©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Methodol. Jul 20, 2022; 12(4): 274-284
Published online Jul 20, 2022. doi: 10.5662/wjm.v12.i4.274
Published online Jul 20, 2022. doi: 10.5662/wjm.v12.i4.274
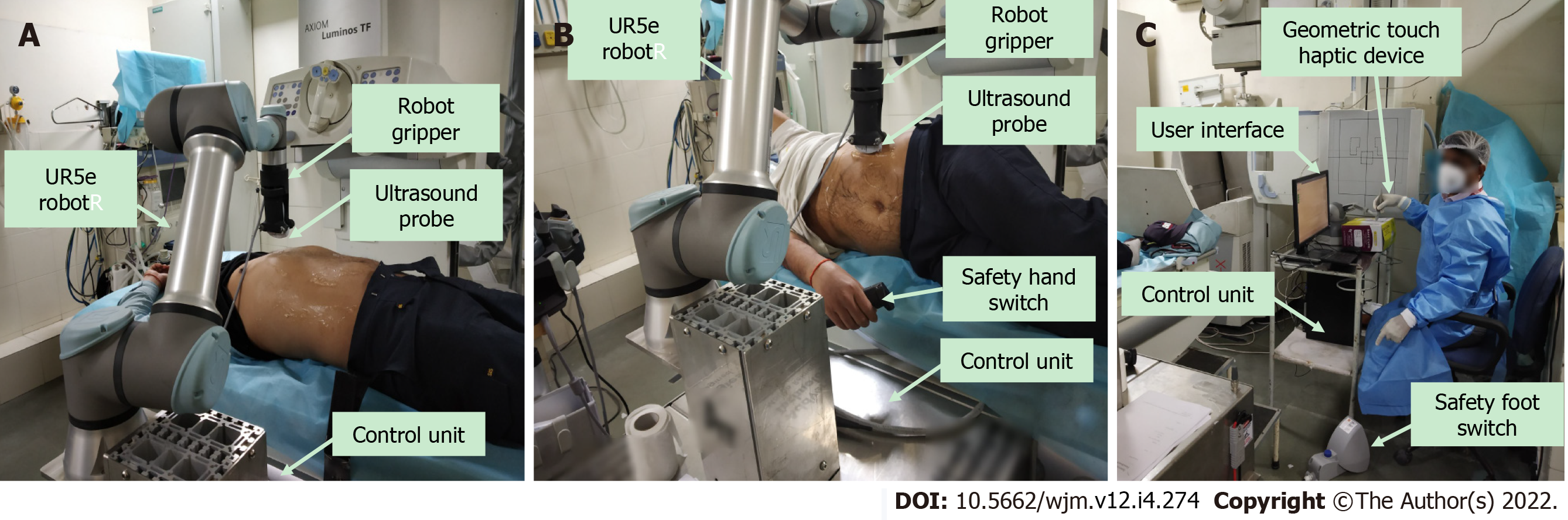
Figure 1 Robotic ultrasound.
A and B: Robotic ultrasound setup, which includes patient site; C: Doctor site.
