©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Methodol. Dec 26, 2017; 7(4): 129-138
Published online Dec 26, 2017. doi: 10.5662/wjm.v7.i4.129
Published online Dec 26, 2017. doi: 10.5662/wjm.v7.i4.129
Figure 1 Typical arrangement of the forced oscillatory impedance measurement, adapted from.
Pao: Input pressure at the airway opening; V’ao: Output flow.
Figure 2 Demonstration of lung function measurements using FOT.
On the left, a photograph of the FOT test being performed in a 5-year-old boy. The hands of the investigator support the cheeks and the floor of the mouth of the child. The nose is blocked using a nose clip. The lips are sealed around the mouthpiece. On the right, Different breathing patterns during FOT measurements are shown, as observed on the flow-time trace in L/s. A: Normal tidal breathing; B: Breath holding spells; C: An aberrant activity (e.g., coughing, swallowing, or noise); D: A leak around the mouthpiece. FOT: Forced oscillation technique.
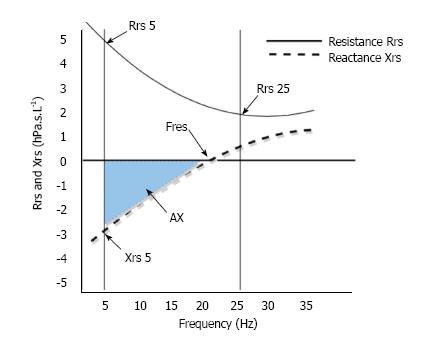
Figure 3 Changes in resistance (Rrs) and reactance (Xrs) as function of oscillation frequency.
- Citation: Alblooshi A, Alkalbani A, Albadi G, Narchi H, Hall G. Is forced oscillation technique the next respiratory function test of choice in childhood asthma. World J Methodol 2017; 7(4): 129-138
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2222-0682/full/v7/i4/129.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5662/wjm.v7.i4.129