©The Author(s) 2004.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 15, 2004; 10(22): 3251-3254
Published online Nov 15, 2004. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i22.3251
Published online Nov 15, 2004. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i22.3251
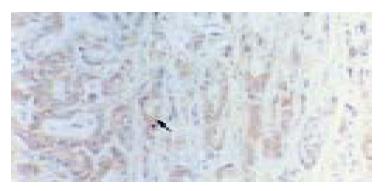
Figure 1 Primary hepatic cholangiocarcinoma.
Brown-yellow staining in cytoplasm of carcinoma cells for bcl-2 protein (arrowhead) Immunohistochemistry staining × 200.
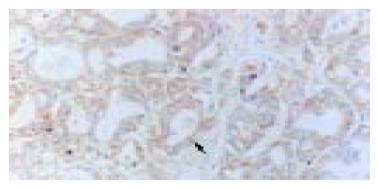
Figure 2 Normal liver.
Brown-yellow staining in cytoplasm of small bile duct epithelial cells for bcl-2 protein (arrowhead) Immunohistochemistry staining × 200.
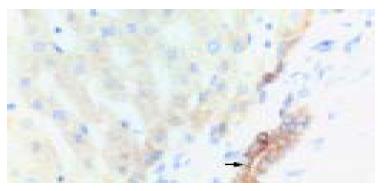
Figure 3 Primary hepatic cholangiocarcinoma.
Brown-yellow staining in cytoplasm of carcinoma cells for bax protein (arrowhead) Immunohistochemistry staining × 200.
Figure 4 Normal liver.
Brown-yellow staining in cytoplasm of small bile duct epithelial cells for bax protein (arrowhead) Immunohistochemistry staining × 200.
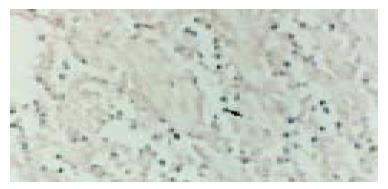
Figure 5 Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma.
Purple-blue deposition in nuclear of lympoma cells (positive for mbr, arrowhead). In situ PCR × 400.
- Citation: Guo LL, Xiao S, Guo Y. Detection of bcl-2 and bax expression and bcl-2/JH fusion gene in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2004; 10(22): 3251-3254
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v10/i22/3251.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v10.i22.3251