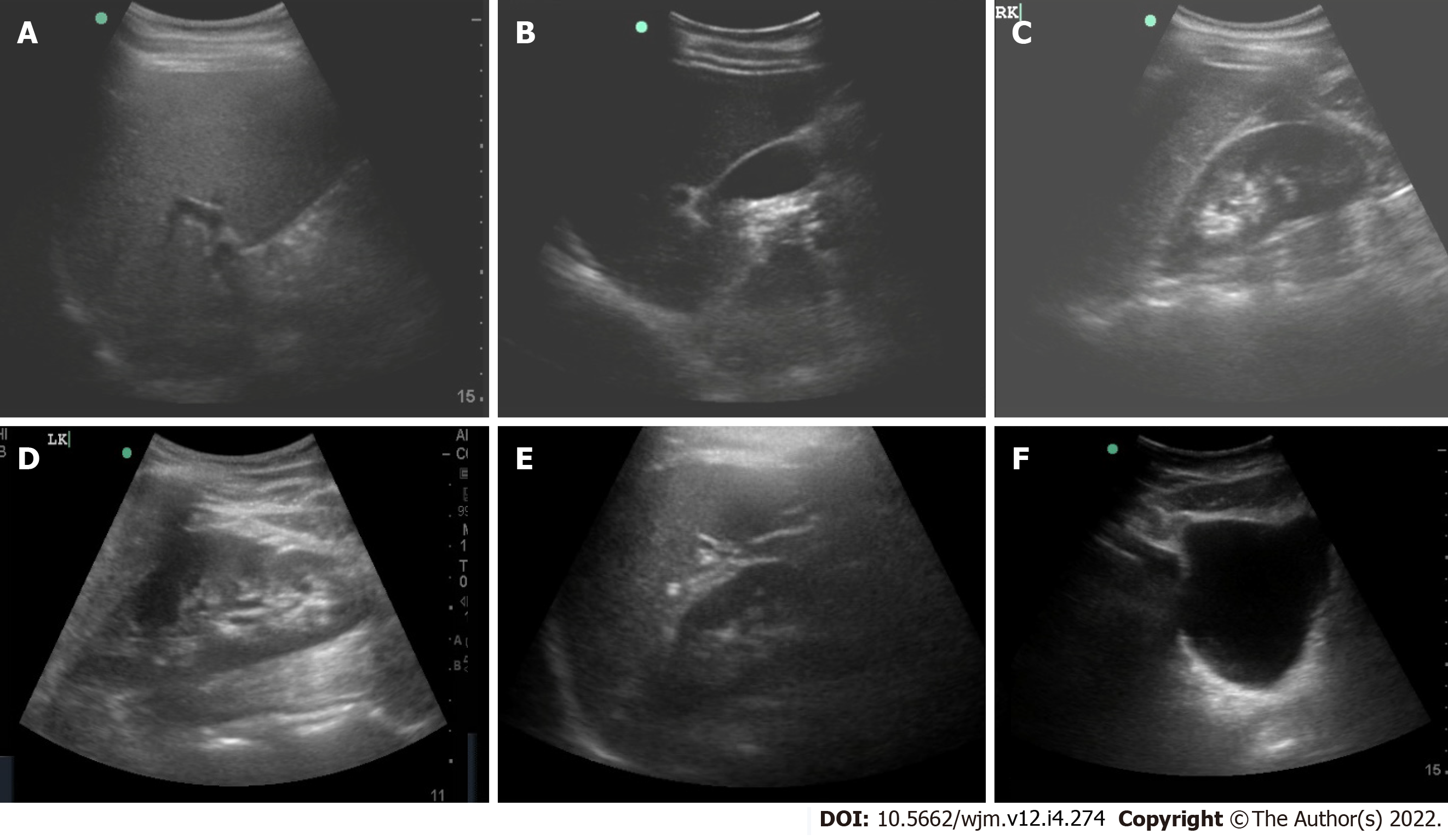
Figure 2 Ultrasound images of abdominal organs acquired using a probe mounted on the robotic arm.
A: Liver; B: Gall bladder; C: Right kidney; D: Left kidney; E: Spleen; F: Urinary bladder.
