©The Author(s) 2022.
World J Methodol. Jan 20, 2022; 12(1): 1-19
Published online Jan 20, 2022. doi: 10.5662/wjm.v12.i1.1
Published online Jan 20, 2022. doi: 10.5662/wjm.v12.i1.1
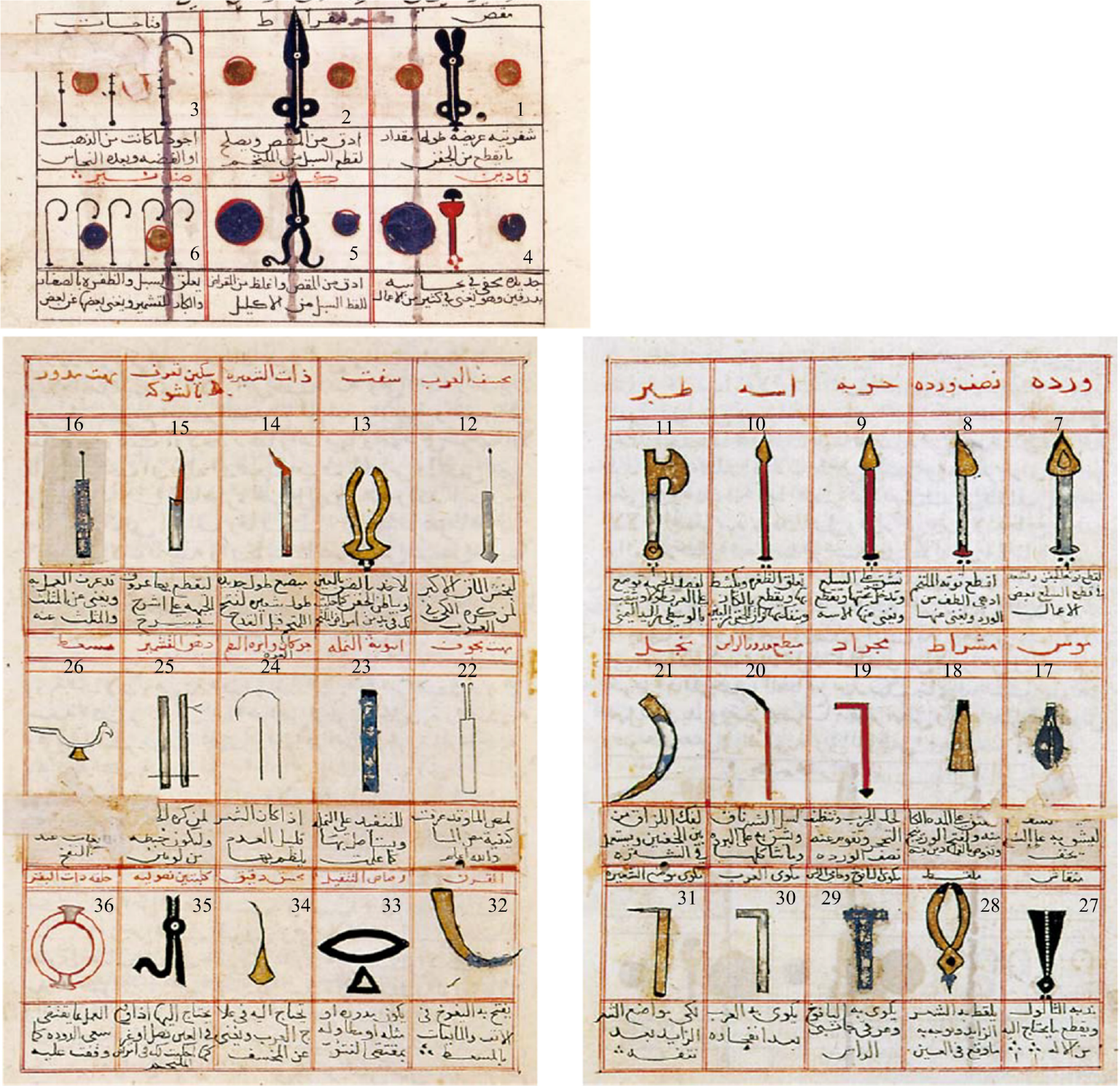
Figure 1 Ophthalmological instruments from Al-Halabi’s book, the Istanbul manuscript of the Süleymaniye Kütüphanesi, Yeni Cami 924.
Citation: Sezgin F, Neubauer E. Volume IV: Catalogue of the collection of instruments of the institute for the history of Arabic and Islamic sciences. In: Sezgin F. Science and technology in Islam. Frankfurt am Main, Germany: Institute for the History of Arabic-Islamic Science, 2010: 6. Copyright ©The Author(s) 2010. Published by Institute for the History of Arabic-Islamic Science (Institut für Geschichte der Arabisch-Islamischen Wissenschaften). The author has obtained the permission for figure using from the Institute for the History of Arabic-Islamic Science (Institut für Geschichte der Arabisch-Islamischen Wissenschaften) (Supplementary Material).
Figure 2 Rose leaf needle (instrument number 7 in Figure 1) used in treatment of trachoma, lagophthalmos, symblepharon, hemangioma at the eyelid, and sebaceous cyst.
Citation: Sezgin F, Neubauer E. Volume IV: Catalogue of the collection of instruments of the institute for the history of Arabic and Islamic sciences. In: Sezgin F. Science and technology in Islam. Frankfurt am Main, Germany: Institute for the History of Arabic-Islamic Science, 2010: 45. Copyright ©The Author(s) 2010. Published by Institute for the History of Arabic-Islamic Science (Institut für Geschichte der Arabisch-Islamischen Wissenschaften). The author has obtained the permission for figure using from the Institute for the History of Arabic-Islamic Science (Institut für Geschichte der Arabisch-Islamischen Wissenschaften) (Supplementary Material).
Figure 3 Scraper (instrument number 19 in Figure 1) for scratching scabies and for digging out concretions.
Citation: Sezgin F, Neubauer E. Volume IV: Catalogue of the collection of instruments of the institute for the history of Arabic and Islamic sciences. In: Sezgin F. Science and technology in Islam. Frankfurt am Main, Germany: Institute for the History of Arabic-Islamic Science, 2010: 49. Copyright ©The Author(s) 2010. Published by Institute for the History of Arabic-Islamic Science (Institut für Geschichte der Arabisch-Islamischen Wissenschaften). The author has obtained the permission for figure using from the Institute for the History of Arabic-Islamic Science (Institut für Geschichte der Arabisch-Islamischen Wissenschaften) (Supplementary Material).
Figure 4 Lancet with rounded tip (instrument number 20 in Figure 1) used in treatment of chalazion, chemosis, lipoma, blepharitis, concretions, hypopyon, headache, and cataract.
