©The Author(s) 2004.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 1, 2004; 10(17): 2540-2543
Published online Sep 1, 2004. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i17.2540
Published online Sep 1, 2004. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i17.2540
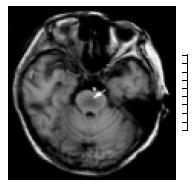
Figure 1 T1-Weighted axial magnetic resonance imaging scan shows symmetric area of hypointensity in the pons.
(arrow).
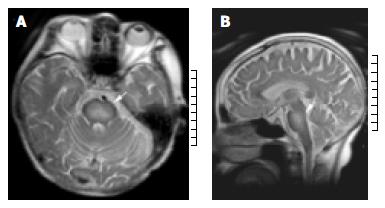
Figure 2 A: T2-Weighted axial magnetic resonance imaging shows bilaterally symmetric high-signal intensity is seen in the central pons; (arrow) B: T2-Weighted sagittal magnetic resonance imaging demonstrates hyperintensity area in central pons.
(arrow).
- Citation: Yu J, Zheng SS, Liang TB, Shen Y, Wang WL, Ke QH. Possible causes of central pontine myelinolysis after liver transplantation. World J Gastroenterol 2004; 10(17): 2540-2543
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v10/i17/2540.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v10.i17.2540