©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Methodol. Mar 20, 2024; 14(1): 89196
Published online Mar 20, 2024. doi: 10.5662/wjm.v14.i1.89196
Published online Mar 20, 2024. doi: 10.5662/wjm.v14.i1.89196
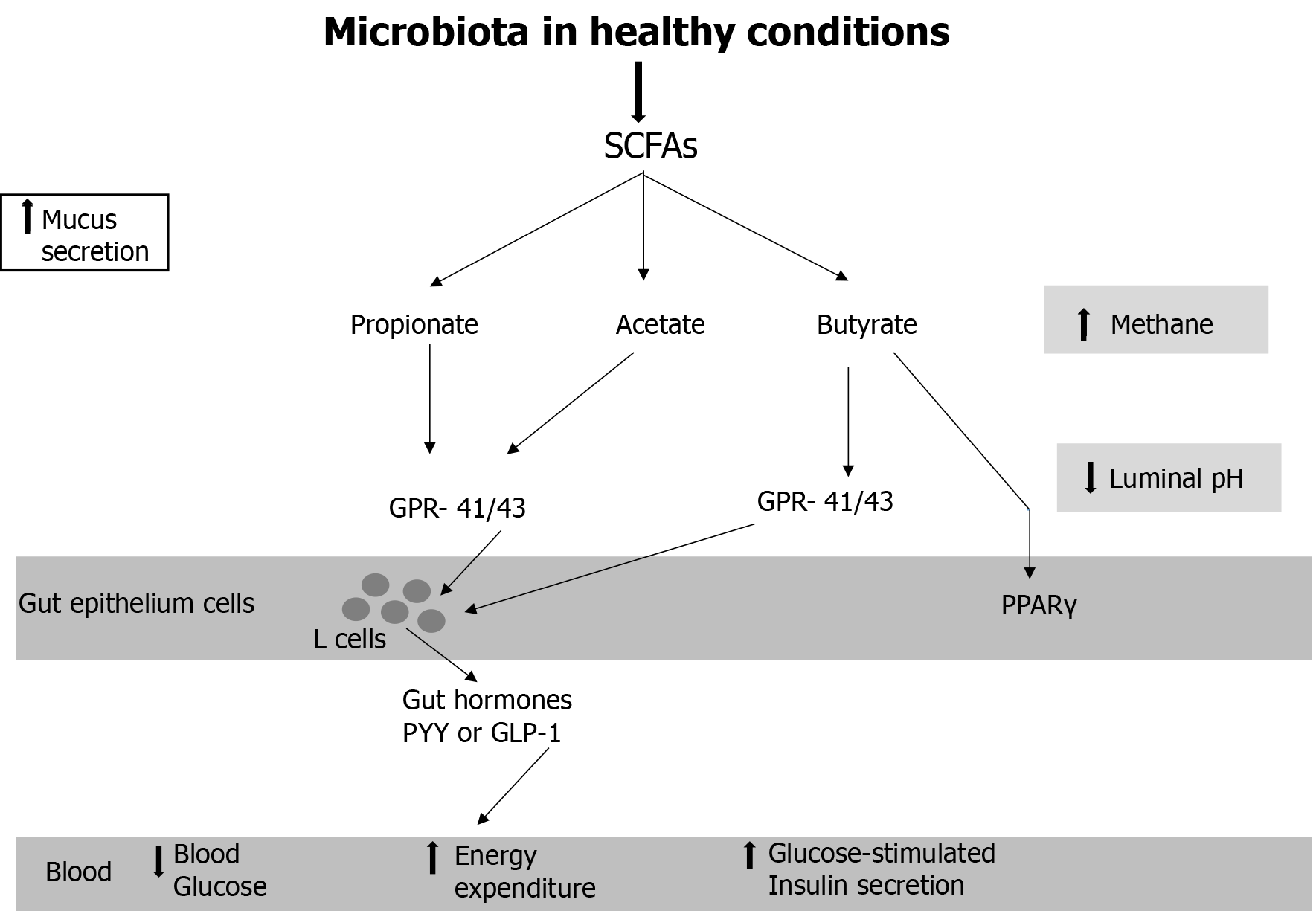
Figure 1 Microbiota in healthy conditions.
GLP-1: Glucagon-like peptide 1; GPCR: G protein-coupled receptor; PPARγ: Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma; PYY: Peptide YY; SCFA: Short chain fatty acid.
