©The Author(s) 2004.
World J Gastroenterol. Sep 1, 2004; 10(17): 2472-2477
Published online Sep 1, 2004. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i17.2472
Published online Sep 1, 2004. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i17.2472
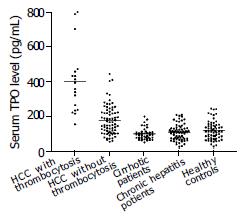
Figure 1 Distribution of serum thrombopoietin levels in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients with and without thrombocytosis, patients with cirrhosis, chronic hepatitis and healthy subjects.
The mean serum thrombopoietin level in HCC patients with thrombocytosis was significantly higher than in HCC patients without thrombocytosis, patients with cirrhosis, chronic hepatitis and healthy subjects.
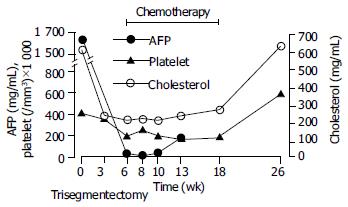
Figure 2 Clinical course of a hepatocellular carcinoma patient with thrombocytosis.
The serum alfa-fetoprotein (AFP) level was 164000 ng/mL before tumor resection. Hypercholesterolemia (serum cholesterol level: 602 mg/dL) and thrombocytosis (platelet count: 403 K/mm3) were noted before operations. The platelet counts, serum levels of cholesterol and AFP fell significantly after a surgical removal of the tumors. However, all re-elevated when the tumor recurred 18 wk after surgical treatments.
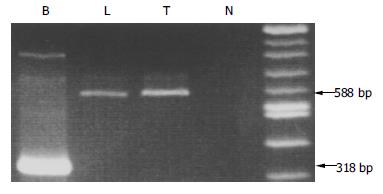
Figure 3 Analyses of thrombopoietin from tumor tissues (T) and non-tumor liver tissues (L) in a hepatocellular carcinoma patient with thrombocytosis using reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction.
β-actin was used as an internal standard (B). N: negative control. Results from an agarose gel electrophoresis showed a more intense density of thrombopoietin band from tumor tissues when compared with non-tumor liver tissues.
- Citation: Hwang SJ, Luo JC, Li CP, Chu CW, Wu JC, Lai CR, Chiang JH, Chau GY, Lui WY, Lee CC, Chang FY, Lee SD. Thrombocytosis: A paraneoplastic syndrome in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2004; 10(17): 2472-2477
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v10/i17/2472.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v10.i17.2472