©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Methodol. Dec 20, 2024; 14(4): 95881
Published online Dec 20, 2024. doi: 10.5662/wjm.v14.i4.95881
Published online Dec 20, 2024. doi: 10.5662/wjm.v14.i4.95881
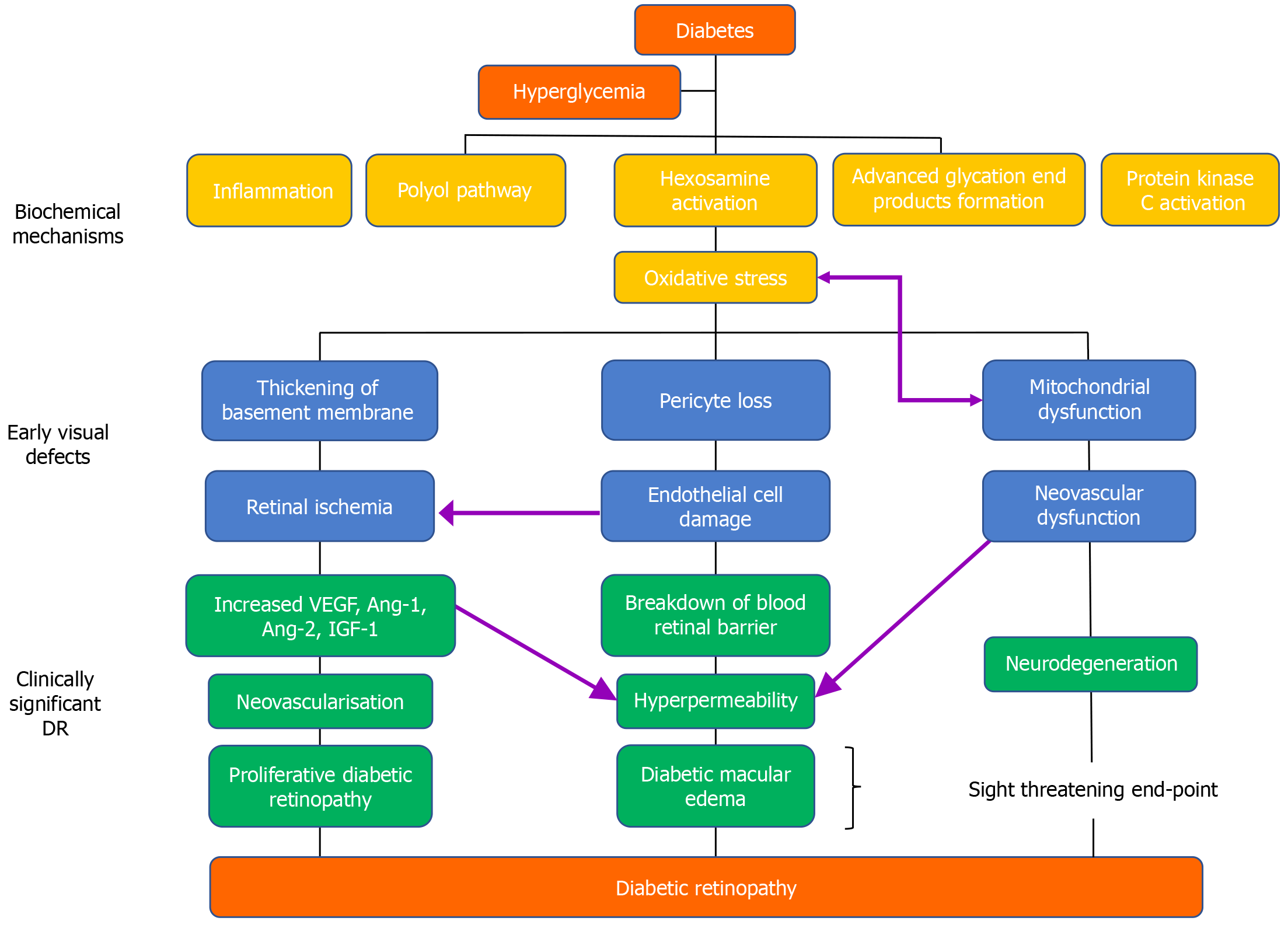
Figure 1 Pathophysiologic process of diabetic retinopathy.