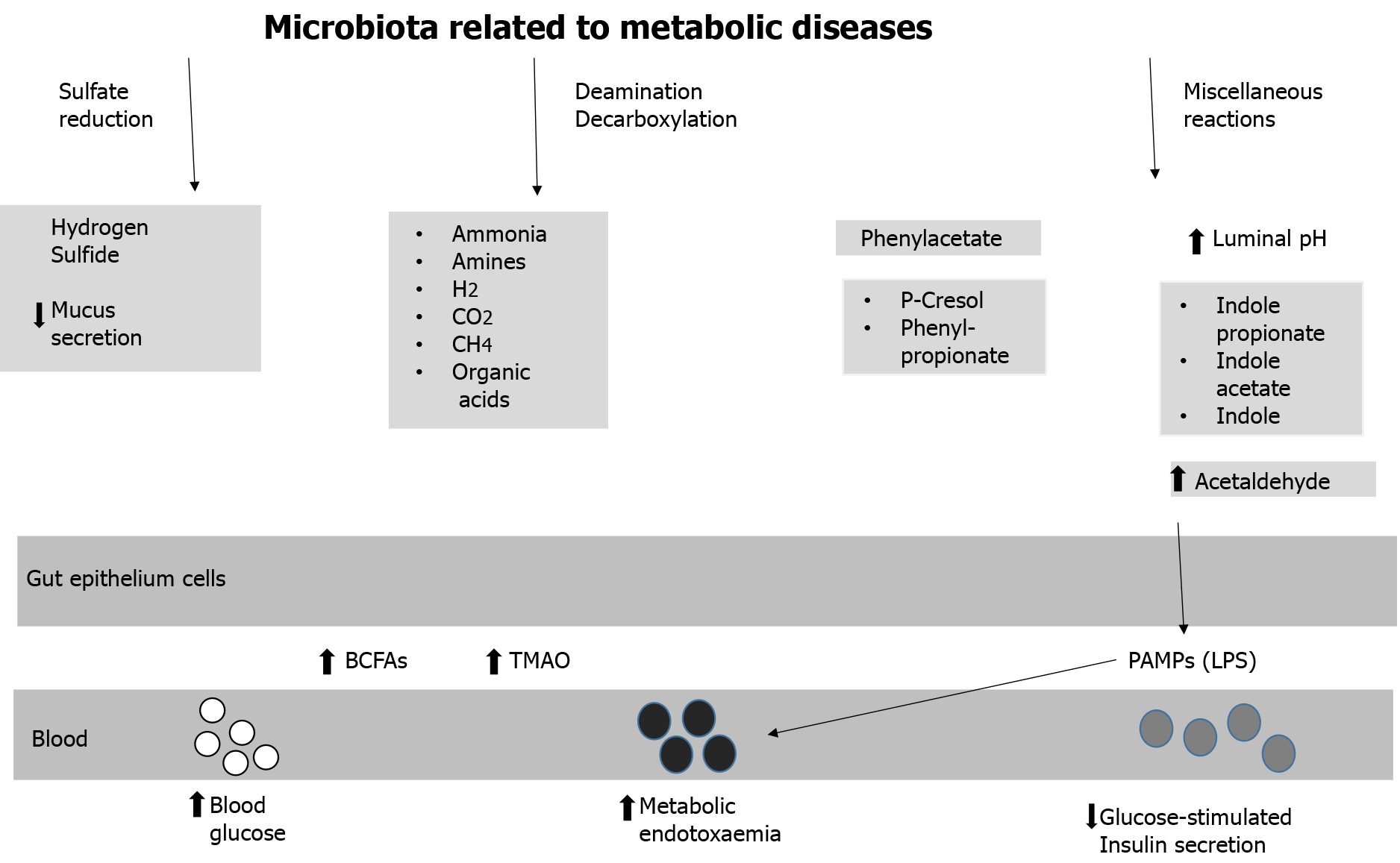
Figure 2 Microbiota related to metabolic diseases.
BCFA: Branched-chain fatty acid; LPS: Lipopolysaccharides; PAMP: Pathogen-associated molecular pattern; TMAO: Trimethilamine oxide.
