©The Author(s) 2021.
World J Meta-Anal. Apr 28, 2021; 9(2): 153-163
Published online Apr 28, 2021. doi: 10.13105/wjma.v9.i2.153
Published online Apr 28, 2021. doi: 10.13105/wjma.v9.i2.153
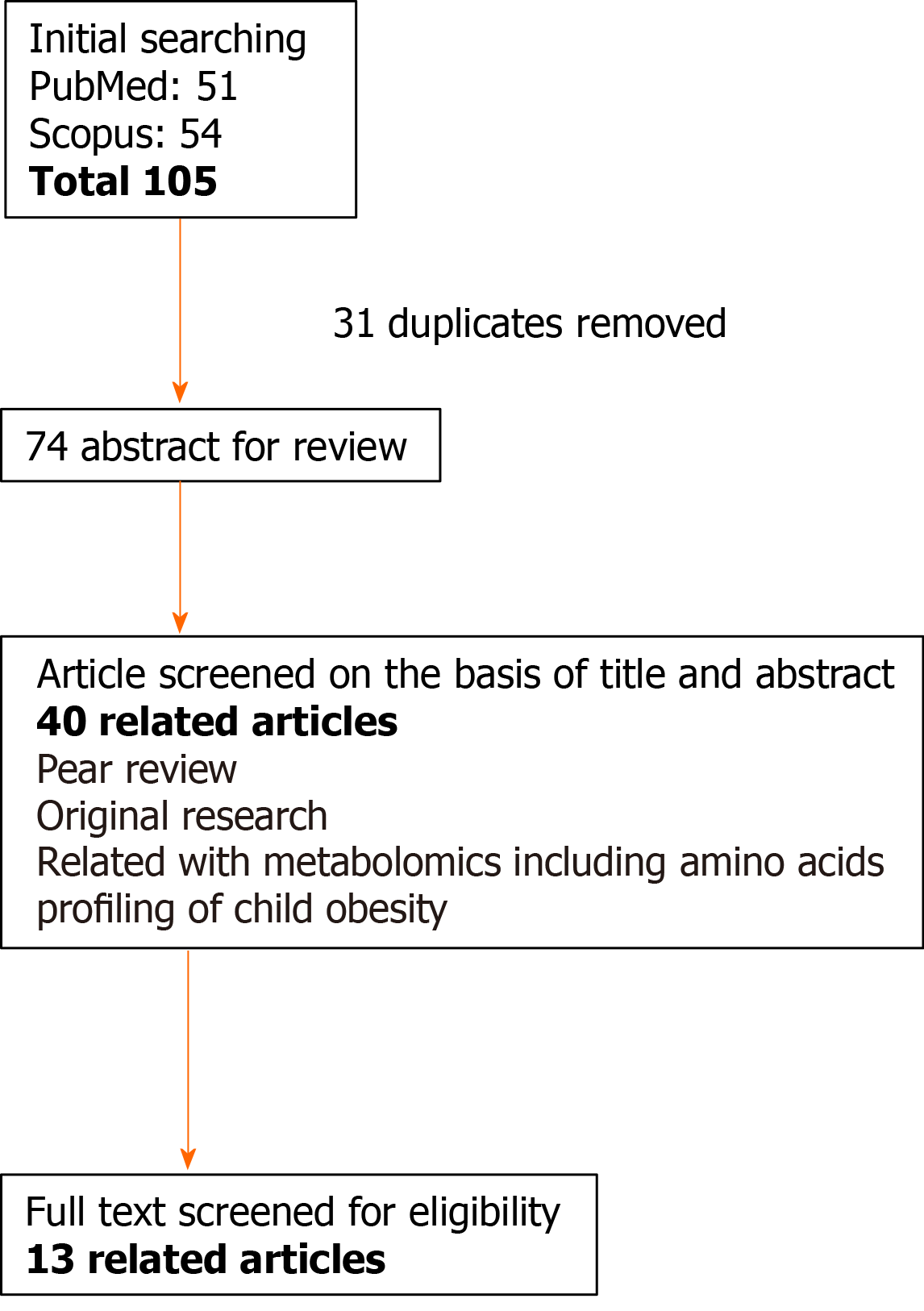
Figure 1 Flow diagram of the literature search and study selection for “metabolic/biological change in children with obesity and diabetes”.