Ang: Angiotensin; IGF: Insulin-like growth factor; VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor.
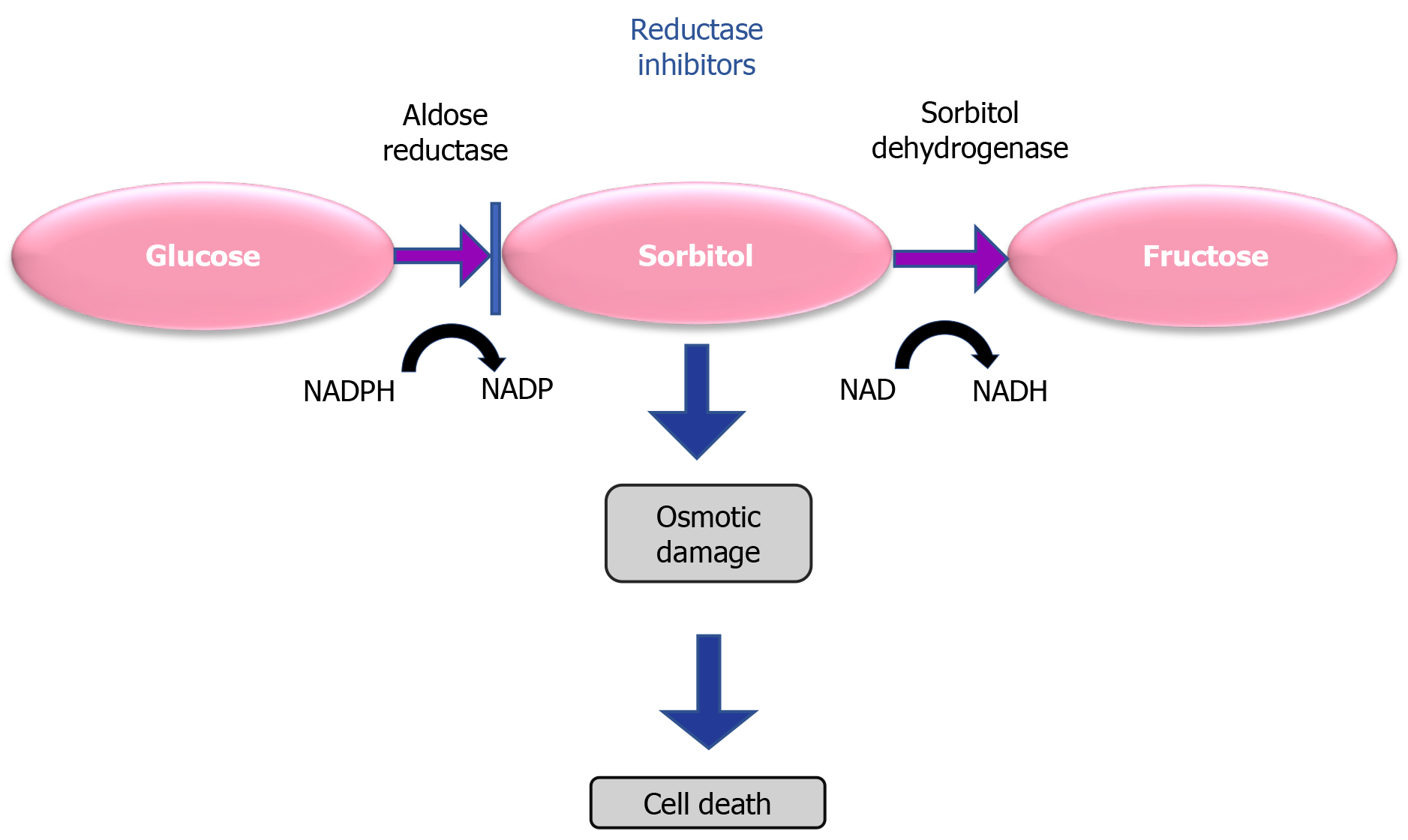
Figure 2 Sorbitol pathway.