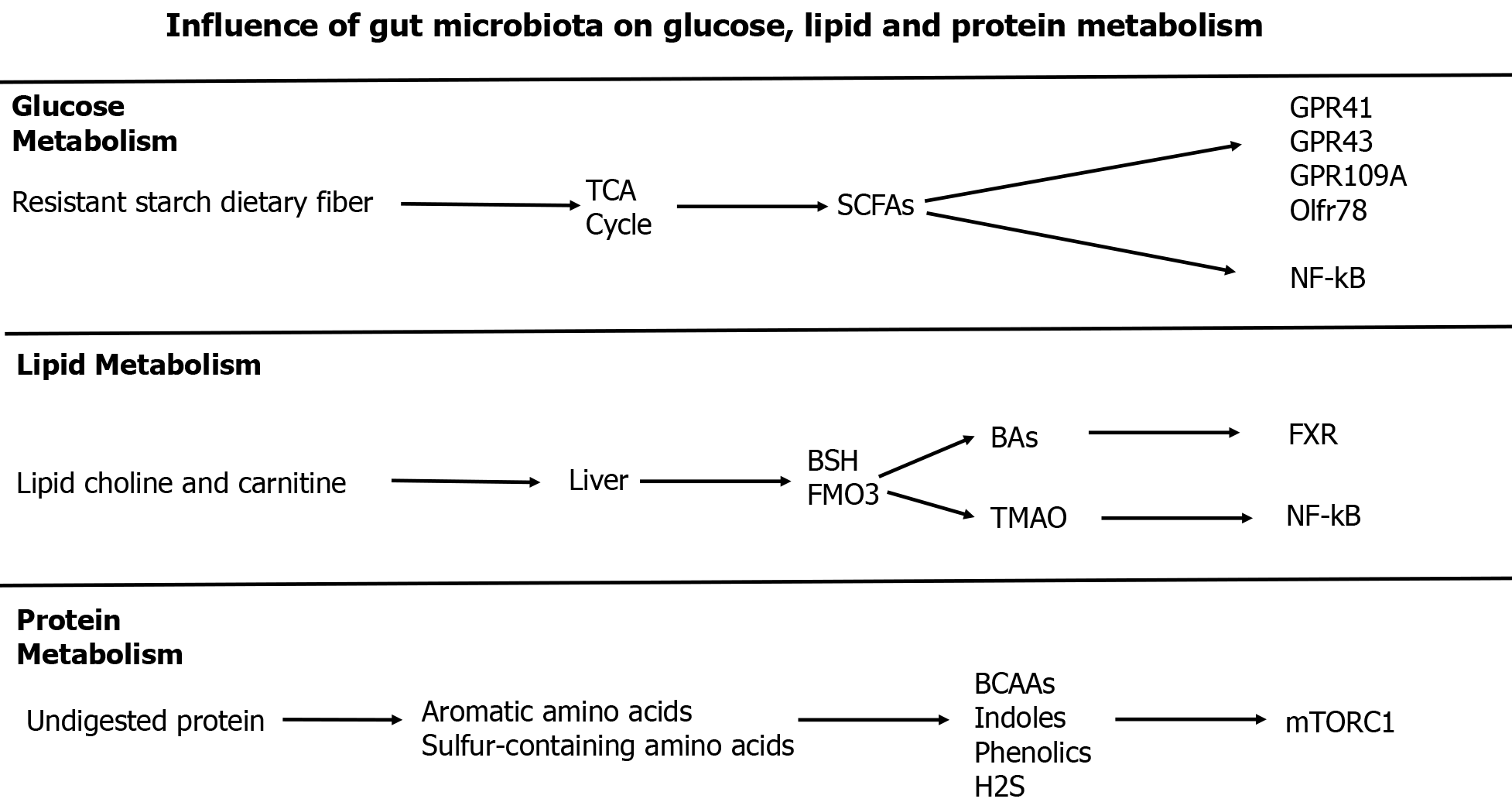
Figure 3 Influence of gut microbiota on glucose, lipid, and protein metabolism.
BCAAs: Branched-chain amino acids; BSH: Bile salt hydrolase; FMO3: Flavin monooxigenase 3; FXR: Farnesoid X receptor; GPR: G protein-coupled receptor; Olftr: Olfactory receptor 78; mTORC1: Mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1; NF-kB: Nuclear factor kappa B; SCFAs: Short-chain fatty acids; TGR5: Takeda G protein-coupled receptor 5; TMAO: Trimethylamine N-oxide.
