©The Author(s) 2023.
World J Meta-Anal. Dec 18, 2023; 11(7): 317-339
Published online Dec 18, 2023. doi: 10.13105/wjma.v11.i7.317
Published online Dec 18, 2023. doi: 10.13105/wjma.v11.i7.317
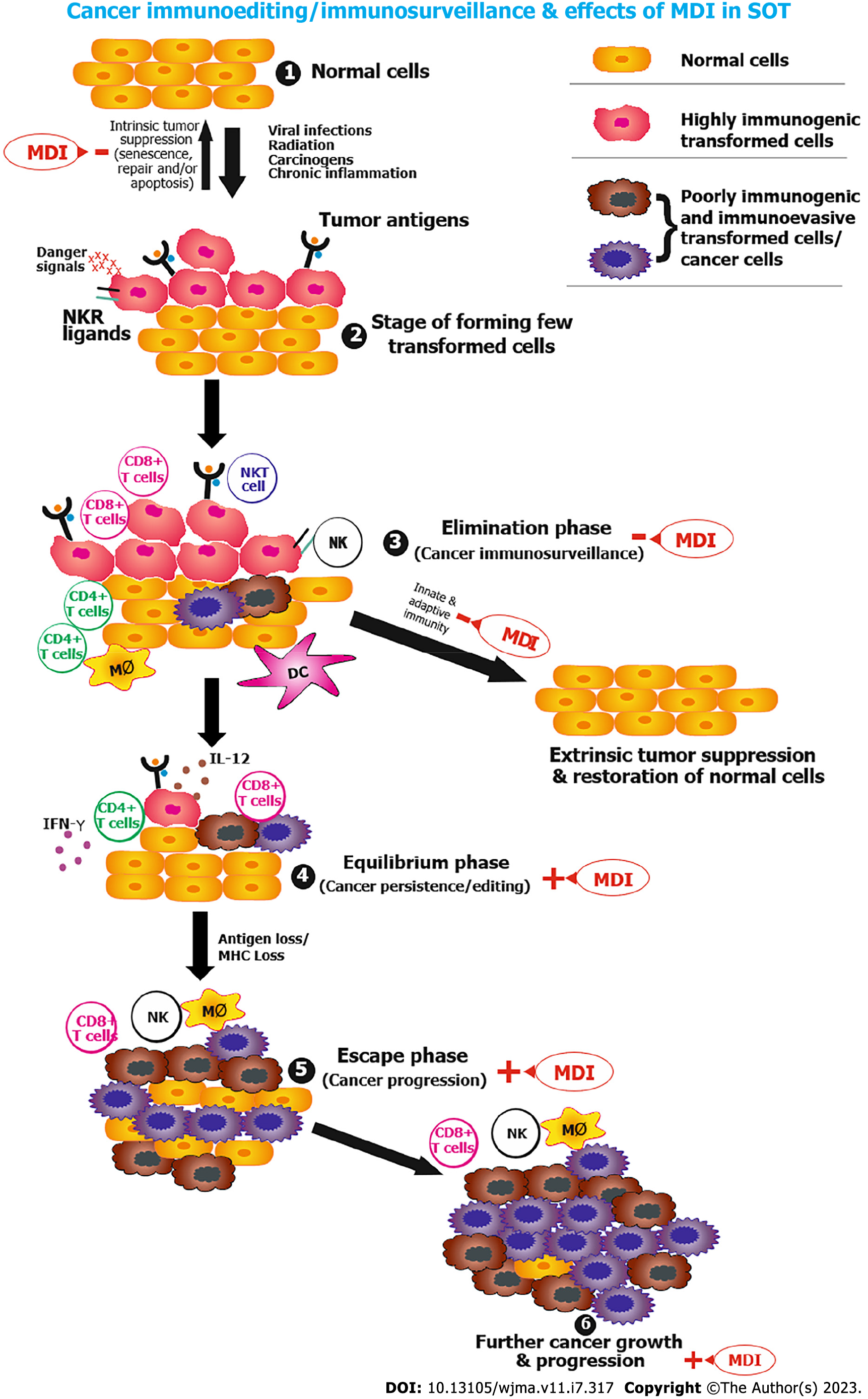
Figure 1 Cancer immunoediting and influence of immunosuppression after transplantation.