NADP: Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate; NADPH: Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate hydrogen.
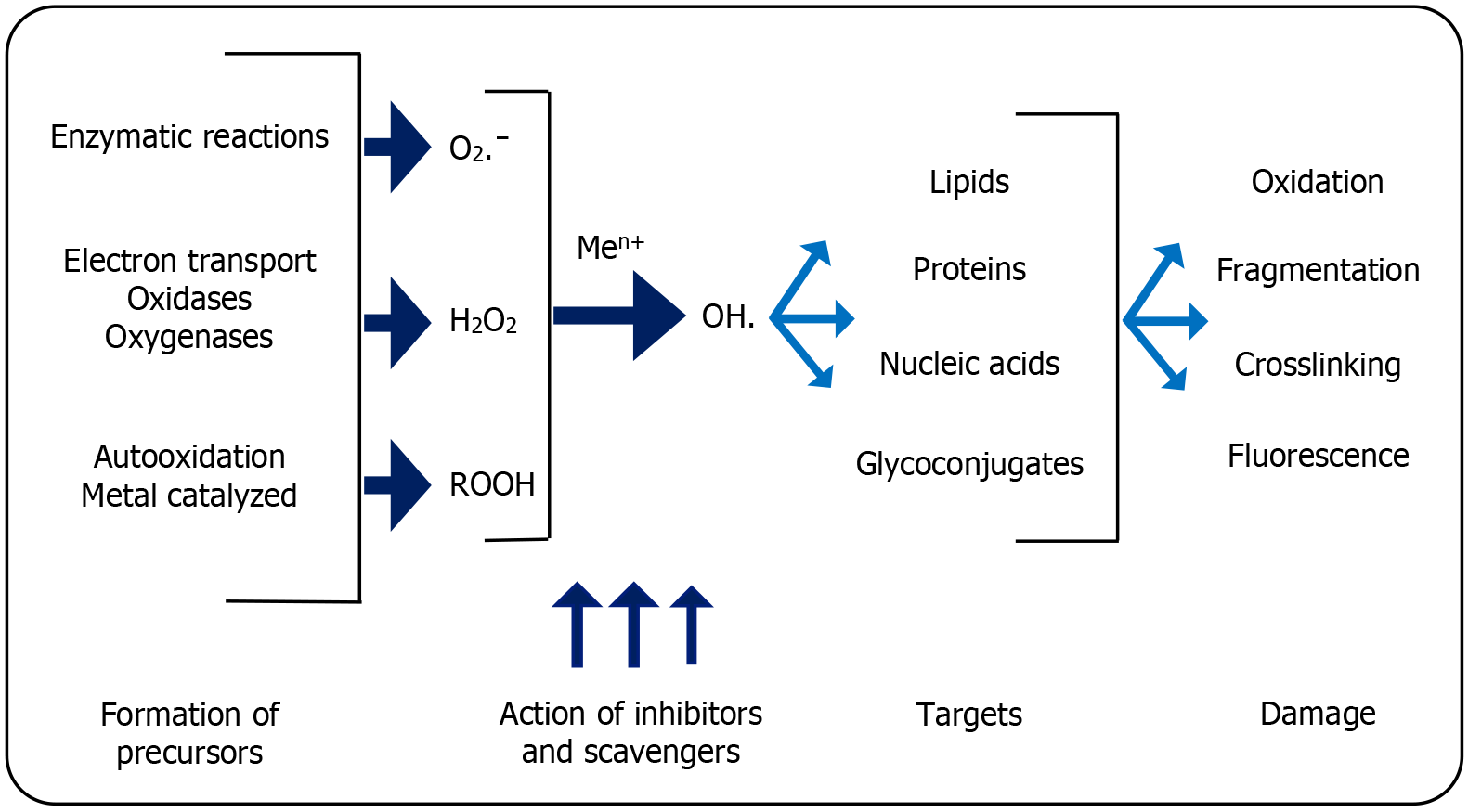
Figure 3 Pathway of oxidative stress on the development of diabetic complications.
