©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Methodol. Dec 26, 2017; 7(4): 112-116
Published online Dec 26, 2017. doi: 10.5662/wjm.v7.i4.112
Published online Dec 26, 2017. doi: 10.5662/wjm.v7.i4.112
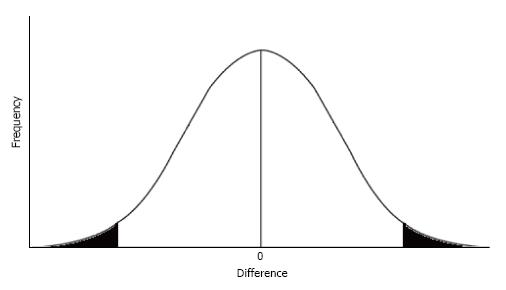
Figure 1 According to the classical definition, research findings are considered statistically significant when the difference observed falls in the upper or lower tails of the frequency distribution, represented above in black.
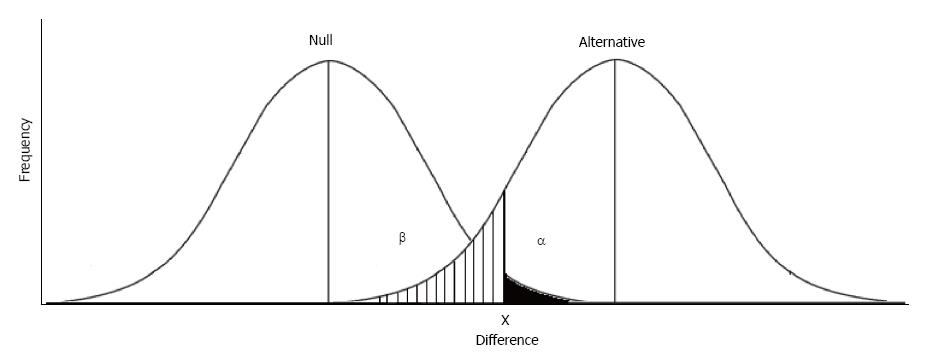
Figure 2 If the observed difference is greater than x, then we consider that the finding is statistically significant and the null hypothesis is rejected.
If the difference found is less than x, then we accept the null hypothesis and reject the alternative hypothesis. The area in black represents a Type I error which occurs when the difference is greater than x, but the null hypothesis is in fact true. The lined area represents a Type II error which occurs when the difference found is less than x, but the alternative hypothesis is in fact true.
- Citation: Heston TF, King JM. Predictive power of statistical significance. World J Methodol 2017; 7(4): 112-116
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2222-0682/full/v7/i4/112.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5662/wjm.v7.i4.112