Citation: Sezgin F, Neubauer E. Volume IV: Catalogue of the collection of instruments of the institute for the history of Arabic and Islamic sciences. In: Sezgin F. Science and technology in Islam. Frankfurt am Main, Germany: Institute for the History of Arabic-Islamic Science, 2010: 49. Copyright ©The Author(s) 2010. Published by Institute for the History of Arabic-Islamic Science (Institut für Geschichte der Arabisch-Islamischen Wissenschaften). The author has obtained the permission for figure using from the Institute for the History of Arabic-Islamic Science (Institut für Geschichte der Arabisch-Islamischen Wissenschaften) (Supplementary Material).
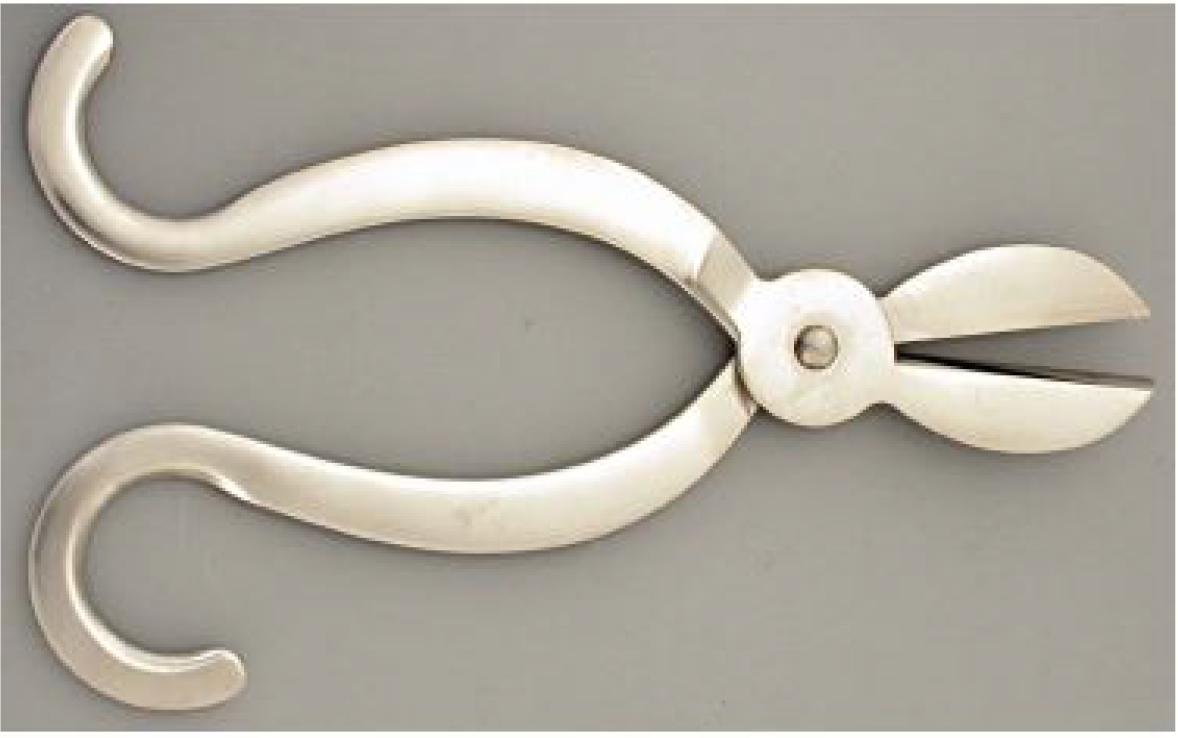
Figure 5 Scissors (Miqrad) (instrument number 2 in Figure 1) used in treatment of concretions, ectropion, stye, hordeolum, lacrimal caruncle swelling, pannus, pterygium, hemangioma, iris prolapse, and headache.
Citation: Sezgin F, Neubauer E. Volume IV: Catalogue of the collection of instruments of the institute for the history of Arabic and Islamic sciences. In: Sezgin F. Science and technology in Islam. Frankfurt am Main, Germany: Institute for the History of Arabic-Islamic Science, 2010: 48. Copyright ©The Author(s) 2010. Published by Institute for the History of Arabic-Islamic