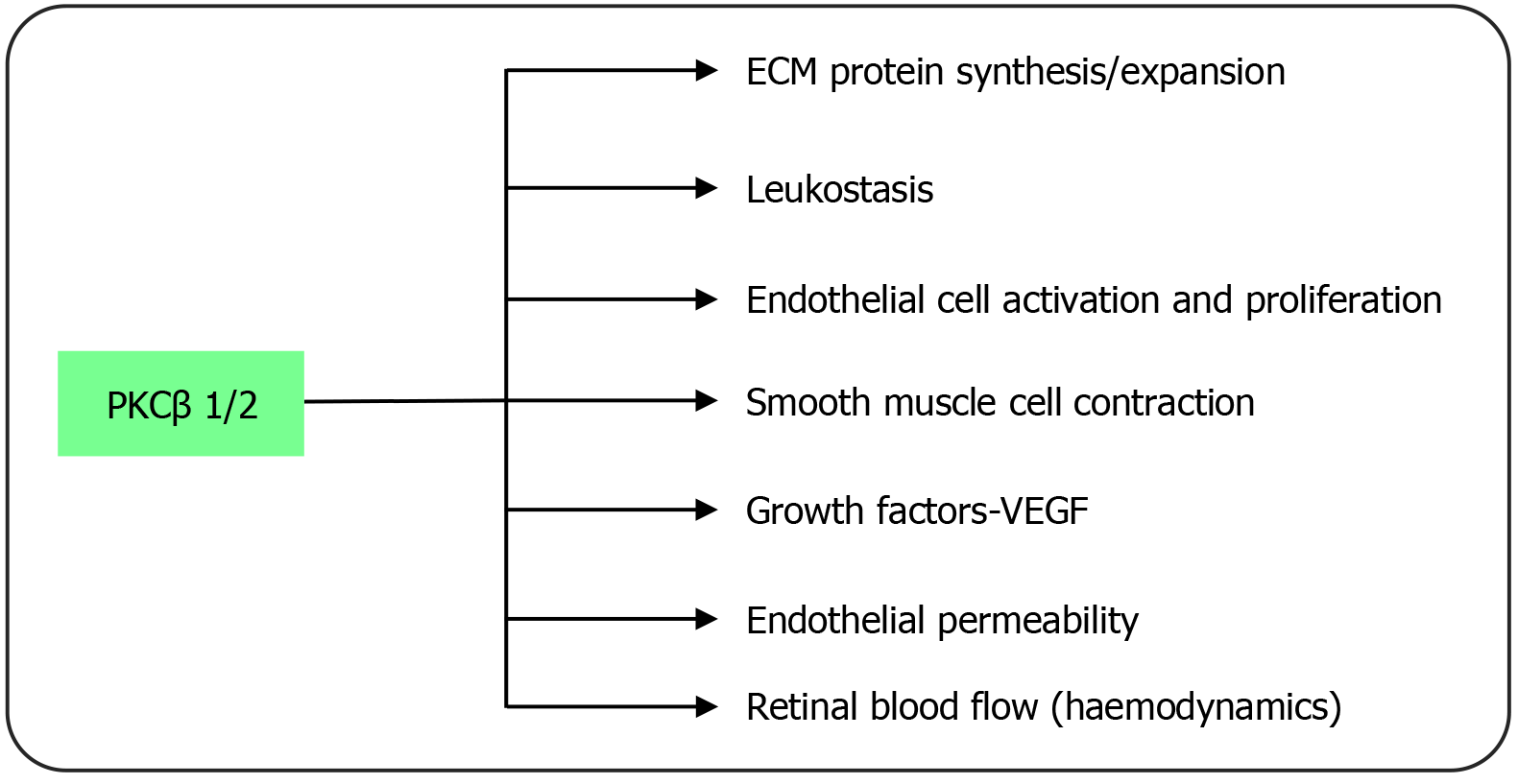
ECM: Extracellular matrix; PKCβ: Protein kinase C beta; VEGF: Vascular endothelial growth factor.