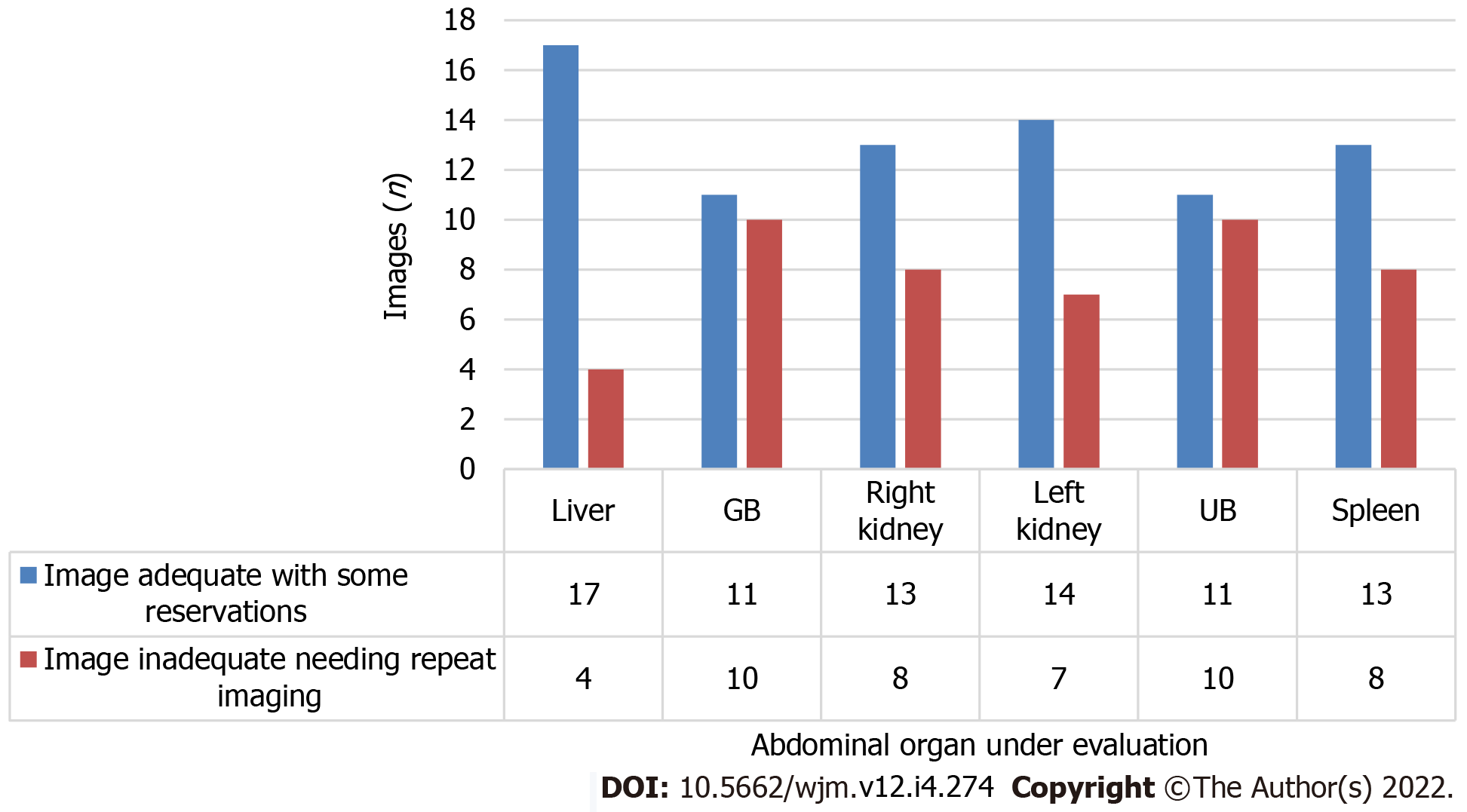
Figure 3 Quality details of images acquired using robotic arm ultrasound.
UB: Urinary bladder.
