©The Author(s) 2004.
World J Gastroenterol. Dec 1, 2004; 10(23): 3424-3427
Published online Dec 1, 2004. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i23.3424
Published online Dec 1, 2004. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i23.3424
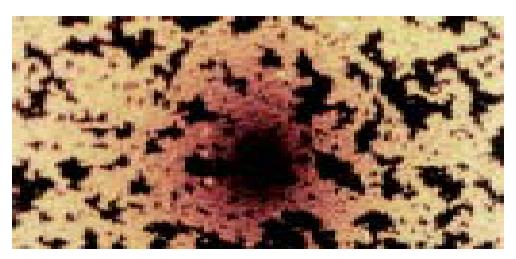
Figure 1 Light micrograph of liposome microbubbles under a × 200 field of microscope.
Figure 2 Direct agglutination of targeted liposome microbubbles in the presence of rabbit anti-mouse serum.
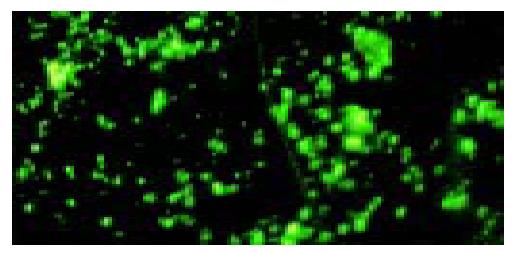
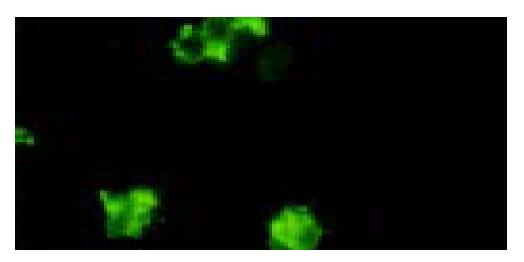
Figure 3 Immunofluoresce staining of targeted liposome microbubbles with FITC conjugated sheep anti-mouse IgG.
Targeted liposome microbubbles were stained in yellow-green under a × 400 field of fluorescence microscope.
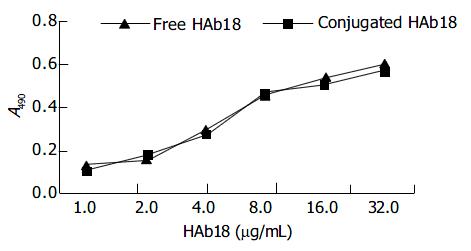
Figure 4 Activity assay of free HAb18 and conjugated HAb18 on microbubbles by ELISA.
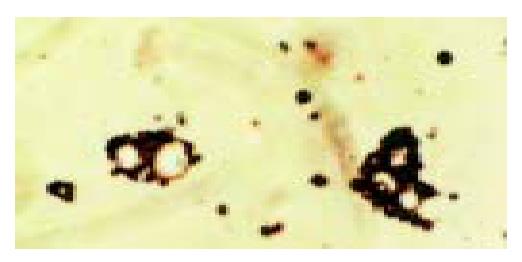
Figure 5 Light micrograph of the binding of targeted lipo-some microbubbles to SMMC-7721 cells under a × 400 field of microscope.
SMMC-7721 cells were surrounded by targeted liposome microbubbles to form rosettes.
Figure 6 Immunofluorescent assay for identification of the binding of targeted liposome microbubbles to SMMC-7721 cells.
SMMC-7721 cells were surrounded by the microbubbles and gave out bright yellow-green fluorescence.
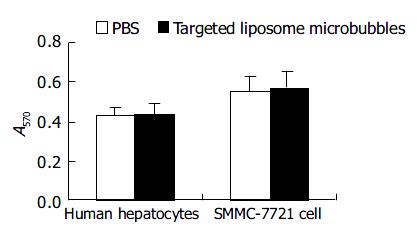
Figure 7 Effect of targeted liposome microbubbles on the proliferation of human hepatocytes and SMMC-7721 cells.
- Citation: Bian AN, Gao YH, Tan KB, Liu P, Zeng GJ, Zhang X, Liu Z. Preparation of human hepatocellular carcinoma-targeted liposome microbubbles and their immunological properties. World J Gastroenterol 2004; 10(23): 3424-3427
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v10/i23/3424.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v10.i23.3424