Figure 4 Regulation of pathophysiological processes in diabetic retinopathy by protein kinase C.
H2O2: Hydrogen peroxide; Men+: Methyl Cation; O2ˉ: Oxygen superoxide anion radical; OH.: Oxygen hydroxyl radical; ROOH: Hydroperoxides.
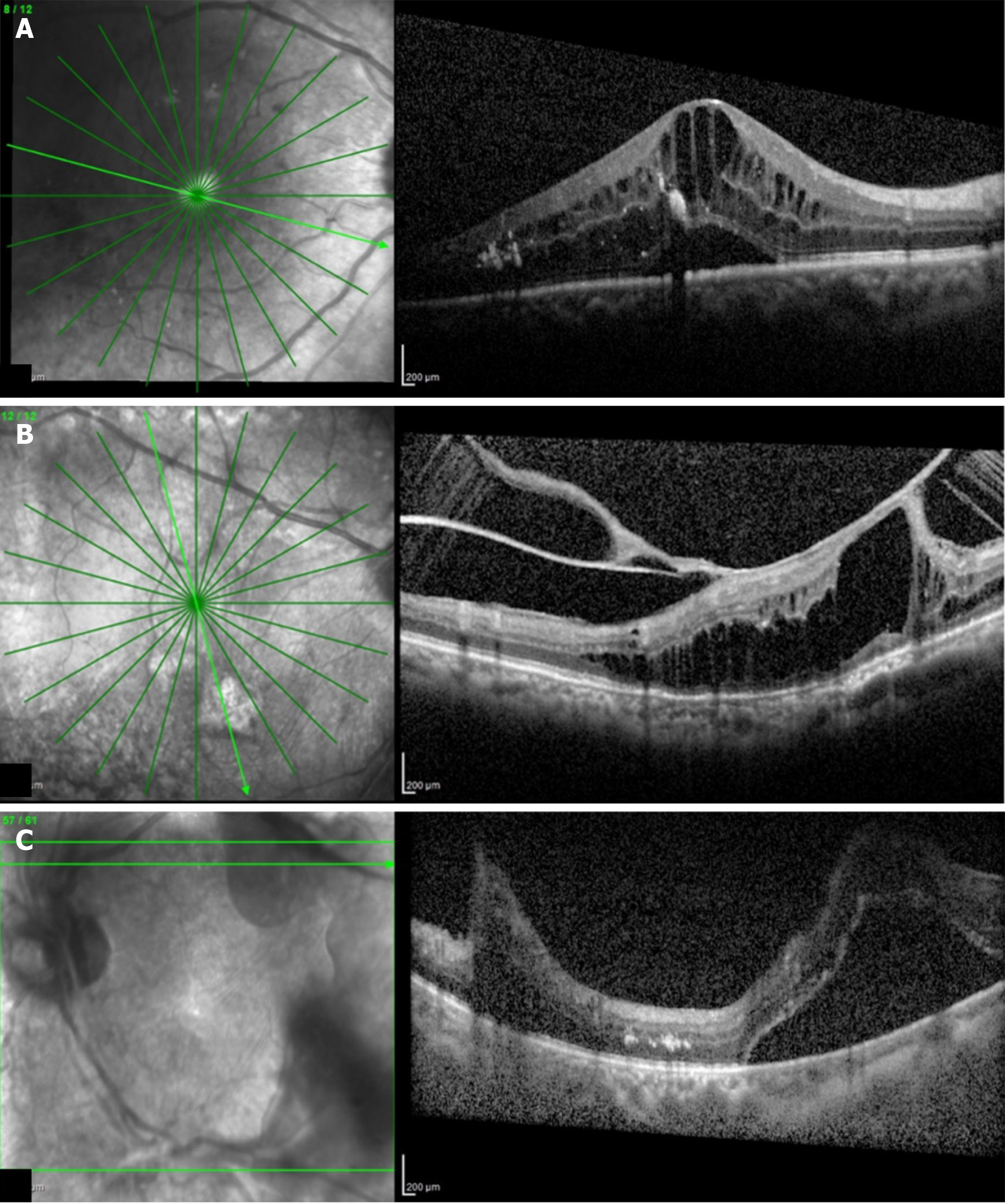
Figure 5 Optical coherence tomography images.