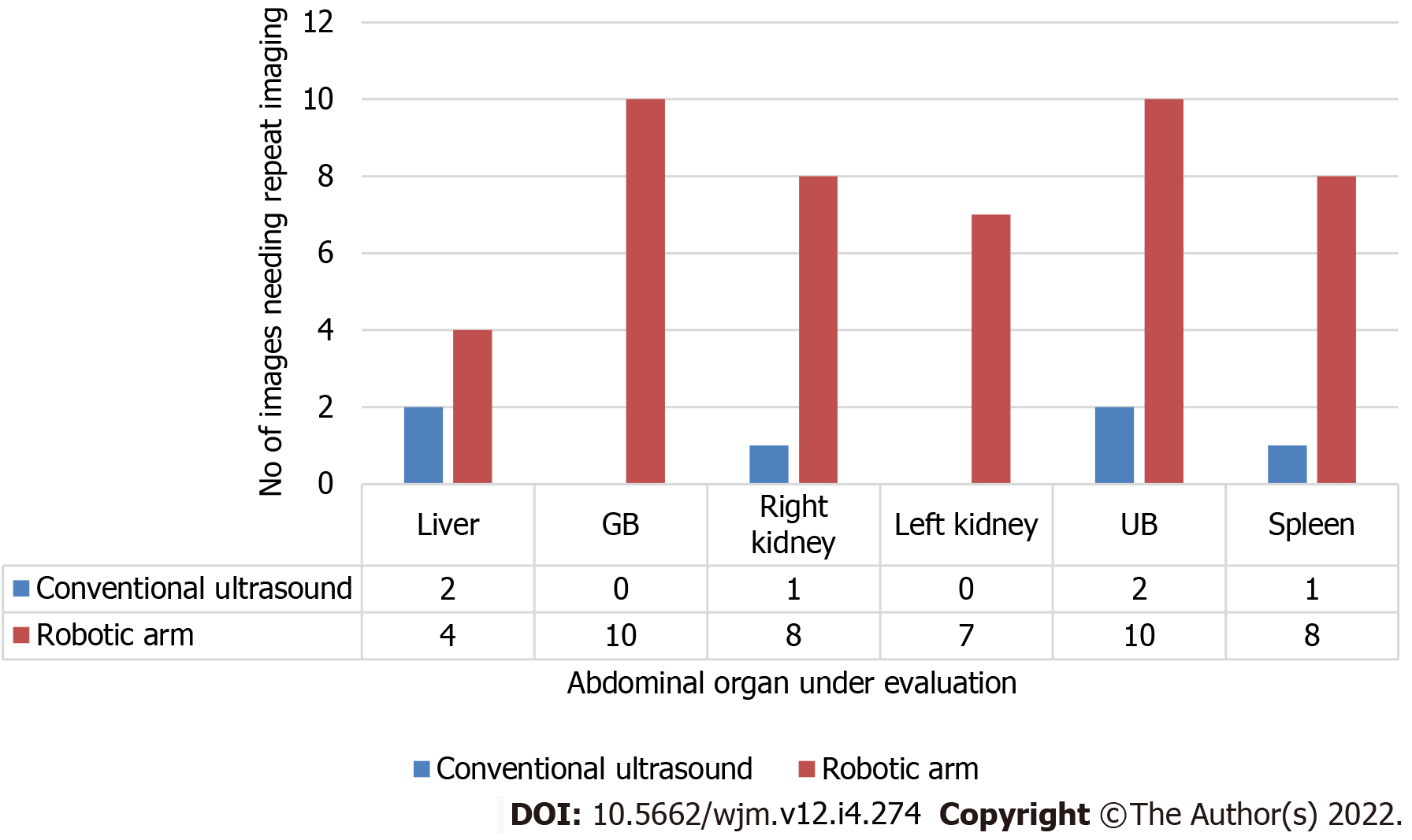
Figure 4 Comparison between conventional and robotic ultrasound regarding the need for repeat imaging.