+: Promote; –: Inhibit; MDI: Multidrug immunosuppression; MHC: Major histocompatibility complex; NK: Natural killer cell; NKR: Natural killer cell receptor; SOT: Solid organ transplant.
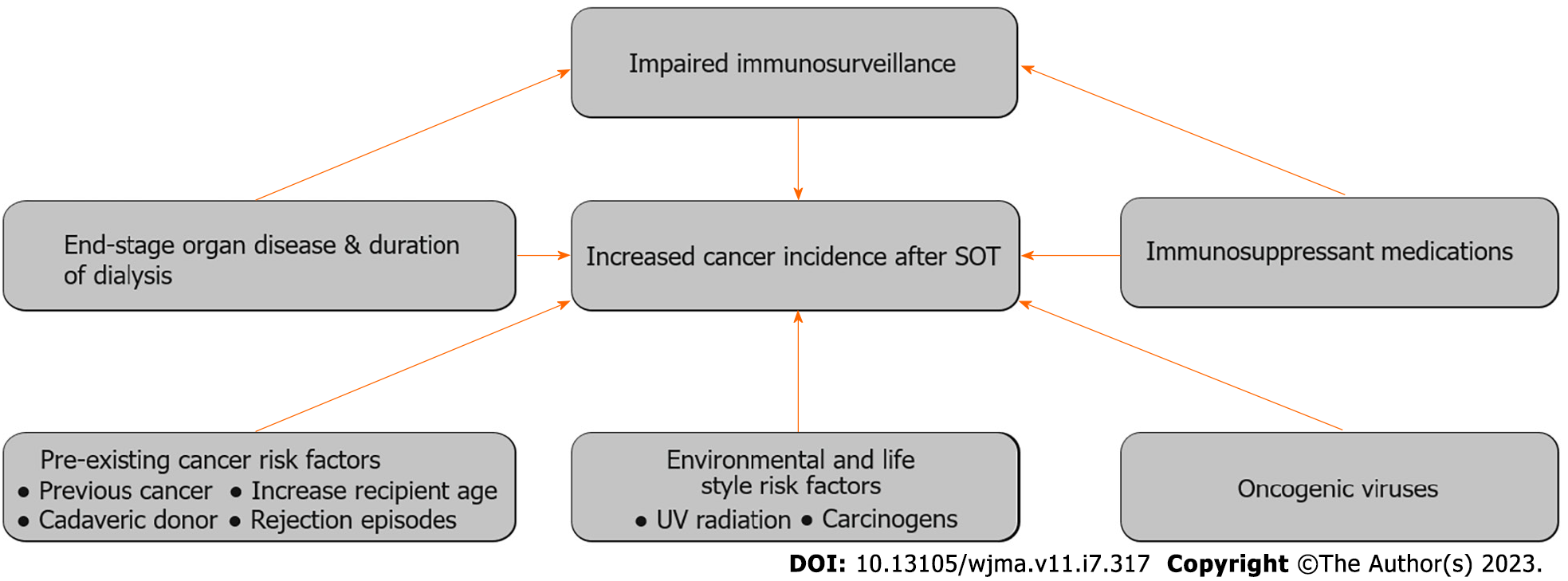
Figure 2 Summary of etiology of increased cancer incidence after transplantation.
SOT: Solid organ transplant; UV: Ultraviolet.
