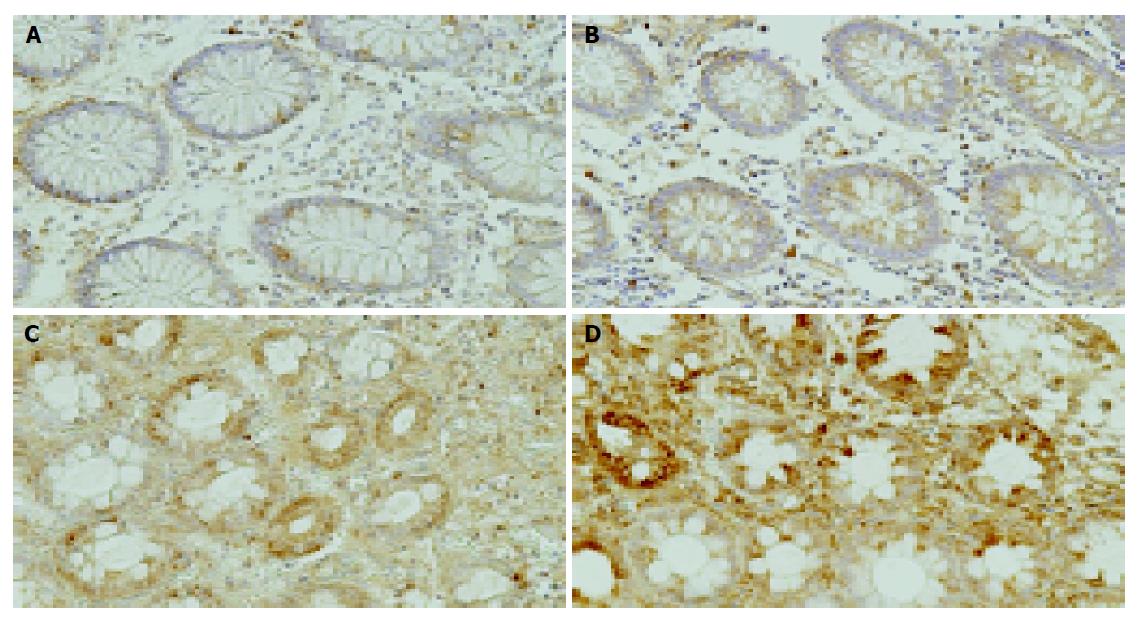
Figure 5 Immunostaining of HIF-1 alpha or VEGF in the colon tissues.
Weak HIF-1 alpha or VEGF immunoreactive cells were scattered in epithelial cells and interstitial cells in normal colon tissue (A: HIF-1 alpha; B: VEGF). In contrast, strong HIF-1 alpha or VEGF immunoreactive cells were diffusely seen in the epithelial and intestinal cells, including inflammatory cells in the ischemic colitis lesions (C: HIF-1 alpha; D: VEGF). Scale bars represent 100 μm.
- Citation: Okuda T, Azuma T, Ohtani M, Masaki R, Ito Y, Yamazaki Y, Ito S, Kuriyama M. Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha and vascular endothelial growth factor overexpression in ischemic colitis. World J Gastroenterol 2005; 11(10): 1535-1539
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v11/i10/1535.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v11.i10.1535