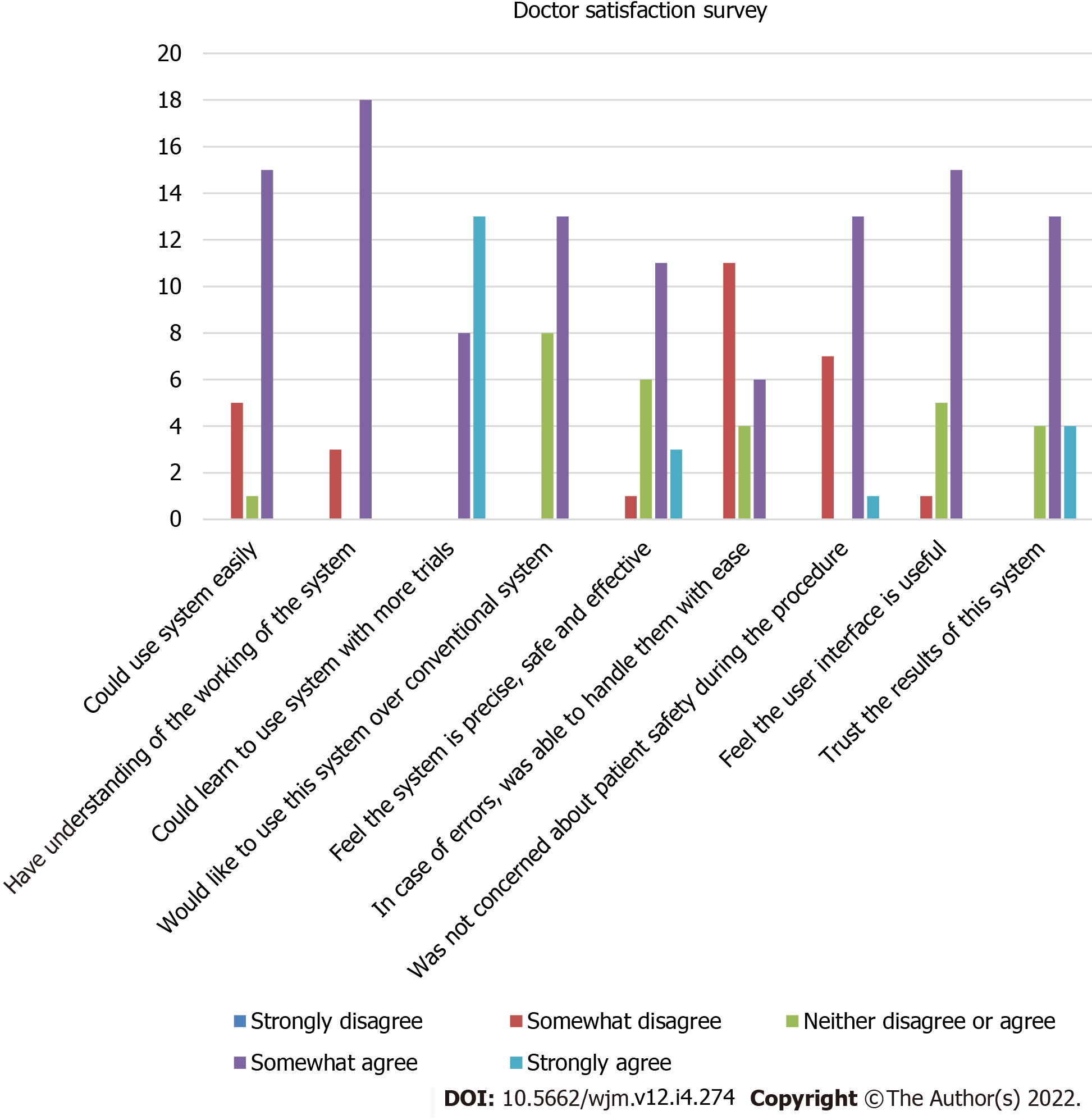
Figure 5 Histogram showing results of the doctor satisfaction survey.