Science (Institut für Geschichte der Arabisch-Islamischen Wissenschaften). The author has obtained the permission for figure using from the Institute for the History of Arabic-Islamic Science (Institut für Geschichte der Arabisch-Islamischen Wissenschaften) (Supplementary Material).
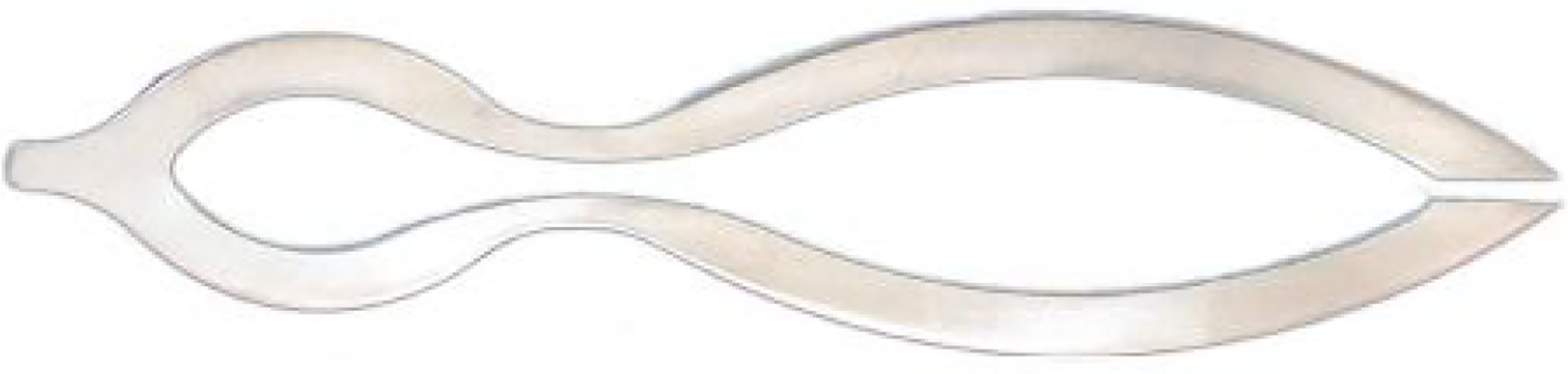
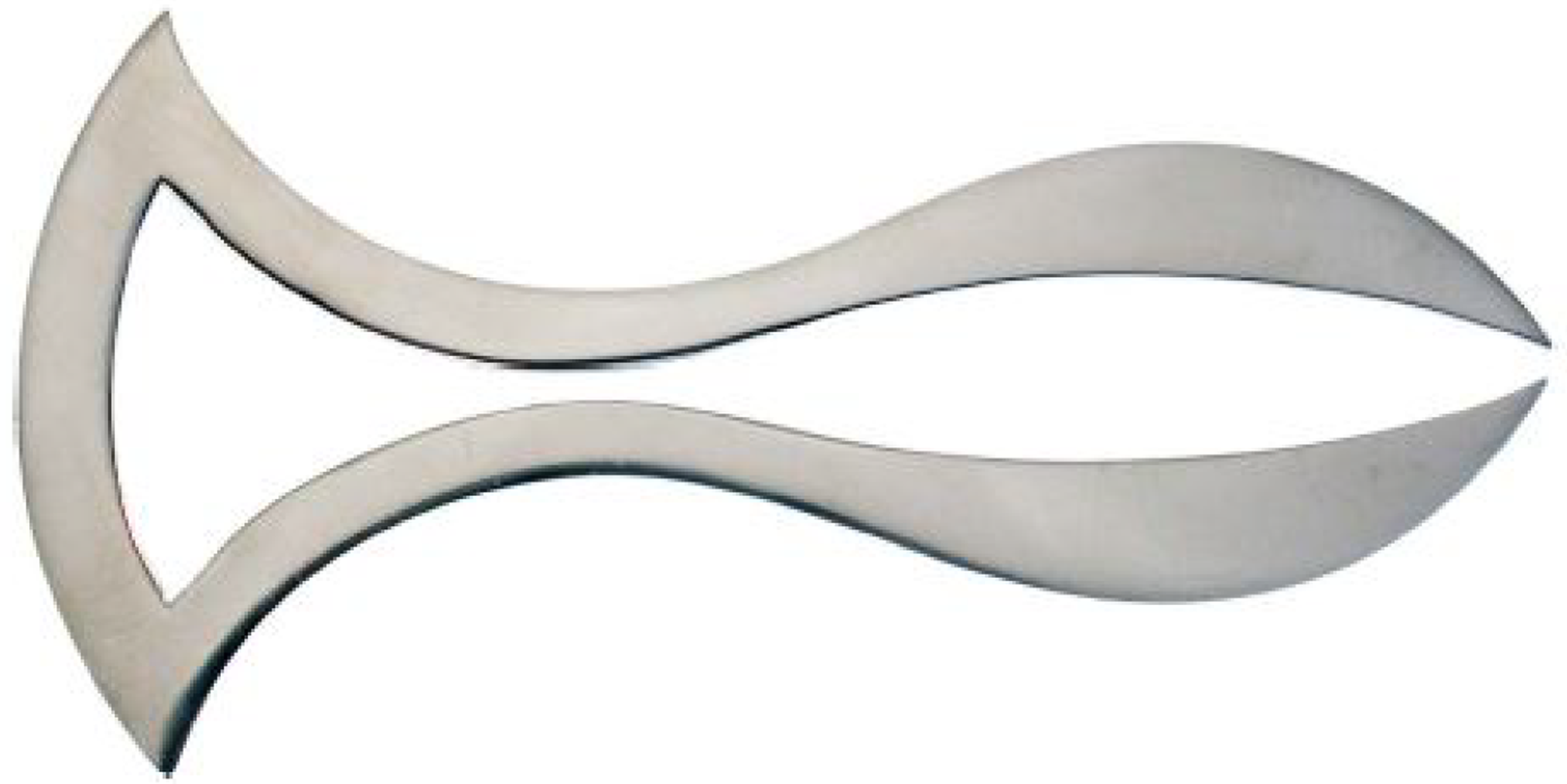
Figure 6 Sickle (instrument number 21 in Figure 1) for splitting adhesions between the two eyelids.
Citation: Sezgin F, Neubauer E. Volume IV: Catalogue of the collection of instruments of the institute for the history of Arabic and Islamic sciences. In: Sezgin F. Science and technology in Islam. Frankfurt am Main, Germany: Institute for the History of Arabic-Islamic Science, 2010: 52. Copyright ©The Author(s) 2010. Published by Institute for the History of Arabic-Islamic Science (Institut für Geschichte der Arabisch-Islamischen Wissenschaften). The author has obtained the permission for figure using from the Institute for the History of Arabic-Islamic Science (Institut für Geschichte der Arabisch-Islamischen Wissenschaften) (Supplementary Material).
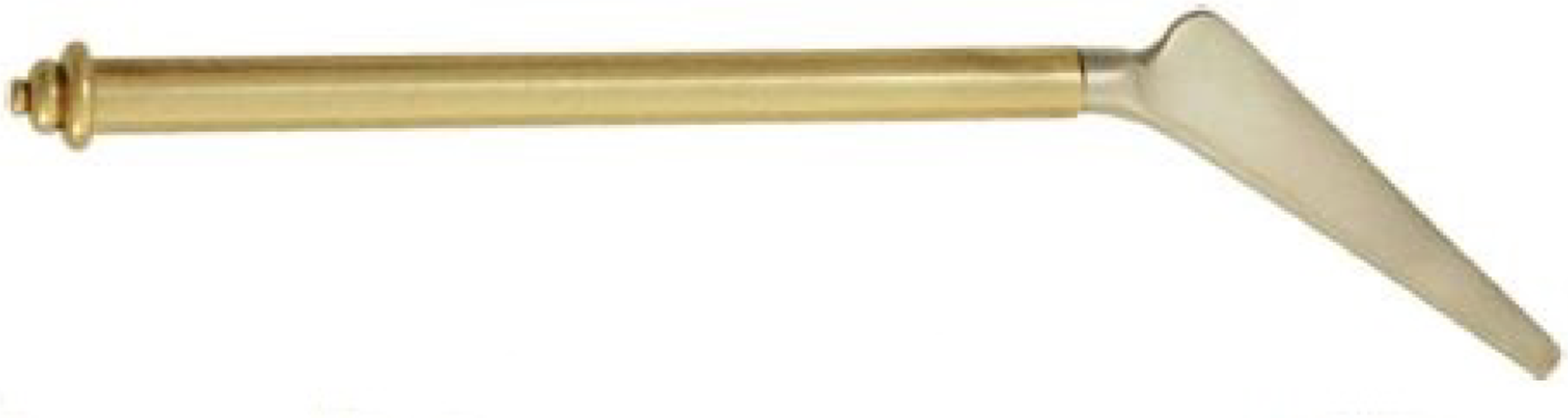
Figure 7 Myrtle leaf needle (instrument number 10 in Figure 1) used in treatment of symblepharon, and pterygium.
