Copyright
©The Author(s) 2004.
World J Gastroenterol. Jul 1, 2004; 10(13): 1881-1884
Published online Jul 1, 2004. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i13.1881
Published online Jul 1, 2004. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v10.i13.1881
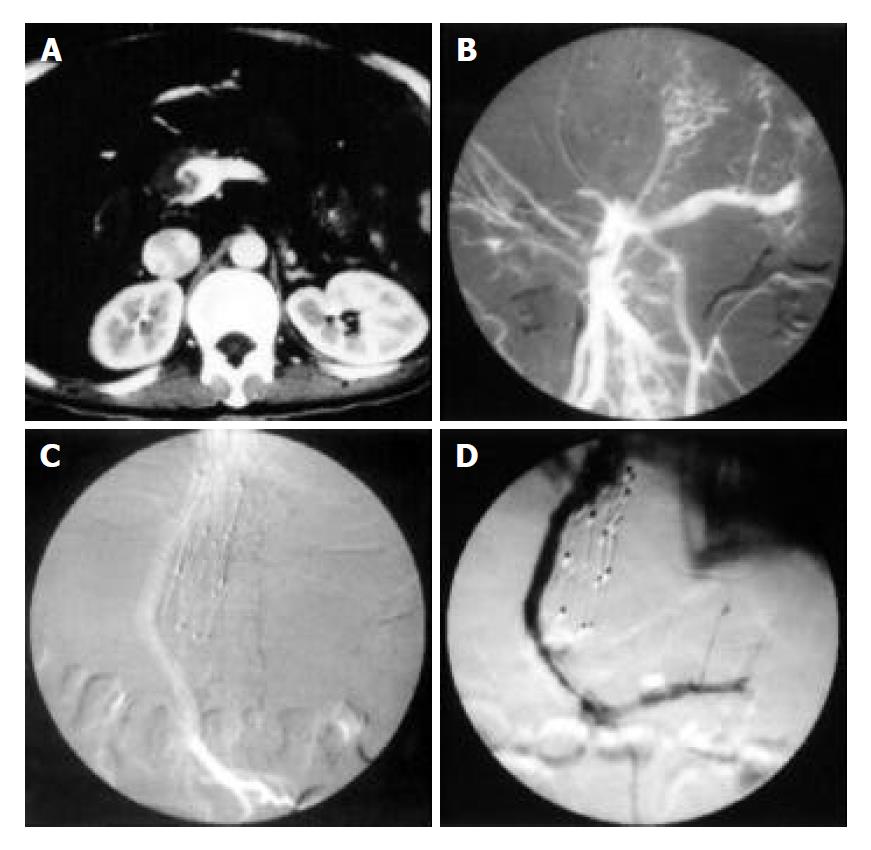
Figure 1 TIPS procedure in patient with incomplete occlusion of portal vein trunk.
A: Main portal vein dilation with eccentric tumor thrombi shoven on enhanced Ctgram. B: Superior mesenteric vein dilation with eccentric filling defect and main portal vein occlusion shown on superior mesenteric vein angiogram. C: Open shunt shown on superior mesenteric vein angiogram after stent implantation. D: Recurrence of symptoms of ascites and diarrhoea 30 d after TIPS and shunt stenosis as wall as segmental filling defects shown on follow-up angiogram.
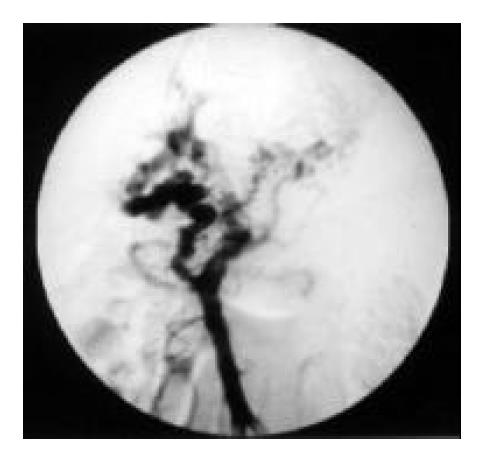
Figure 2 Occlusive portal vein, dialated superior mesenteric vein, portal vein cavernous transformation, and esophagogastric varices shown on portal vein angiogram after introducing a catheter into superior mesenteric vein.
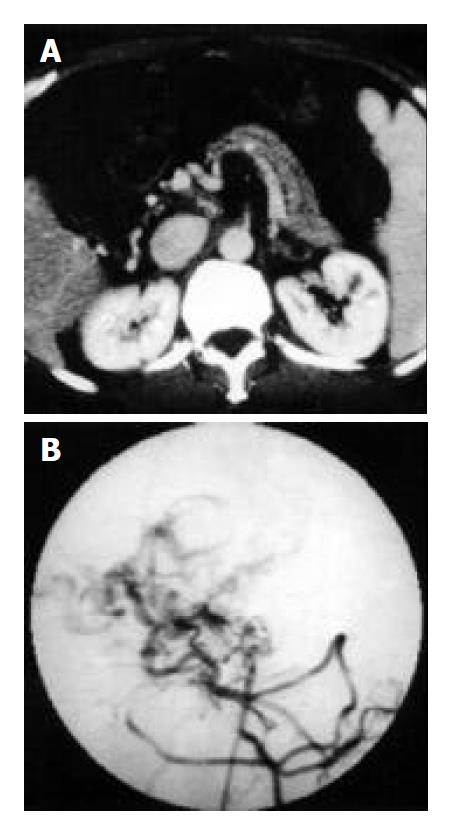
Figure 3 Main portal vein occlusion, hepatic arteric portal shunt and portal cavernous transformation in a 64-year-old patient with refractory ascites and hematemesis.
A: Thin splenic and superior mesenteric vein shown on enhanced CT gram. B: Thin superior mesenteric vein and disordered drainage vein shown on angiogram.
- Citation: Jiang ZB, Shan H, Shen XY, Huang MS, Li ZR, Zhu KS, Guan SH. Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt for palliative treatment of portal hypertension secondary to portal vein tumor thrombosis. World J Gastroenterol 2004; 10(13): 1881-1884
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/1007-9327/full/v10/i13/1881.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v10.i13.1881