©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Meta-Anal. Mar 31, 2019; 7(3): 80-95
Published online Mar 31, 2019. doi: 10.13105/wjma.v7.i3.80
Published online Mar 31, 2019. doi: 10.13105/wjma.v7.i3.80
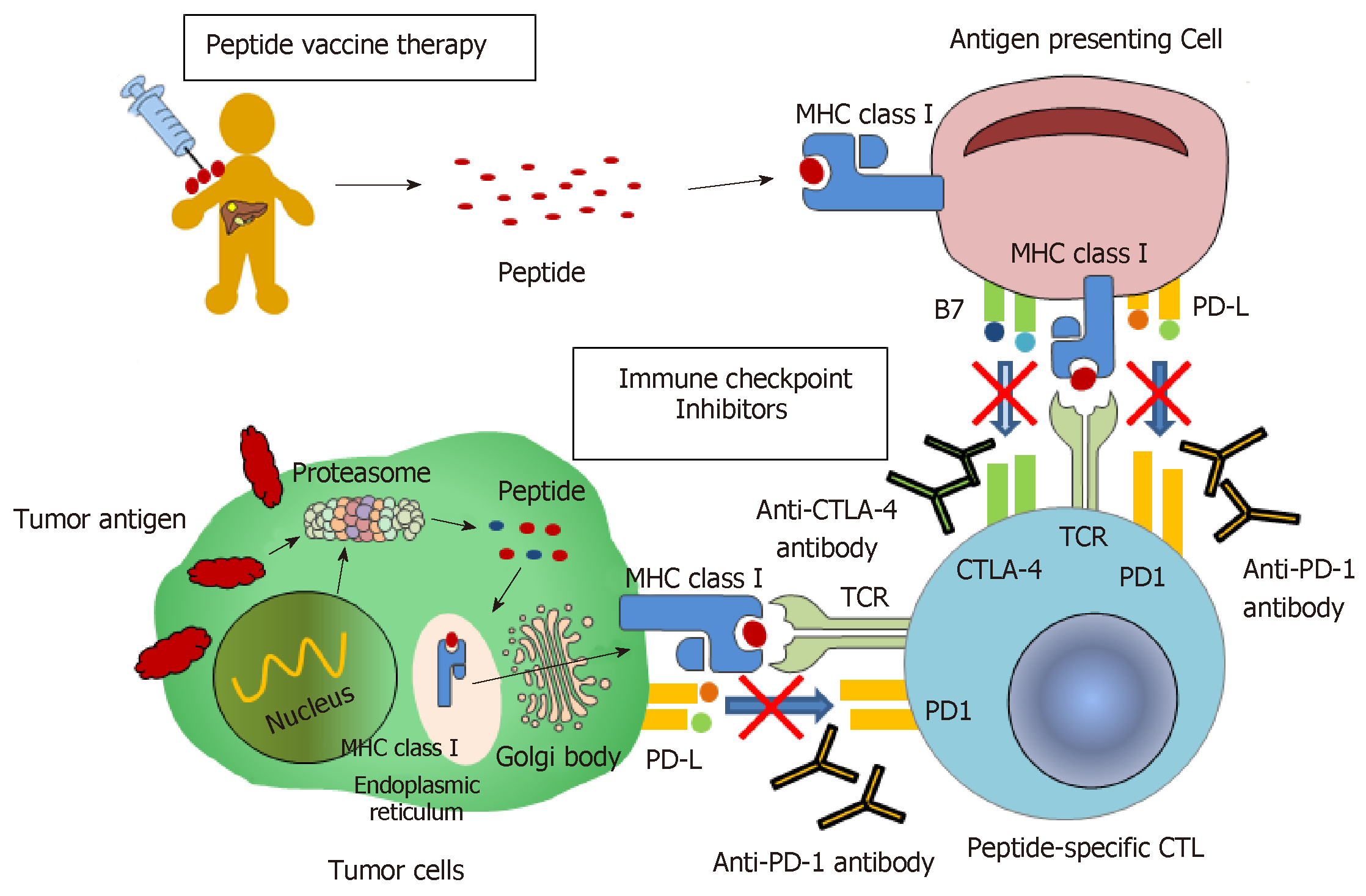
Figure 1 A scheme of mechanisms of peptide vaccine therapy and immune checkpoint inhibition therapy.
In peptide vaccine therapy, a injected tumor-associated peptides induce peptide-specific cytotoxic T-lymphocyte via antigen presenting cells, with resulting in an antitumor effect on cancer cells. Immune checkpoint inhibition therapy could result in anti-tumor effects by inhibiting the mechanism that negatively suppresses the immune response to tumor cells; anti-CTLA-4 antibody and anti-PD-1 antibody play a role of blocking the PD-1/PDL1 and CTLA4/B7 pathways, respectively. MHC: Major histocompatibility complex; CTLA-4: Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated antigen 4; PD-1: Programmed cell death-1; CTL: Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte.
- Citation: Akazawa Y, Suzuki T, Yoshikawa T, Mizuno S, Nakamoto Y, Nakatsura T. Prospects for immunotherapy as a novel therapeutic strategy against hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Meta-Anal 2019; 7(3): 80-95
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2308-3840/full/v7/i3/80.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.13105/wjma.v7.i3.80