Citation: Sezgin F, Neubauer E. Volume IV: Catalogue of the collection of instruments of the institute for the history of Arabic and Islamic sciences. In: Sezgin F. Science and technology in Islam. Frankfurt am Main, Germany: Institute for the History of Arabic-Islamic Science, 2010: 47. Copyright ©The Author(s) 2010. Published by Institute for the History of Arabic-Islamic Science (Institut für Geschichte der Arabisch-Islamischen Wissenschaften). The author has obtained the permission for figure using from the Institute for the History of Arabic-Islamic Science (Institut für Geschichte der Arabisch-Islamischen Wissenschaften) (Supplementary Material).
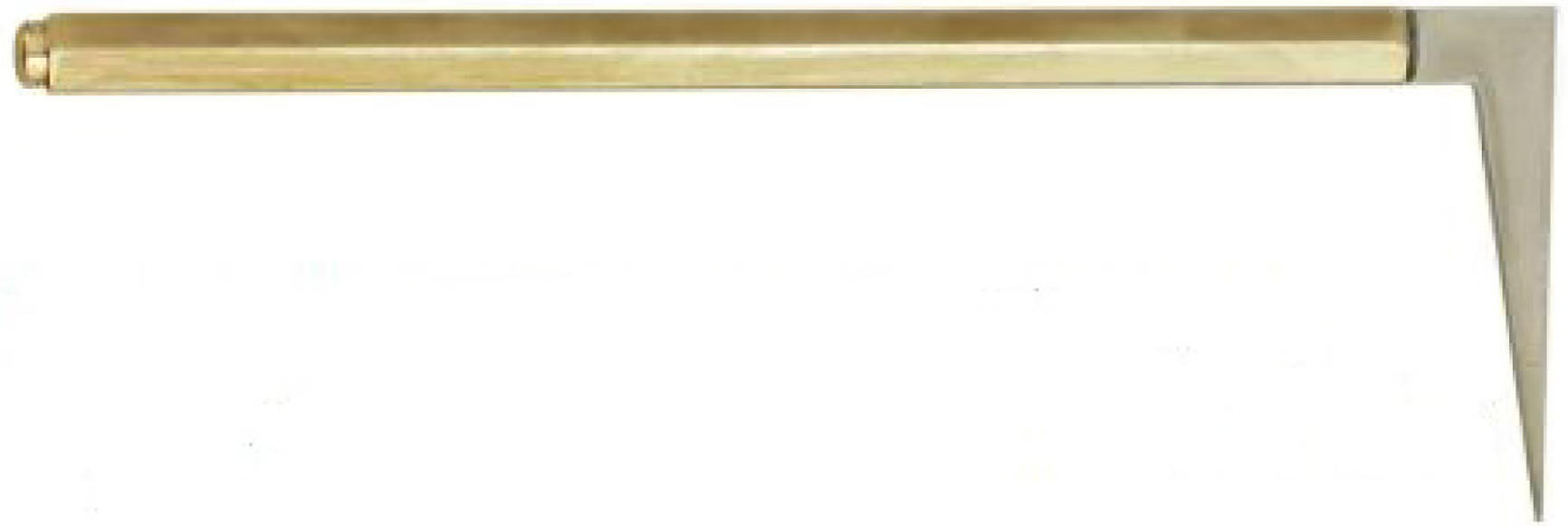
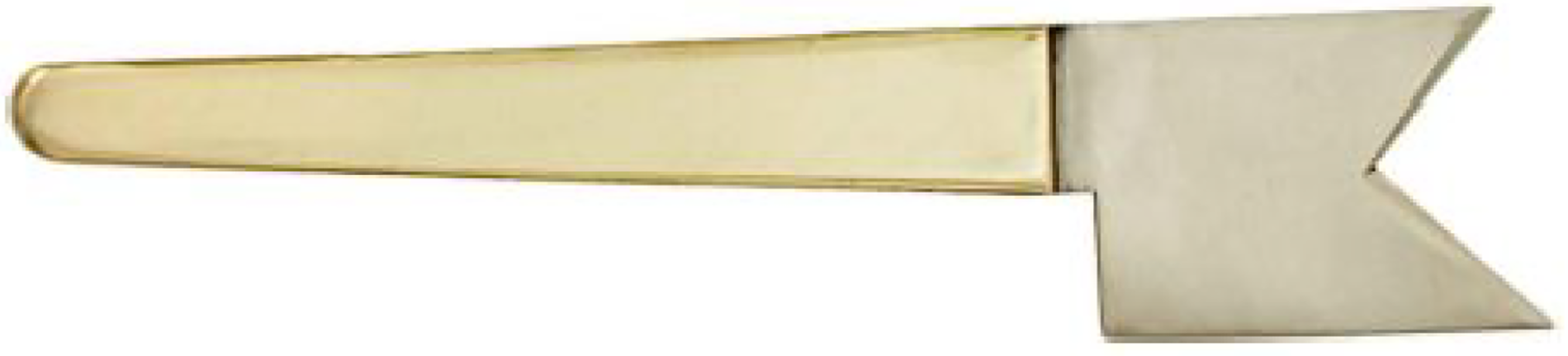
Figure 8 Spear (instrument number 9 in Figure 1) used in treatment of symblepharon, ectropion, and sebaceous cyst.
Citation: Sezgin F, Neubauer E. Volume IV: Catalogue of the collection of instruments of the institute for the history of Arabic and Islamic sciences. In: Sezgin F. Science and technology in Islam. Frankfurt am Main, Germany: Institute for the History of Arabic-Islamic Science, 2010: 45. Copyright ©The Author(s) 2010. Published by Institute for the History of Arabic-Islamic Science (Institut für Geschichte der Arabisch-Islamischen Wissenschaften). The author has obtained the permission for figure using from the Institute for the History of Arabic-Islamic Science (Institut für Geschichte der Arabisch-Islamischen Wissenschaften) (Supplementary Material).
Figure 9 Gatherer (instrument number 28 in Figure 1) used in treatment of distichiasis.
Citation: Sezgin F, Neubauer E. Volume IV: Catalogue of the collection of instruments of the institute for the history of Arabic and Islamic sciences. In: Sezgin F. Science and technology in Islam. Frankfurt am Main, Germany: Institute for the History of Arabic-Islamic Science, 2010: 53. Copyright ©The Author(s) 2010. Published by Institute for the History of Arabic-Islamic Science (Institut für Geschichte der Arabisch-Islamischen Wissenschaften). The author has obtained the permission for figure using from the Institute for the History of Arabic-Islamic Science (Institut für Geschichte der Arabisch-Islamischen Wissenschaften) (Supplementary Material).