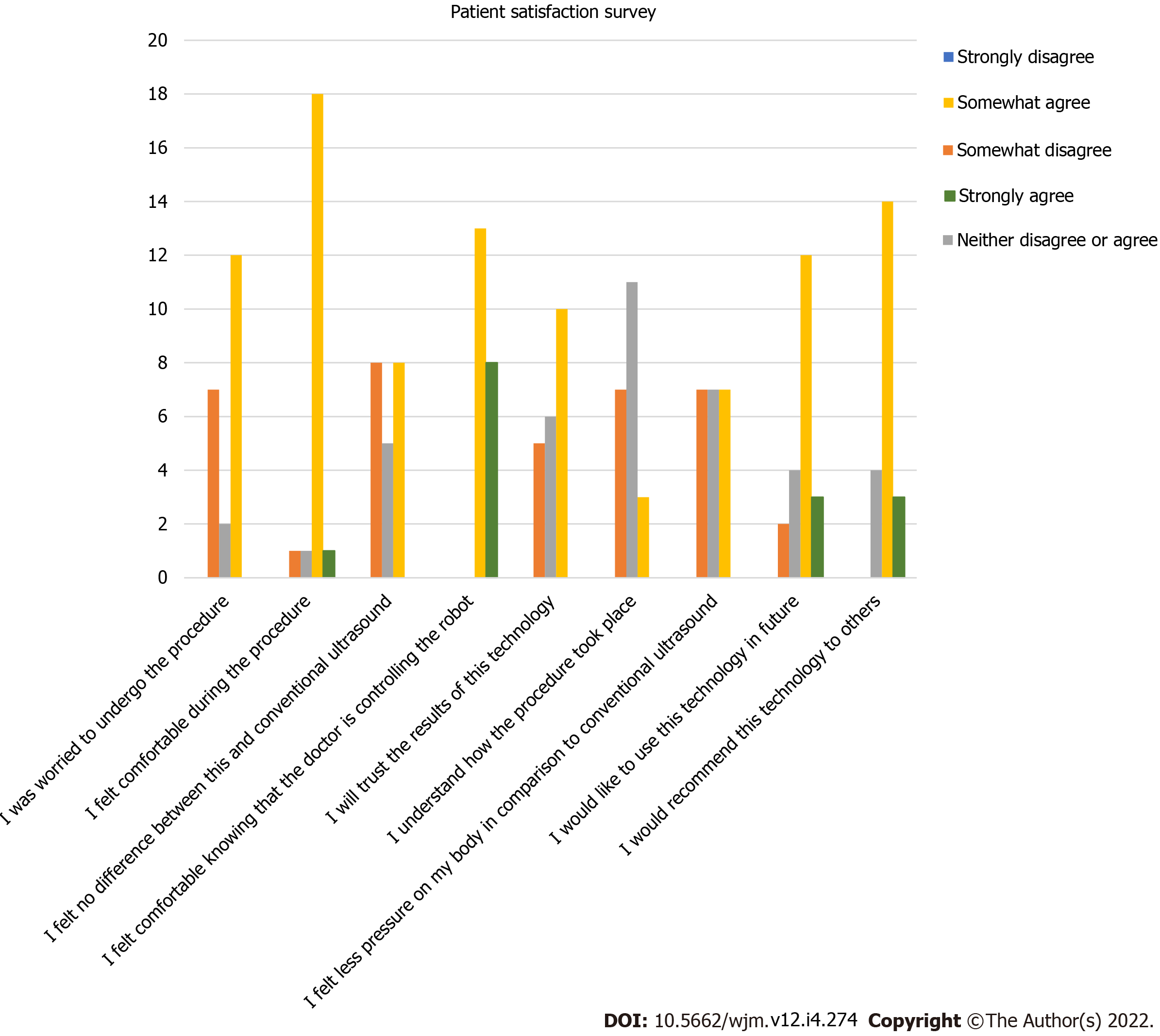
Figure 6 Histogram showing results of the patient satisfaction survey.
- Citation: Chandrashekhara SH, Rangarajan K, Agrawal A, Thulkar S, Gamanagatti S, Raina D, Saha SK, Arora C. Robotic ultrasound: An initial feasibility study. World J Methodol 2022; 12(4): 274-284
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2222-0682/full/v12/i4/274.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5662/wjm.v12.i4.274