A: Cystoid macular edema; B: Tractional retinal detachment; C: Tractional retinal detachment due to vitreous hemorrhage.
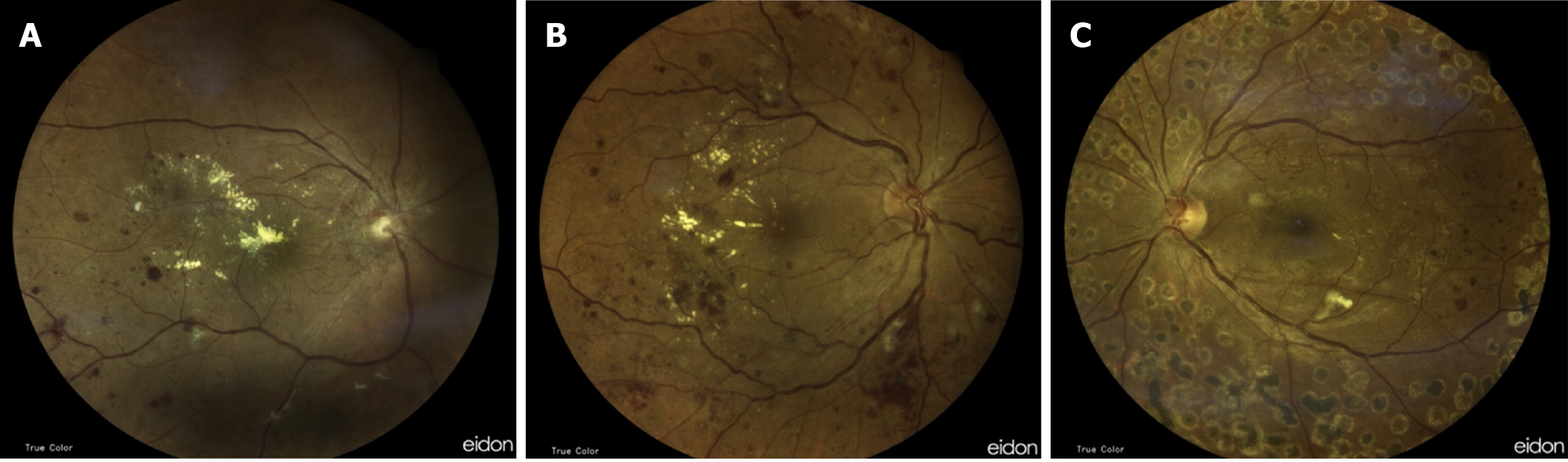
Figure 6 Fundus.
A: All suggestive findings of severe non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy; B: Severe proliferative diabetic retinopathy; C: Pan-retinal photocoagulation laser marks.