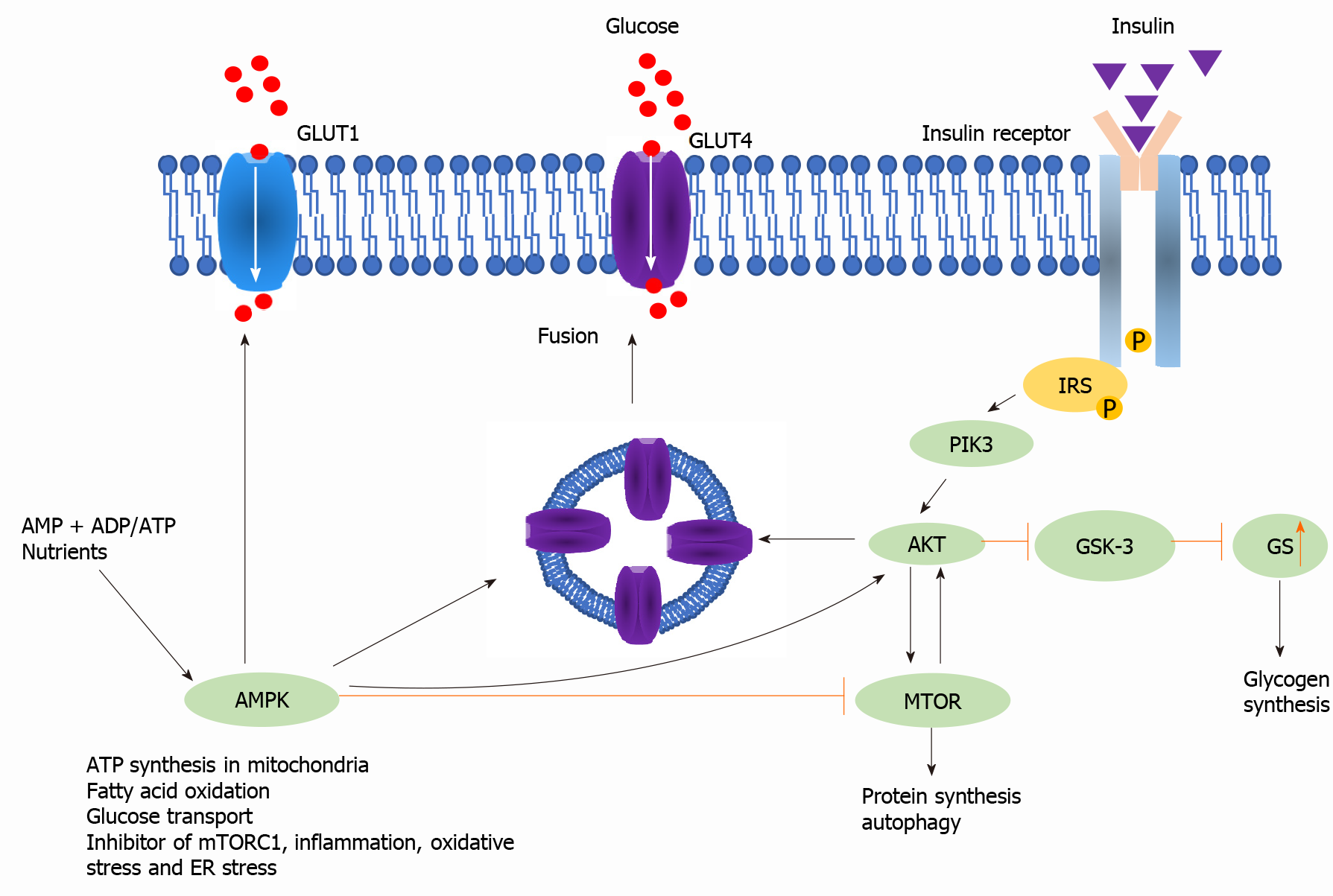
Figure 2 Insulin signaling pathway.
After insulin binds to the insulin receptor, which is a type of tyrosine kinase, signal transduction mediated by insulin-receptor substrate-1, PI3K, and AKT is activated by phosphorylation. AKT phosphorylates the Ser9 site of GSK-3b, which inhibits glycogen synthetase (GS). Hence, the insulin signaling pathway leads to glycogen synthesis. AMPK and MTOR are major modulators in metabolism. Insulin resistance and branched-chain amino acids are indicated to influence these mediators.