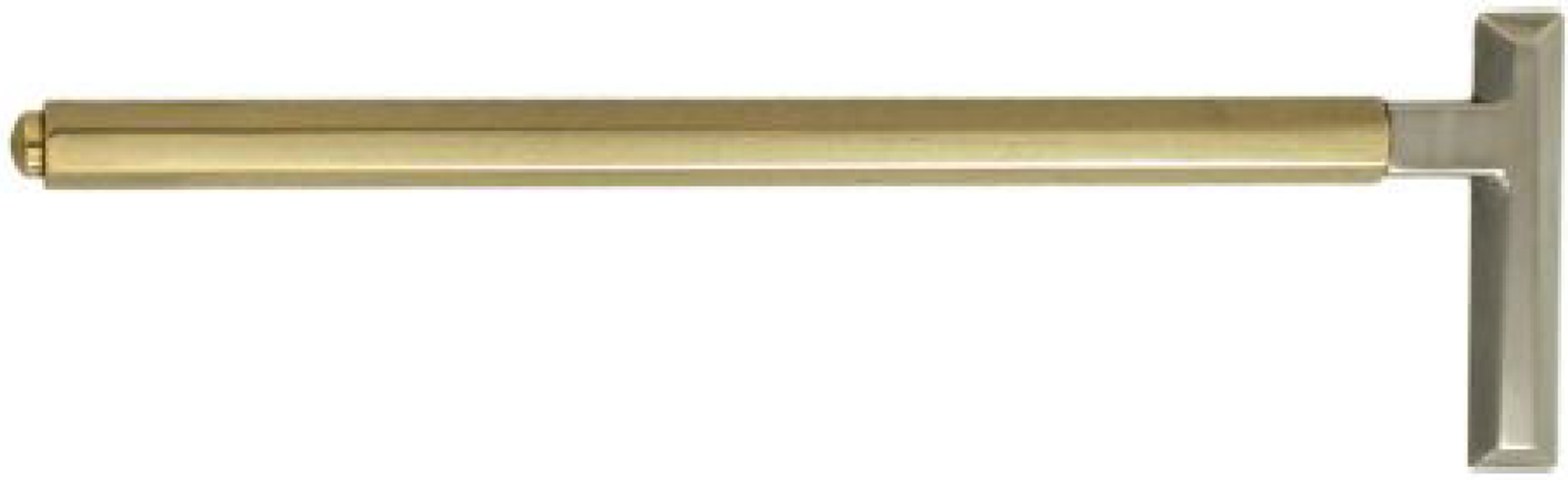
Figure 10 Pointed cautery (instrument number 31 in Figure 1) for cauterizing the places of superfluous eyelashes after they have been pulled out.
Citation: Sezgin F, Neubauer E. Volume IV: Catalogue of the collection of instruments of the institute for the history of Arabic and Islamic sciences. In: Sezgin F. Science and technology in Islam. Frankfurt am Main, Germany: Institute for the History of Arabic-Islamic Science, 2010: 51. Copyright ©The Author(s) 2010. Published by Institute for the History of Arabic-Islamic Science (Institut für Geschichte der Arabisch-Islamischen Wissenschaften). The author has obtained the permission for figure using from the Institute for the History of Arabic-Islamic Science (Institut für Geschichte der Arabisch-Islamischen Wissenschaften) (Supplementary Material).
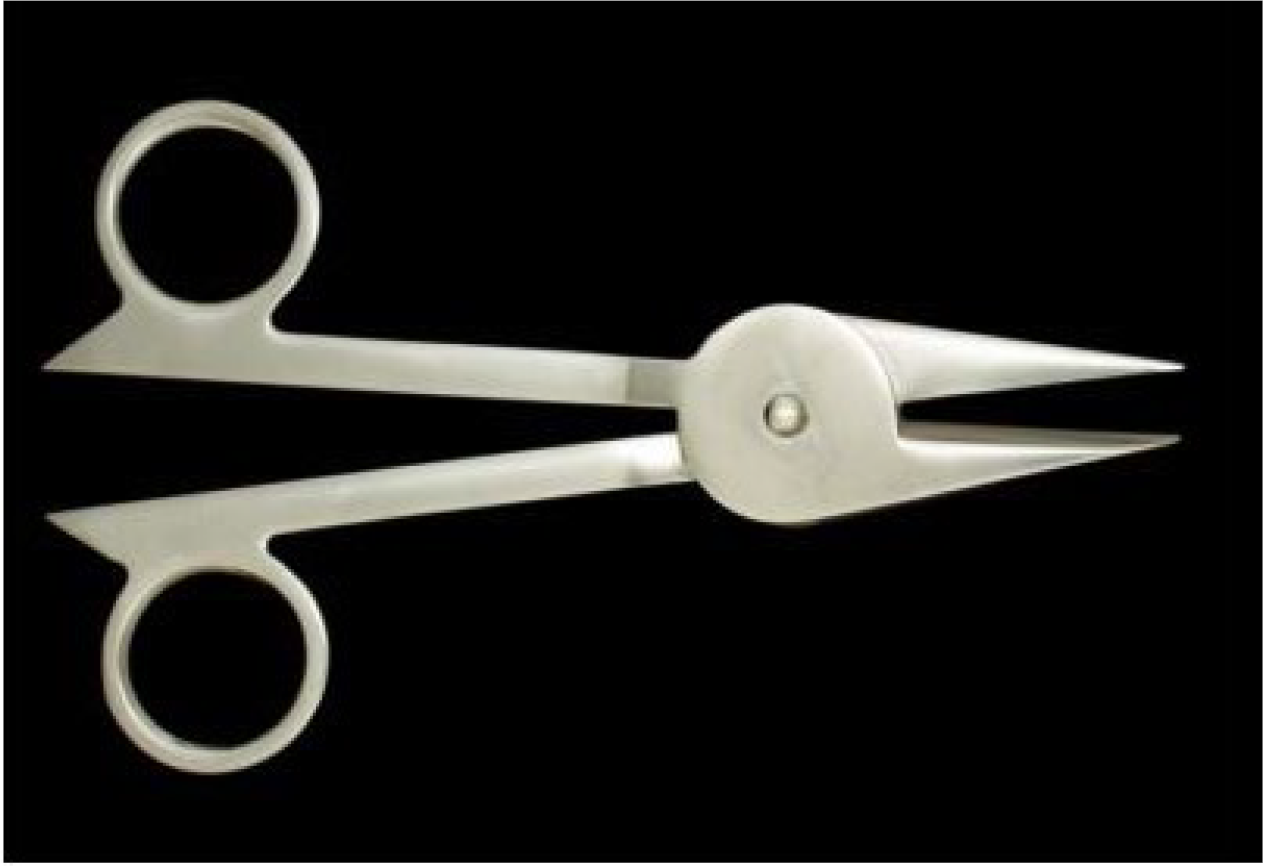
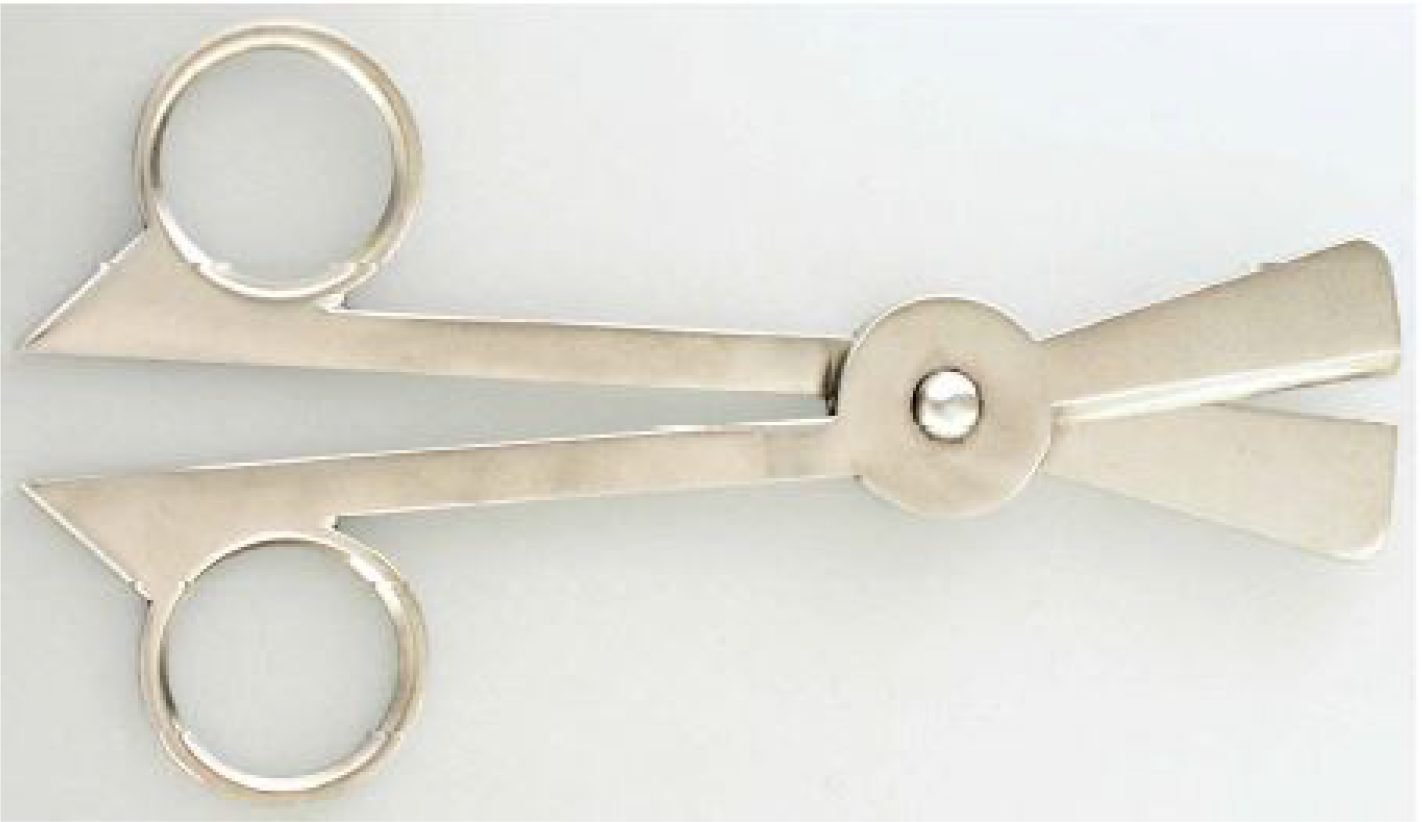
Figure 11 Scissors (Miqass) (instrument number 1 in Figure 1) used in treatment of distichiasis.
Citation: Sezgin F, Neubauer E. Volume IV: Catalogue of the collection of instruments of the institute for the history of Arabic and Islamic sciences. In: Sezgin F. Science and technology in Islam. Frankfurt am Main, Germany: Institute for the History of Arabic-Islamic Science, 2010: 46. Copyright ©The Author(s) 2010. Published by Institute for the History of Arabic-Islamic Science (Institut für Geschichte der Arabisch-Islamischen Wissenschaften). The author has obtained the permission for figure using from the Institute for the History of Arabic-Islamic Science (Institut für Geschichte der Arabisch-Islamischen Wissenschaften) (Supplementary Material).
Figure 12 Cautery (instrument number 30 in Figure 1) used in treatment of dacryocystitis.
