Copyright
©The Author(s) 2004.
World J Gastroenterol. Nov 1, 2004; 10(21): 3081-3087
Published online Nov 1, 2004. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i21.3081
Published online Nov 1, 2004. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i21.3081
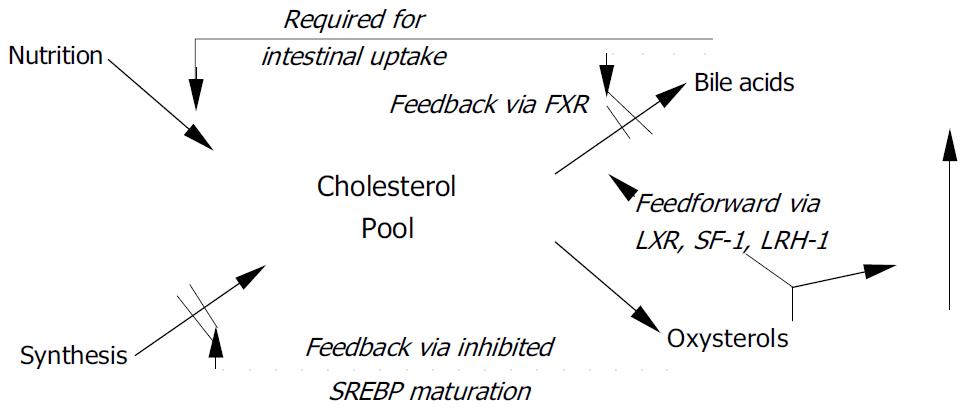
Figure 1 Feedforward and feedback effects of oxysterols FXR = farnesoid × receptor; LRH-1 = liver receptor homologue-1; LXR = liver × receptor; SF-1 = steroidogenic factor-1; SREBP = sterol responsive element binding protein.
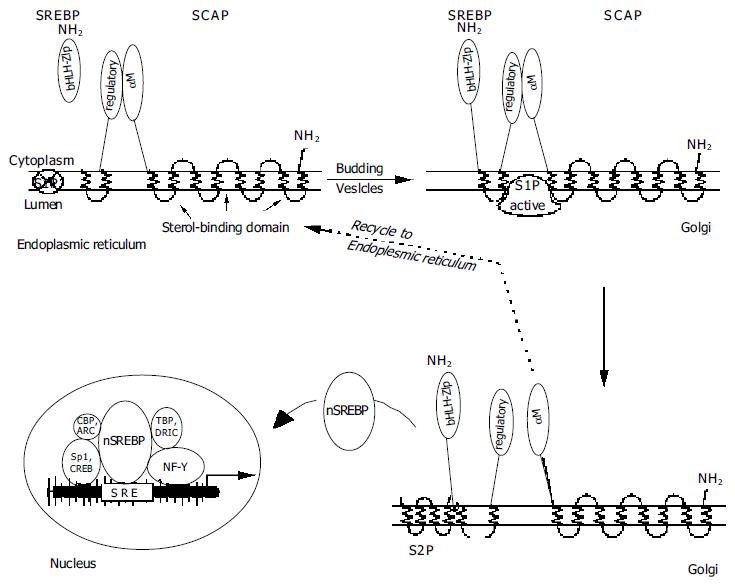
Figure 2 Maturation of SREBPs -NH2 = amino-terminal ends of SREBP or SCAP.
S1P = Site-1 protease (crossed-out = inactive); S2P = Site-2 protease. SRE = sterol-responsive element; nSREBP = nuclear SREBP. Arrangement of the additional transcription factors NF-Y, Sp1, CREB, ARC, CBP, TBP, and DRIC (see text) is tentative as their requirements are not exactly known.
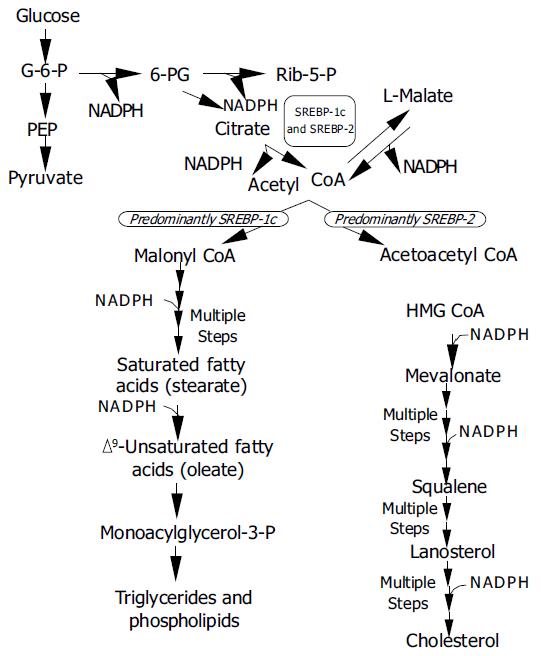
Figure 3 Metabolic pathways regulated by SREBPs G-6-P = glucose-6-phosphate; 6-PG = 6-phosphogluconate; Rib-5-P = ribulose-5-phosphate; PEP = phosphoenol pyruvate; CoA = coenzyme A; HMGCoA = 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coen-zyme A.
SREBP-1c and SREBP-2 activate genes for the genera-tion of NADPH (ATP citrate lyase, malic enzyme, G-6-P dehydrogenase, 6-PG dehydrogenase) required in various steps of lipid synthesis.
- Citation: Weber LW, Boll M, Stampfl A. Maintaining cholesterol homeostasis: Sterol regulatory element-binding proteins. World J Gastroenterol 2004; 10(21): 3081-3087
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v10/i21/3081.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v10.i21.3081