©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Methodol. Sep 26, 2015; 5(3): 122-126
Published online Sep 26, 2015. doi: 10.5662/wjm.v5.i3.122
Published online Sep 26, 2015. doi: 10.5662/wjm.v5.i3.122
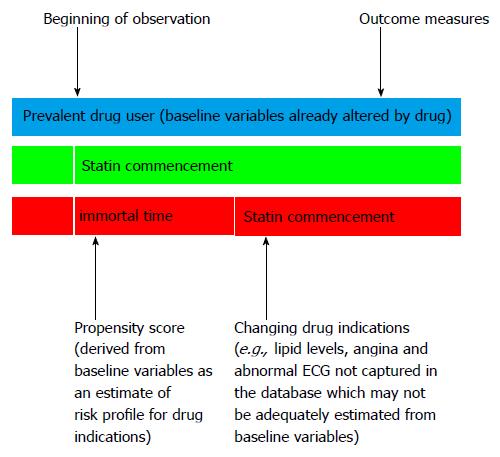
Figure 1 Schematic diagram to explain the multiple biases in epidemiological analysis of cardiovascular disease with use of statins in observational cohorts.
While baseline variables may be used to derive a propensity score to adjust for drug indications, this will not apply to prevalent drug users whose risk profile has already been influenced by drug use (blue panel). For patients who were started on the drug after a period of immortal time (non-drug exposure), insufficient data capturing during the observation period may not allow full adjustment for confounders resulting in an inflated hazard ratio of cardiovascular disease, while inclusion of immortal time in a time-dependent Cox model may lead to a reduced hazard ratio by including a period of non-drug exposure during estimation of event rates (red panel). In patients with detailed documentation of risk factors followed by drug commencement as in a clinical trial setting, time fixed analysis may yield hazards unbiased by immortal time (green panel). ECG: Electrocardiogram.
- Citation: Yang XL, Huo XX, Chan JC. Methodological challenges to control for immortal time bias in addressing drug effects in type 2 diabetes. World J Methodol 2015; 5(3): 122-126
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2222-0682/full/v5/i3/122.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5662/wjm.v5.i3.122