©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Meta-Anal. Aug 26, 2014; 2(3): 127-134
Published online Aug 26, 2014. doi: 10.13105/wjma.v2.i3.127
Published online Aug 26, 2014. doi: 10.13105/wjma.v2.i3.127
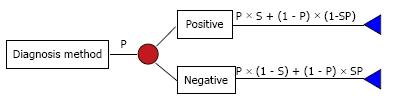
Math 6 Math(A1).
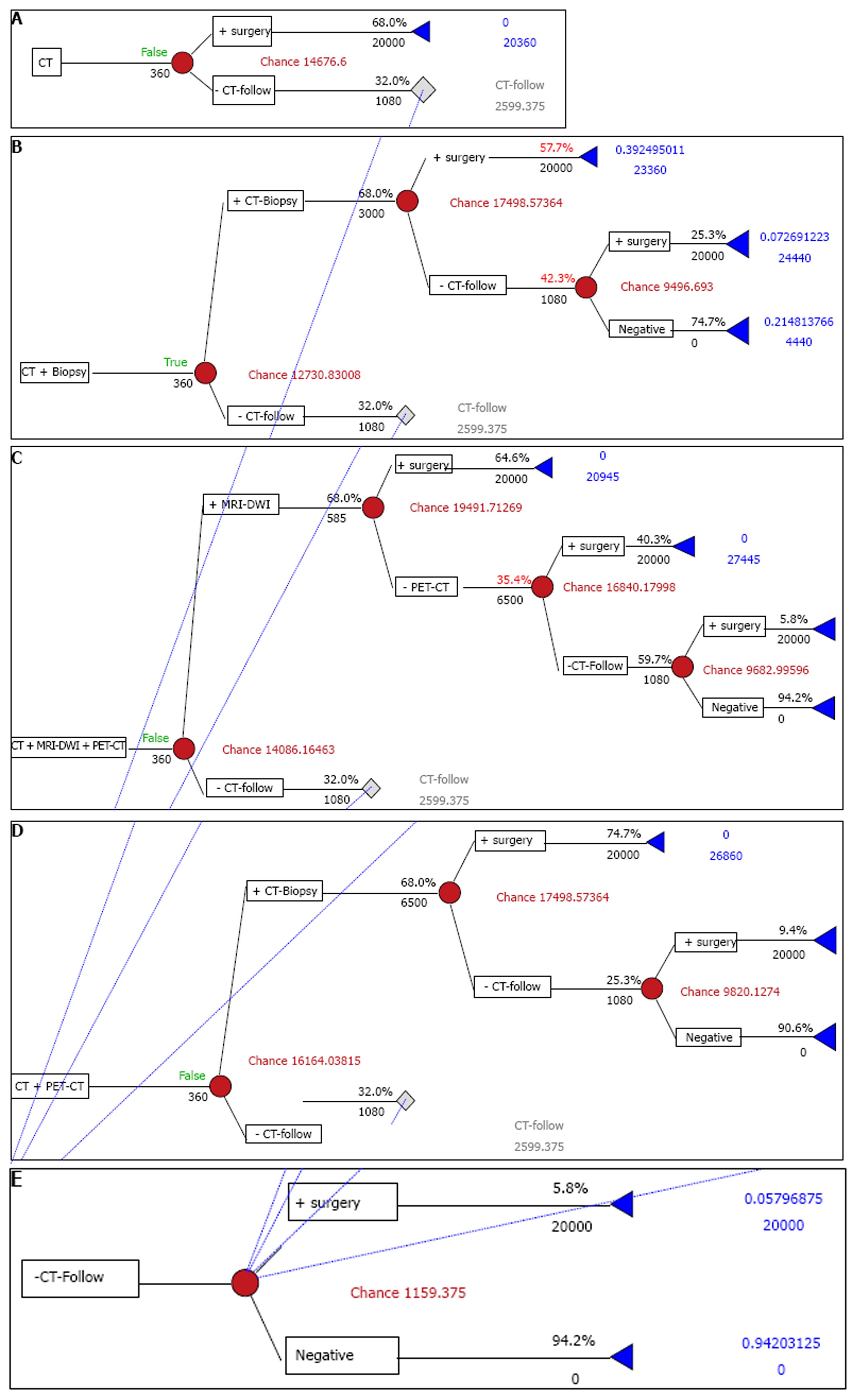
Figure 1 Strategies for the management of solitary pulmonary nodule.