Citation: Sezgin F, Neubauer E. Volume IV: Catalogue of the collection of instruments of the institute for the history of Arabic and Islamic sciences. In: Sezgin F. Science and technology in Islam. Frankfurt am Main, Germany: Institute for the History of Arabic-Islamic Science, 2010: 43. Copyright ©The Author(s) 2010. Published by Institute for the History of Arabic-Islamic Science (Institut für Geschichte der Arabisch-Islamischen Wissenschaften). The author has obtained the permission for figure using from the Institute for the History of Arabic-Islamic Science (Institut für Geschichte der Arabisch-Islamischen Wissenschaften) (Supplementary Material).
Figure 13 Drill (instrument number 12 in Figure 1) for cleaning the entire corner of the eye.
Citation: Sezgin F, Neubauer E. Volume IV: Catalogue of the collection of instruments of the institute for the history of Arabic and Islamic sciences. In: Sezgin F. Science and technology in Islam. Frankfurt am Main, Germany: Institute for the History of Arabic-Islamic Science, 2010: 43. Copyright ©The Author(s) 2010. Published by Institute for the History of Arabic-Islamic Science (Institut für Geschichte der Arabisch-Islamischen Wissenschaften). The author has obtained the permission for figure using from the Institute for the History of Arabic-Islamic Science (Institut für Geschichte der Arabisch-Islamischen Wissenschaften) (Supplementary Material).
Figure 14 Scissors (Kaz) (instrument number 5 in Figure 1) used in treatment of pannus, pterygium, and granuloma at the conjunctiva.
Citation: Sezgin F, Neubauer E. Volume IV: Catalogue of the collection of instruments of the institute for the history of Arabic and Islamic sciences. In: Sezgin F. Science and technology in Islam. Frankfurt am Main, Germany: Institute for the History of Arabic-Islamic Science, 2010: 48. Copyright ©The Author(s) 2010. Published by Institute for the History of Arabic-Islamic Science (Institut für Geschichte der Arabisch-Islamischen Wissenschaften). The author has obtained the permission for figure using from the Institute for the History of Arabic-Islamic Science (Institut für Geschichte der Arabisch-Islamischen Wissenschaften) (Supplementary Material).