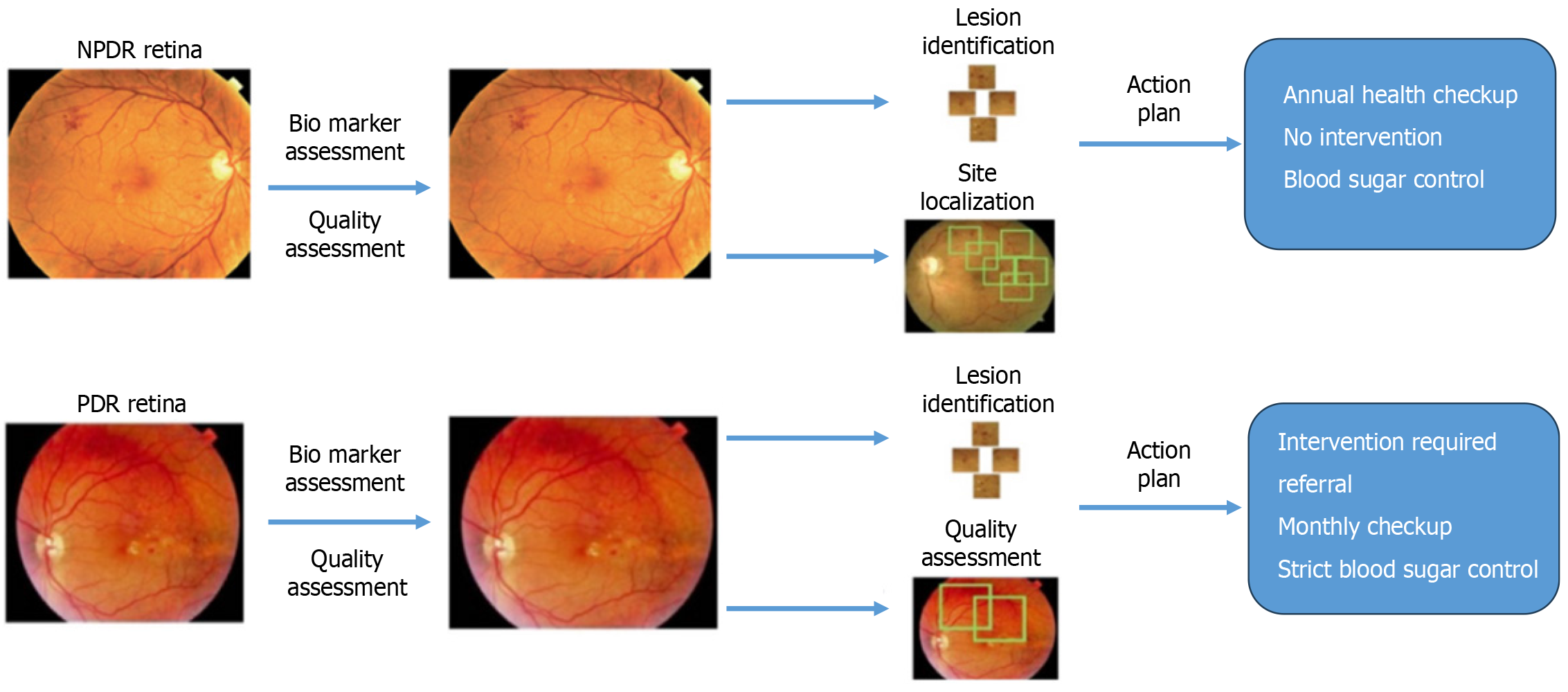
Figure 7 How artificial intelligence software assesses diabetic retinopathy into referable and non-referable interventions.
NPDR; Non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy; PDR: Proliferative diabetic retinopathy.
- Citation: Morya AK, Ramesh PV, Nishant P, Kaur K, Gurnani B, Heda A, Salodia S. Diabetic retinopathy: A review on its pathophysiology and novel treatment modalities. World J Methodol 2024; 14(4): 95881
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2222-0682/full/v14/i4/95881.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5662/wjm.v14.i4.95881