A: CT alone strategy (base line); B: CT plus CT-guided needle biopsy strategy; C: CT plus DWI plus PET strategy; D: CT plus PET strategy. PET: Positron emission tomography; CT: Computed tomography; DWI: Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging.
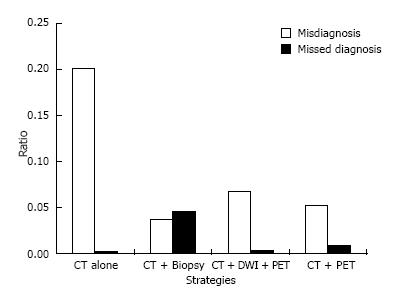
Figure 2 Ratio of the patients who undergo unnecessary surgery for a benign solitary pulmonary nodule and in whom lung cancer is misdiagnosed as a benign nodule.
The strategies using CT + DWI + PET and CT + ACNB dramatically decrease the ratio of the patients who undergo unnecessary surgery for a benign SPN, although the ratio of cancer which is missed at diagnosis is increased. PET: Positron emission tomography; CT: Computed tomography; DWI: Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging; SPN: Solitary pulmonary nodule; ACNB: Automated cutting needle biopsy.
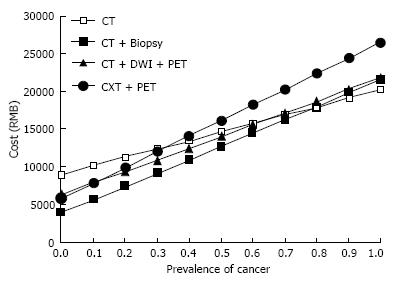
Figure 3 Correlation between the prevalence of cancer and total costs per patient.
The total costs per patients were increased regardless of the strategies and the difference among the strategies became small, although the CT+PET alone strategy had the highest cost at the prevalence of 50%. PET: Positron emission tomography; CT: Computed tomography.
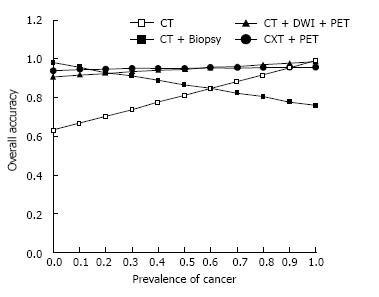
Figure 4 Correlation between the prevalence of cancer and the overall accuracy.
The use of CT+PET or CT+DWI+PET resulted in a higher accuracy between the prevalence of 20%-90% compared to CT alone strategy and CT+Biopsy. PET: Positron emission tomography; CT: Computed tomography; DWI: Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging.
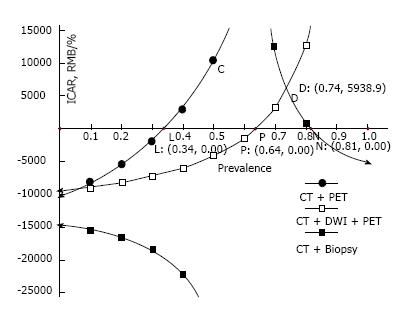
Figure 5 Incremental cost-accuracy ratio compared with computed tomography alone strategy as the baseline.
A negative ICAR means cost-effectiveness. At the prevalence of cancer up to 34%, all strategies being compared are cost effective; in particular, the CT plus PET plus DWI strategy is cost-effective at the prevalence up to 63%. ICAR: Incremental cost-accuracy ratio; PET: Positron emission tomography; CT: Computed tomography; DWI: Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging.
- Citation: Lu B, Sun LX, Yan X, Ai ZZ, Xu JZ. Decision-tree analysis for cost-effective management of solitary pulmonary nodules in China. World J Meta-Anal 2014; 2(3): 127-134
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2308-3840/full/v2/i3/127.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.13105/wjma.v2.i3.127