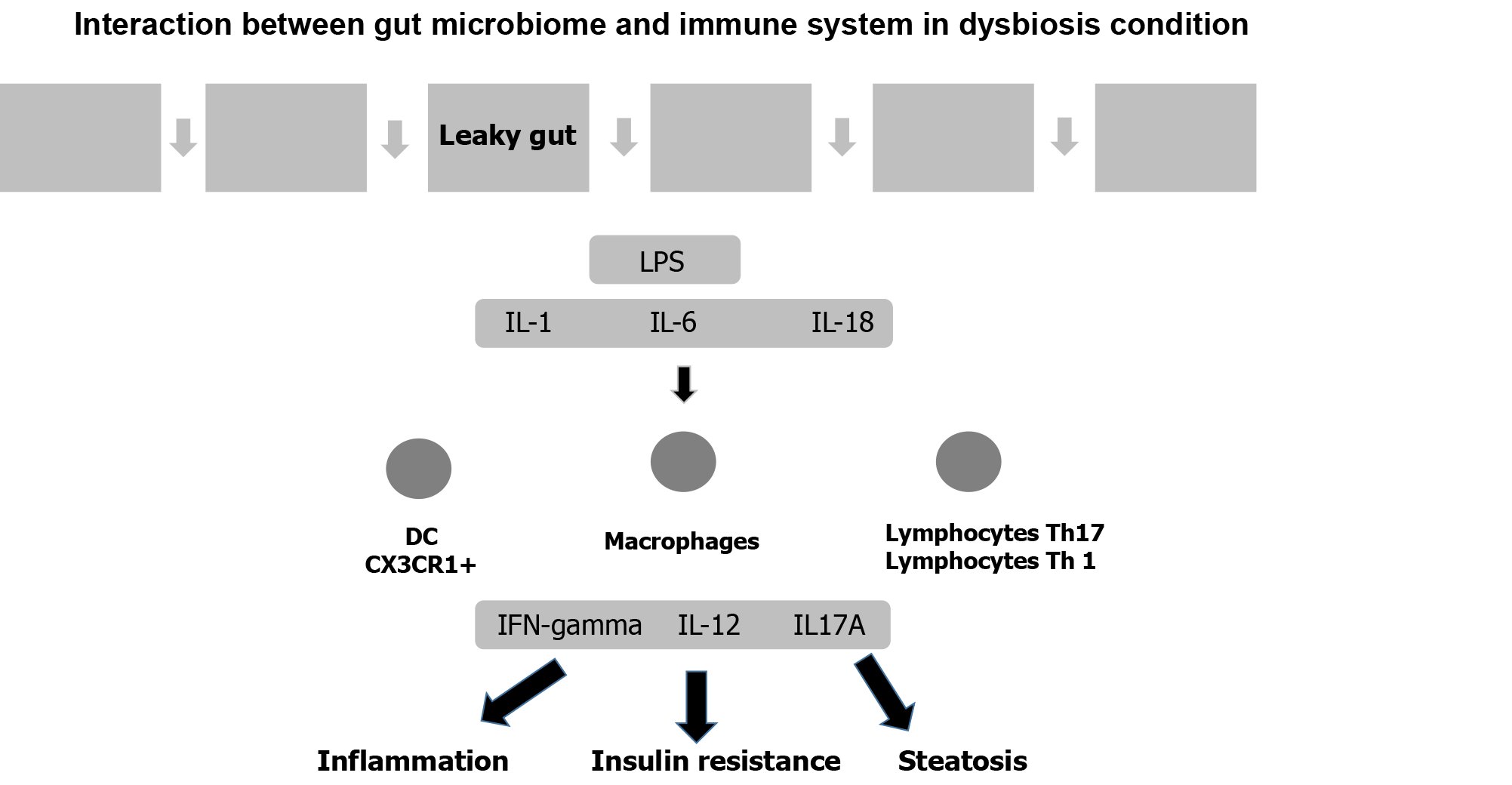
Figure 4 Interaction between gut microbiome and immune system in dysbiosis condition.
DC: Dendritic cell; IFN-γ: Interferon gamma; IL-1: Interleukin 1; IL-6: Interleukin 6; IL-18: Interleukin 18; LPS: Lipopolysaccharides.
- Citation: Salvadori M, Rosso G. Update on the gut microbiome in health and diseases. World J Methodol 2024; 14(1): 89196
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2222-0682/full/v14/i1/89196.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5662/wjm.v14.i1.89196