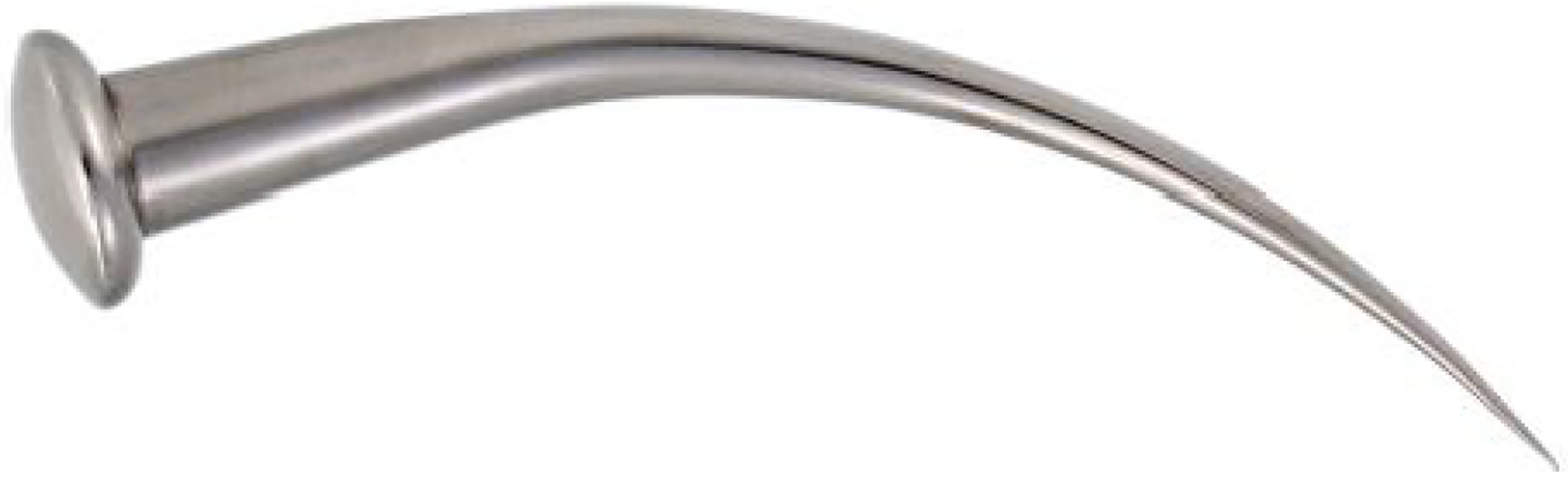
Figure 15 Raven’s beak (instrument number 13 in Figure 1) for removing whatever sticks to the eye or the inner side of the eyelid.
Citation: Sezgin F, Neubauer E. Volume IV: Catalogue of the collection of instruments of the institute for the history of Arabic and Islamic sciences. In: Sezgin F. Science and technology in Islam. Frankfurt am Main, Germany: Institute for the History of Arabic-Islamic Science, 2010: 52. Copyright ©The Author(s) 2010. Published by Institute for the History of Arabic-Islamic Science (Institut für Geschichte der Arabisch-Islamischen Wissenschaften). The author has obtained the permission for figure using from the Institute for the History of Arabic-Islamic Science (Institut für Geschichte der Arabisch-Islamischen Wissenschaften) (Supplementary Material).
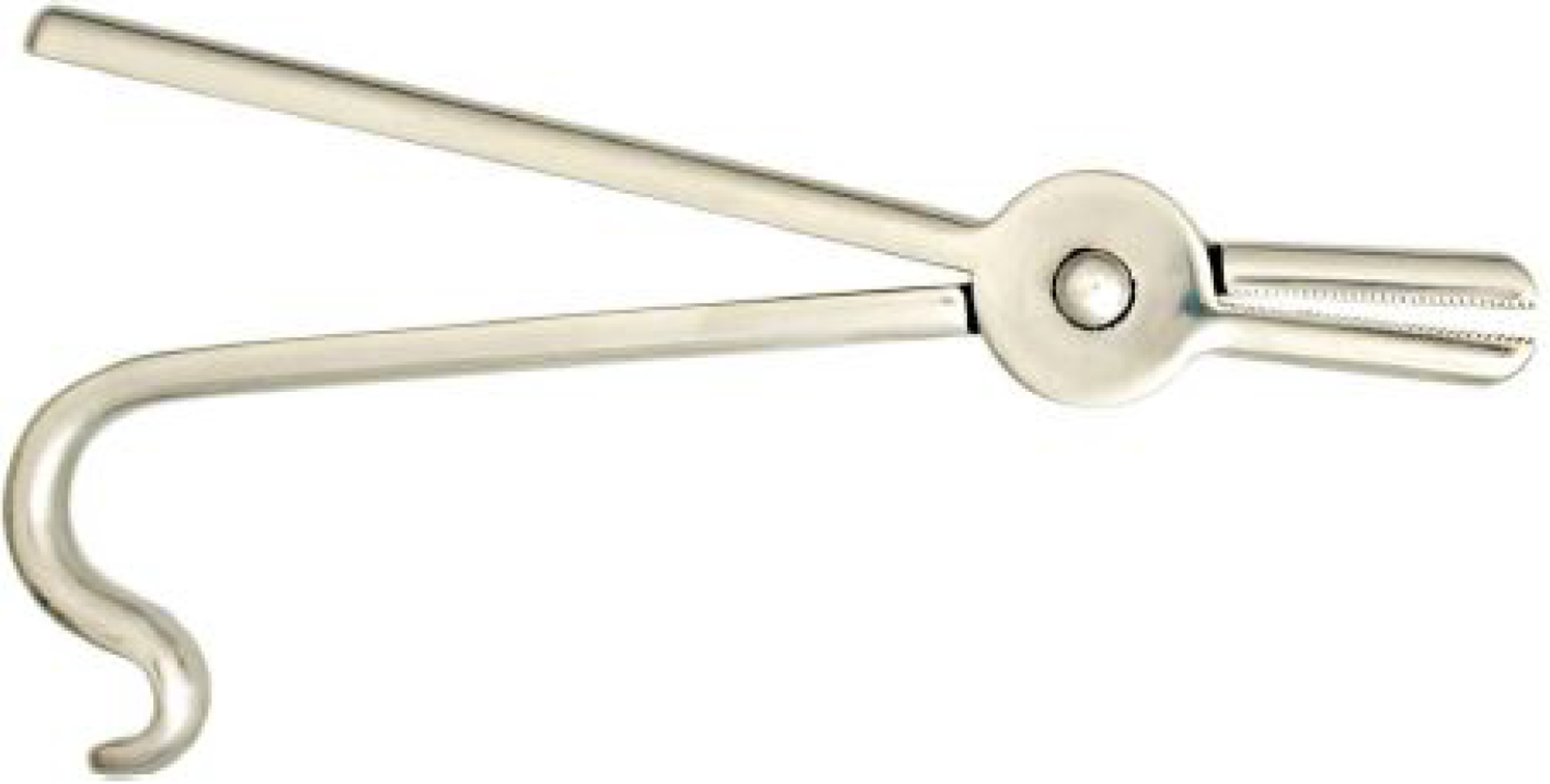
Figure 16 Awn tongs (instrument number 35 in Figure 1) used when an awn or something of that kind falls into the eye.