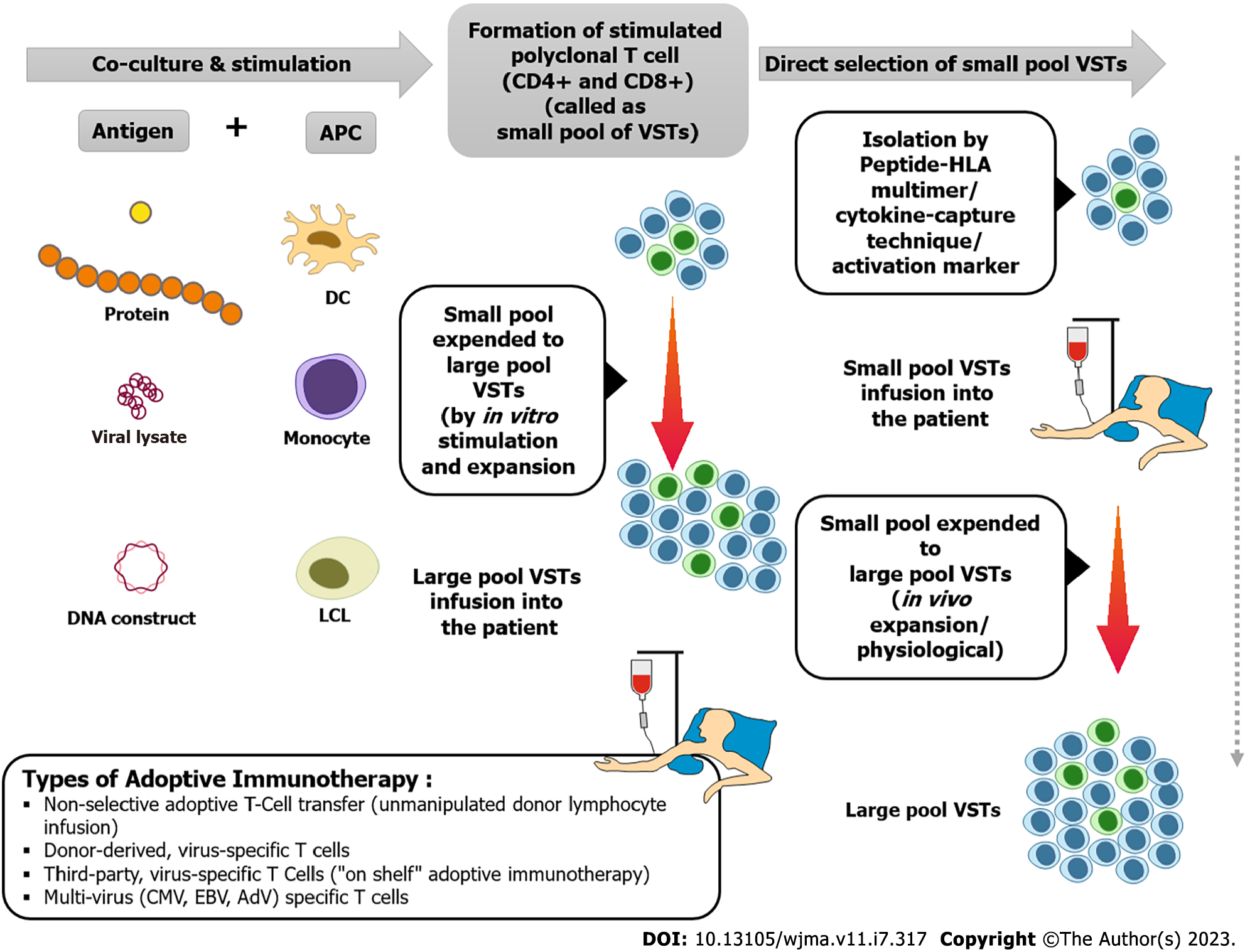
Figure 3 Technique of adoptive immunotherapy (steps, isolation and types of virus-specific T cells).
AdV: Adenovirus; APC: Antigen presenting cells; CMV: Cytomegalovirus; DC: Dendritic cells; EBV: Epstein–Barr virus; HLA: Human leukocyte antigen; LCL: Lymphoblastoid cell lines; VSTs: Virus-specific T cells.
- Citation: Yadav R, El Kossi M, Belal D, Sharma A, Halawa A. Post-transplant malignancy: Focusing on virus-associated etiologies, pathogenesis, evidence-based management algorithms, present status of adoptive immunotherapy and future directions. World J Meta-Anal 2023; 11(7): 317-339
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2308-3840/full/v11/i7/317.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.13105/wjma.v11.i7.317