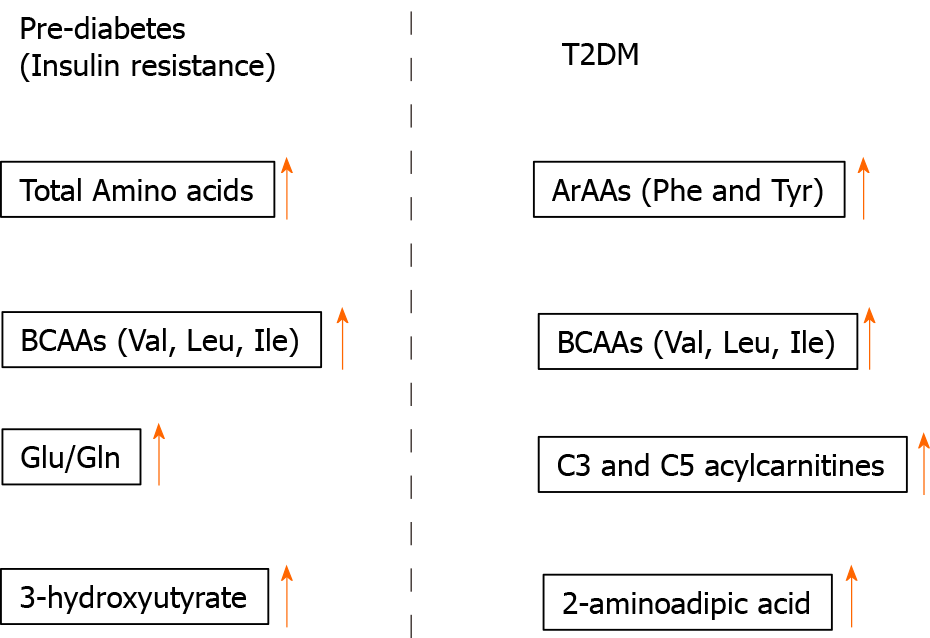
Figure 3 Insulin signaling pathway.
BCAAs: Branched-chain amino acids; T2DM: Type 2 diabetes mellitus.
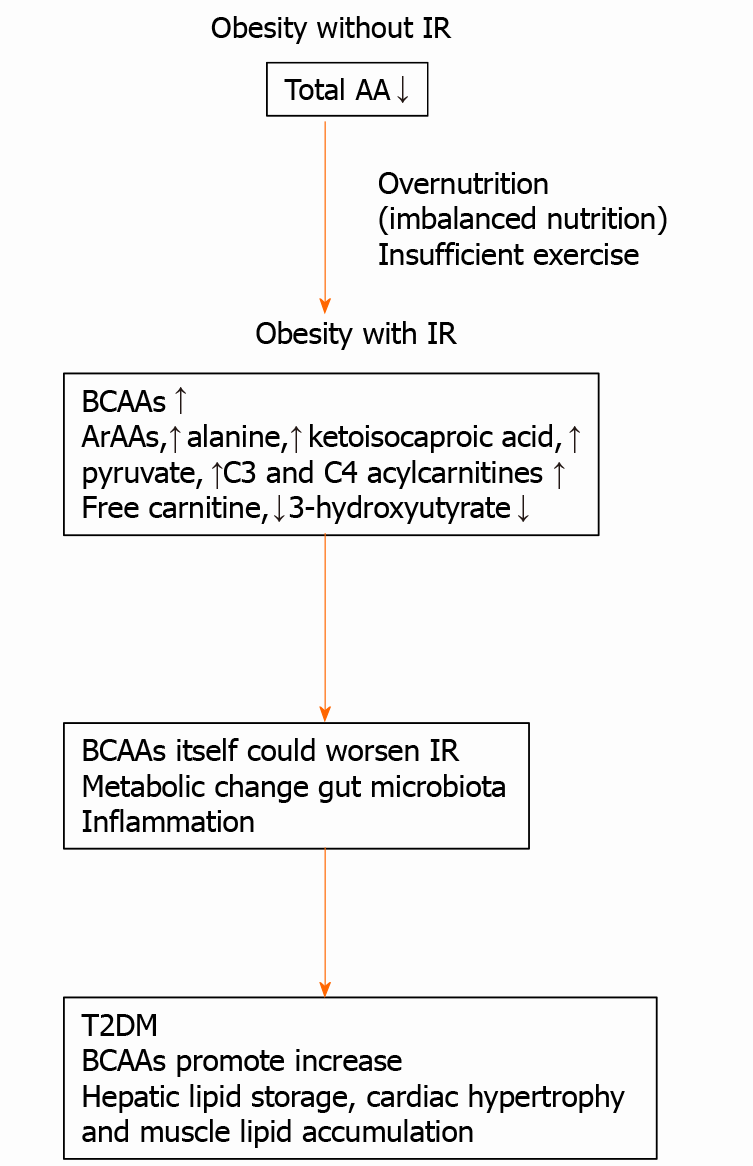
Figure 4 Metabolic change in children with obesity.
BCAAs: Branched-chain amino acids; T2DM: Type 2 diabetes mellitus.
- Citation: Matsumoto S, Nakamura T, Nagamatsu F, Kido J, Sakamoto R, Nakamura K. Metabolic and biological changes in children with obesity and diabetes. World J Meta-Anal 2021; 9(2): 153-163
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2308-3840/full/v9/i2/153.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.13105/wjma.v9.i2.153