Citation: Sezgin F, Neubauer E. Volume IV: Catalogue of the collection of instruments of the institute for the history of Arabic and Islamic sciences. In: Sezgin F. Science and technology in Islam. Frankfurt am Main, Germany: Institute for the History of Arabic-Islamic Science, 2010: 53. Copyright ©The Author(s) 2010. Published by Institute for the History of Arabic-Islamic Science (Institut für Geschichte der Arabisch-Islamischen Wissenschaften). The author has obtained the permission for figure using from the Institute for the History of Arabic-Islamic Science (Institut für Geschichte der Arabisch-Islamischen Wissenschaften) (Supplementary Material).
Figure 17 Olivary-shaped cautery (instrument number 29 in Figure 1) used for headache, and migraine.
Citation: Sezgin F, Neubauer E. Volume IV: Catalogue of the collection of instruments of the institute for the history of Arabic and Islamic sciences. In: Sezgin F. Science and technology in Islam. Frankfurt am Main, Germany: Institute for the History of Arabic-Islamic Science, 2010: 50. Copyright ©The Author(s) 2010. Published by Institute for the History of Arabic-Islamic Science (Institut für Geschichte der Arabisch-Islamischen Wissenschaften). The author has obtained the permission for figure using from the Institute for the History of Arabic-Islamic Science (Institut für Geschichte der Arabisch-Islamischen Wissenschaften) (Supplementary Material).
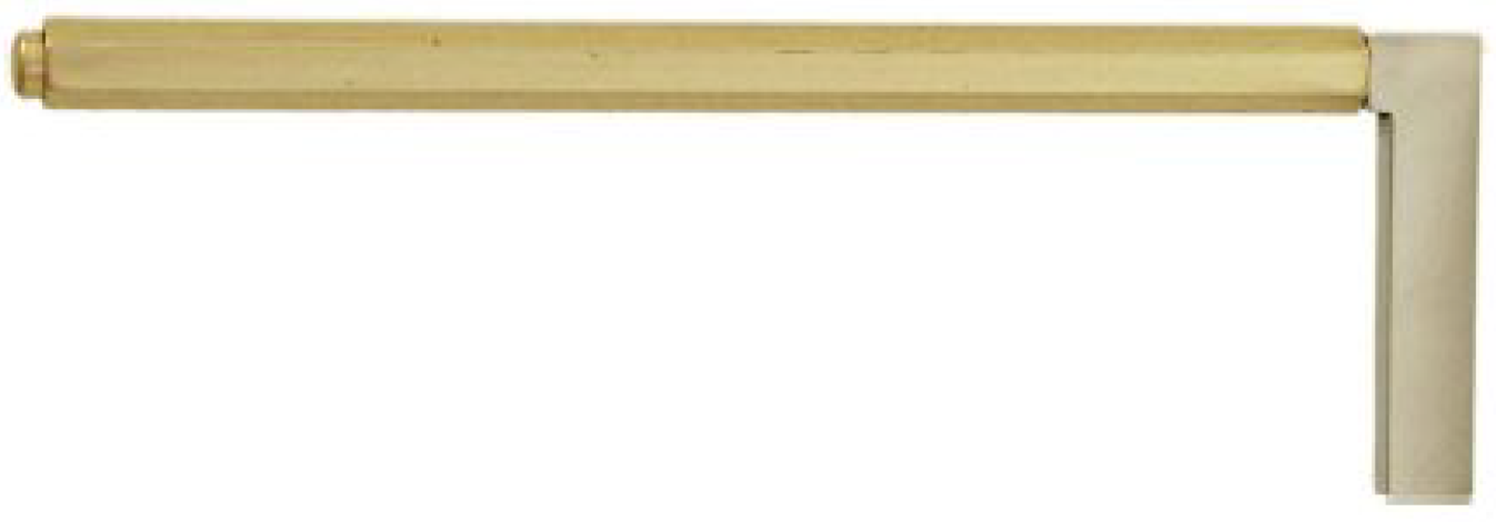
Figure 18 Axe (instrument number 11 in Figure 1) for bloodletting the supraorbital vein.
Citation: Sezgin F, Neubauer E. Volume IV: Catalogue of the collection of instruments of the institute for the history of Arabic and Islamic sciences. In: Sezgin F. Science and technology in Islam. Frankfurt am Main, Germany: Institute for the History of Arabic-Islamic Science, 2010: 50. Copyright ©The Author(s) 2010. Published by Institute for the History of Arabic-Islamic Science (Institut für Geschichte der Arabisch-Islamischen Wissenschaften). The author has obtained the permission for figure using from the Institute for the History of Arabic-Islamic Science (Institut für Geschichte der Arabisch-Islamischen Wissenschaften) (Supplementary Material).
Figure 19 Optic nerve crossing together with that of the eye and the brain from Al-Halabi’s book, the Istanbul manuscript of the Süleymaniye Kütüphanesi, Yeni Cami 924.
Citation: Sezgin F, Neubauer E. Volume IV: Catalogue of the collection of instruments of the institute for the history of Arabic and Islamic sciences. In: Sezgin F. Science and technology in Islam. Frankfurt am Main, Germany: Institute for the History of Arabic-Islamic Science, 2010: 27. Copyright ©The Author(s) 2010. Published by Institute for the History of Arabic-Islamic Science (Institut für Geschichte der Arabisch-Islamischen Wissenschaften). The author has obtained the permission for figure using from the Institute for the History of Arabic-Islamic Science (Institut für Geschichte der Arabisch-Islamischen Wissenschaften) (Supplementary Material).
- Citation: Saad MN. Ophthalmological instruments of Al-Halabi fill in a gap in the biomedical engineering history. World J Methodol 2022; 12(1): 1-19
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2222-0682/full/v12/i1/1.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.5662/wjm.v12.i1.1